前言
前面一篇介绍了自定义View的基础概念(皮毛),接下来全部是自定义View实战,让我们一起开启自定义View之旅吧!
1. 实现目标
本篇将实现一个自定义的TextView,通过自定义属性让我们可以配置文本内容、颜色、字体大小。主要是掌握自定义View中画文字的基础概念。
- 在
attrs.xml中定义自定义属性 - 在自定义View中解析自定义属性
- 绘制文本
- 测量控件宽高
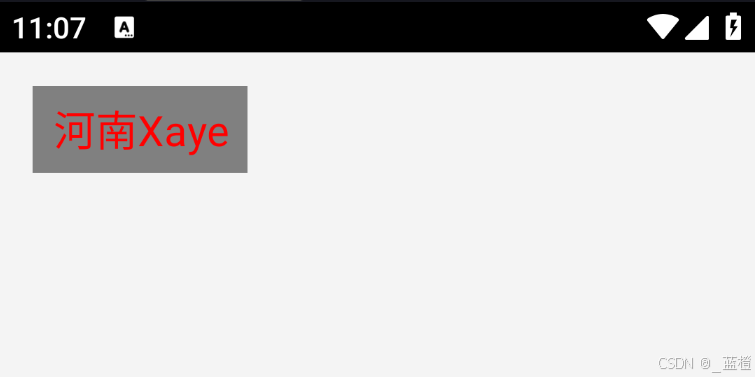
以下是完成效果图:
效果1:不带Padding

效果2:带Padding
看似很简单,其实有一点绕,先来看一张图。

首先我们需要知道一点,文字的绘制是从左下角开始的,并不是 文字左上角的坐标,这一点与其他自定义view的绘制会有一些不同,因为文字的绘制是以基线为基础的,就是上图的Baseline,当自定义Textview时,我们要么拿到确定的宽高,要么是根据文本的长度和大小去自适应宽高,不管怎样我们得到的都是一个矩形。
而我们要绘制文本,最重要的是确认基线坐标,那么基线坐标怎么获取呢?这时候就要用到 Paint.FontMetricsInt了。
Paint.FontMetricsInt 的基本概念
Paint.FontMetricsInt 是 Paint 类中的一个内部类,用于提供字体的度量信息。它的字段主要表示从基线(baseline)到不同字符边界的距离,通常用来计算文本在垂直方向上的绘制位置。
主要字段如下:
- top:从基线到字符最高点的距离,通常是负值。
- ascent:从基线到字符实际顶部的距离,也是负值,但通常比 top 小。
- descent:从基线到字符实际底部的距离,通常是正值。
- bottom:从基线到字符最低点的距离,一般用于字符尾部的间距,是正值。
- leading:字符之间的间距,通常用于行间距的控制。它的值可能是正的、负的或者零。
这些字段的单位通常是像素,且它们的值相对于基线来计算,如所示:
这里主要用到的是 top 和 bottom。计算基线的公式如下:
getHeight() / 2是控件高度的一半,(bottom - top) / 2 是字体中心与顶部的距离,用来计算从基线到中心点的位移dy。减去 bottom 是为了调整基线,使得绘制效果居中。
OK!了解了这些基础概念后,你就能画一个很正的文本了。
2. 定义自定义属性
在 res/values/attrs.xml 中,我们定义了三个自定义属性:xText(文本内容)、xTextColor(文本颜色)、xTextSize(文本大小)。
3. 自定义TextView的实现
- 解析自定义属性
- 初始化画笔
- 测量View的宽高(onMeasure)
- 绘制文本(onDraw)
onLayout 呢?,不是说好三步走的吗?这是因为 onLayout 方法的主要作用是对子View(即子元素)进行布局,而 MyTextView 继承自 View,它本身就是一个单一的视图控件,没有任何子元素,因此无需重写 onLayout。
大部分自定义View都是单View的,一般不需要自定义onLayout。
4. 完整代码实现
5. 使用:
显示结果就是开篇的图片。
6. 最后
知识点不多,主要是两点:1. 实现wrap_content的支持,2. 使用Paint绘制文本内容,调整基线位置以实现文本居中。
























 2211
2211

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










