使用容器multiset(允许元素重复)
内部是红黑树,insert操作就保证了排好了序。
标准库有个::find()函数,大家都可以用。容器本身也有一个c.find(),通过键值对查找非常快!
测试
#include <set>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj06
{
void test_multiset(long& value)
{
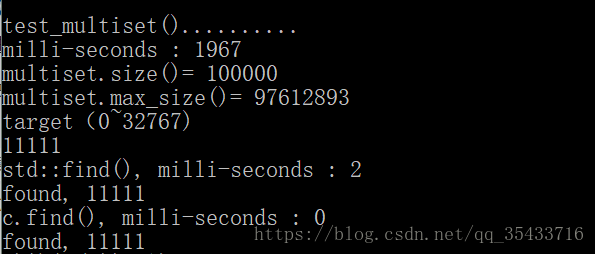
cout << "\ntest_multiset().......... \n";
multiset<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.insert(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "multiset.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "multiset.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //214748364
string target = get_a_target_string();
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); //比 c.find(...) 慢很多
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target); //比 std::find(...) 快很多
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
c.clear();
//test_moveable(multiset<MyString>(),multiset<MyStrNoMove>(), value);
}
}
1)使用容器multimap(允许元素重复)
2)内部是红黑树,key-value键值对。
3)multiset不可用[]做insertion
4)c.insert(pair<long,string>(i,buff))
(*pItem).second
测试
#include <map>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj07
{
void test_multimap(long& value)
{
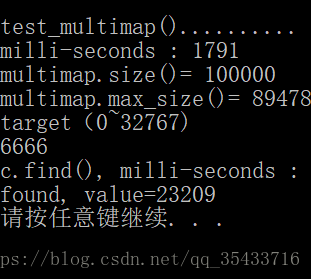
cout << "\ntest_multimap().......... \n";
multimap<long, string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
//multimap 不可使用 [] 做 insertion
c.insert(pair<long,string>(i,buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "multimap.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "multimap.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //178956970
long target = get_a_target_long();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target);
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, value=" << (*pItem).second << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
c.clear();
}
}
使用unordered_multiset容器
使用hashtable使用分离链地址方法实现
gnu C之前的名称hash_multiset
unorder_multiset.bucket_count篮子的个数
load_factor,max_load_factor,max_bucket_count方法
篮子后面的链表不能太长,元素的个数大于等于篮子的个数,就需要重新分配篮子的大小,重新进行插入元素
c.find()容器自身的find操作快很多
#include <unordered_set>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj08
{
void test_unordered_multiset(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_unordered_multiset().......... \n";
unordered_multiset<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.insert(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //357913941
cout << "unordered_multiset.bucket_count()= " << c.bucket_count() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.load_factor()= " << c.load_factor() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.max_load_factor()= " << c.max_load_factor() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.max_bucket_count()= " << c.max_bucket_count() << endl;
for (unsigned i=0; i< 20; ++i) {
cout << "bucket #" << i << " has " << c.bucket_size(i) << " elements.\n";
}
string target = get_a_target_string();
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); //比 c.find(...) 慢很多
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target); //比 std::find(...) 快很多
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
c.clear();
test_moveable(unordered_multiset<MyString>(),unordered_multiset<MyStrNoMove>(), value);
}
}
test_unordered_multiset()..........
milli-seconds : 2209
unordered_multiset.size()= 100000
unordered_multiset.max_size()= 119304647
unordered_multiset.bucket_count()= 131072
unordered_multiset.load_factor()= 0.762939
unordered_multiset.max_load_factor()= 1
unordered_multiset.max_bucket_count()= 131072
bucket #0 has 0 elements.
bucket #1 has 0 elements.
bucket #2 has 0 elements.
bucket #3 has 0 elements.
bucket #4 has 4 elements.
target(0~32767)
1111
std::find(), milli-seconds : 29
found, 1111
c.find(), milli-seconds : 0
found, 1111
请按任意键继续. . .测试结果
这个好理解。无序容器的内部是由一个个的bucket(桶)构成的,
每个bucket里面由相同hash的元素构成。
因此无序容器的搜索是先根据hash值,定位到bucket,然后再在bucket里面搜索符合条件的元素。
buck_count - 就是无序容器内部bucket的数量;
size - 无序容器中总的元素数量;
max_load_factor - 就是bucket所容纳的最大平均元素的数量(可以是分数值)。
『例如』:如果一个容器中有100个元素,容器中bucket的最大平均元素值是12.5,那么需要多少个桶才能完全装下这100个元素呢? 100/12.5 = 8, 为确保有足够的桶,bucket数量起码是>8(即最少9个)。
使用unordered_multimap容器
#include <unordered_map>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj09
{
void test_unordered_multimap(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_unordered_multimap().......... \n";
unordered_multimap<long, string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
//multimap 不可使用 [] 進行 insertion
c.insert(pair<long,string>(i,buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "unordered_multimap.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multimap.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //357913941
long target = get_a_target_long();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target);
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, value=" << (*pItem).second << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
}测试结果
test_unordered_multimap()..........
milli-seconds : 1995
unordered_multimap.size()= 100000
unordered_multimap.max_size()= 107374182
target(0~32767)
11111
c.find(), milli-seconds : 0
found, value=22712后面一篇对set,map进行介绍





 本文对比了C++标准库中的multiset、multimap、unordered_multiset及unordered_multimap的性能,详细介绍了各容器的特性,如红黑树、哈希表实现原理,以及find()函数的效率测试。
本文对比了C++标准库中的multiset、multimap、unordered_multiset及unordered_multimap的性能,详细介绍了各容器的特性,如红黑树、哈希表实现原理,以及find()函数的效率测试。
















 1053
1053

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








