文章目录
104二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回它的最大深度 3 。
c++ 代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
// 递归三要素,函数参数
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
// 停止条件
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
// 单个判断
int left = maxDepth(root->left);
int right = maxDepth(root->right);
// 加 1 是根节点数
return max(left, right) + 1;
}
};
// 利用层序遍历,求深度
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
int depth = 0;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode * node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return depth;
}
};
python 代码实现
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0;
l = self.maxDepth(root.left)
r = self.maxDepth(root.right)
return max(l, r) + 1
559.n叉树的最大深度
给定一个 N 叉树,找到其最大深度。
最大深度是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点总数。
N 叉树输入按层序遍历序列化表示,每组子节点由空值分隔(请参见示例)。
示例 1:

输入:root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
输出:3
示例 2:
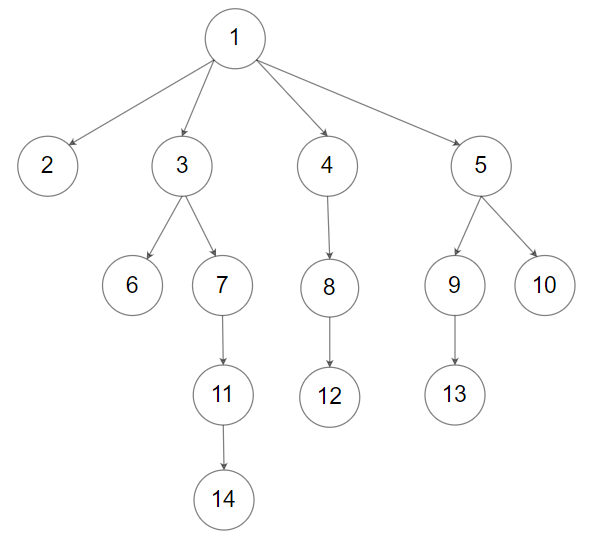
输入:root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
输出:5
提示:
- 树的深度不会超过
1000。 - 树的节点数目位于
[0, 104]之间。
c++ 代码实现
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
queue<Node*> que;
que.push(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node* node = que.front();
que.pop();
for (int j = 0; j < node->children.size(); j++) {
if (node->children[j]) que.push(node->children[j]);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
};
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
int depth = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < root->children.size(); i++) {
depth = max(depth, maxDepth(root->children[i]));
}
return depth + 1;
}
};
python 代码实现
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: 'Node') -> int:
if not root:
return 0
depth = 0
for i in range(len(root.children)):
depth = max(depth, self.maxDepth(root.children[i]))
return depth + 1
111二叉树的最小深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
**说明:**叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
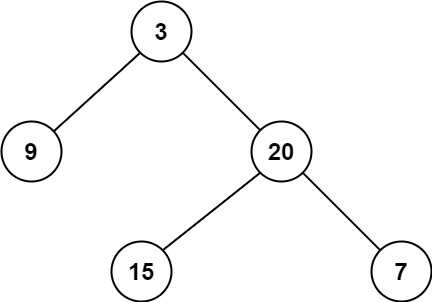
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:2
示例 2:
输入:root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
输出:5
提示:
- 树中节点数的范围在
[0, 105]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
c++ 代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
int left = minDepth(root->left);
int right = minDepth(root->right);
// 因为,根节点不为最小,左右孩子是否为空
// 当一个左子树为空,右不为空,这时并不是最低点
if (root->left != nullptr && root->right == nullptr){
return 1 + left;
}
// 当一个右子树为空,左不为空,这时并不是最低点
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right != nullptr) {
return 1 + right;
}
int depth = min(left, right) + 1;
return depth;
}
};
// 迭代实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode * node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
// 如果左右子树都为空则返回深度
if (node->left == nullptr && node->right == nullptr) {
return depth;
}
}
}
return depth;
}
};
python代码实现
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def minDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
l = self.minDepth(root.left)
r = self.minDepth(root.right)
if root.left and not root.right:
return 1 + l
if root.right and not root.left:
return 1 + r
result = min(l, r) + 1
return result;
222完全二叉树的节点个数
给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
示例 1:
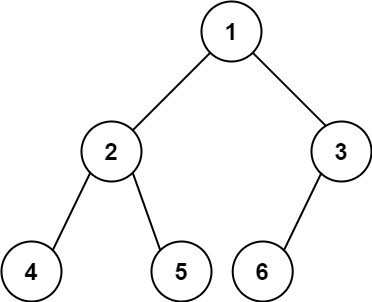
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
输出:6
示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:0
示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:1
提示:
- 树中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5 * 104] 0 <= Node.val <= 5 * 104- 题目数据保证输入的树是 完全二叉树
**进阶:**遍历树来统计节点是一种时间复杂度为 O(n) 的简单解决方案。你可以设计一个更快的算法吗?
c++ 代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
int l = countNodes(root->left);
int r = countNodes(root->right);
return (l+r+1);
}
};
python 代码实现
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def countNodes(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
l = self.countNodes(root.left)
r = self.countNodes(root.right)
return l+r+1



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








