这篇paper,感觉有点牛哎~只有两页
为了克服之前提出来的两个问题,我们提供一个新的训练算法,这个算法继承了元学习和遗传学习的优势。
这个联合训练方法使用了两个损失函数:
1)task-specific(遗传学习):![]() 定义在整个基础模型的训练集上
定义在整个基础模型的训练集上
2)task-agnostic(元学习):![]() 定义在任务分布的元学习损失(例如:5个分类的分类任务)
定义在任务分布的元学习损失(例如:5个分类的分类任务)
从这两个 损失函数 中独立计算两个梯度更新,然后用这两个 更新向量 的 加权平均值 更新模型
元学习中的任务是 从分布中 采样出来的,然而在采样中的所有的实例都是为了遗传学习中的优化
为了适应一个未知的任务,将使用规则随机梯度下降(损失函数每计算一次就更新一次,速度快但是会在最小值那震荡,因为有的数值是往反方向更新)
对于元学习模型,我们用MAML和Repyil评估我们的方法,我们用这类的元学习算法是因为:由于这类算法反对匹配网络和他们的一阶形式,他们的模型不可知,可以直接应用到任何一个被梯度下降训练法训练过的模型上。
这个被提出的模型在某种意义上相似于Gradient Agreement ,因为它把模型参数推动到朝着一方向的推动,即整个任务的分布和整个类别的训练的单个特殊任务的分布相一致。
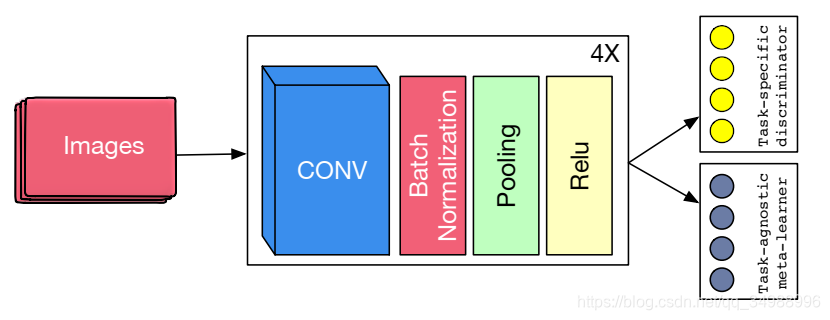
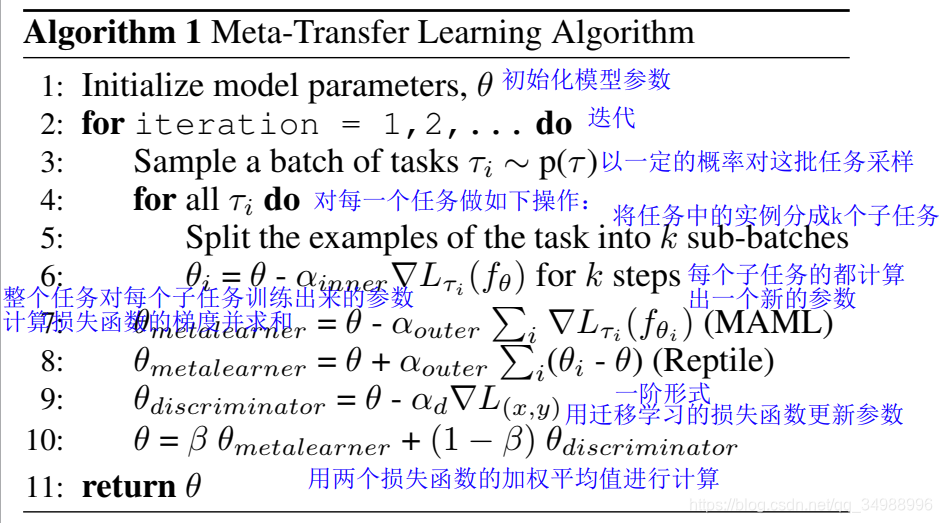








 本文提出了一种结合遗传学习和元学习优势的联合训练算法,通过定义task-specific和task-agnostic损失函数,独立计算梯度并加权平均更新模型参数,以解决先前存在的问题。该方法适用于所有梯度下降训练模型。
本文提出了一种结合遗传学习和元学习优势的联合训练算法,通过定义task-specific和task-agnostic损失函数,独立计算梯度并加权平均更新模型参数,以解决先前存在的问题。该方法适用于所有梯度下降训练模型。
















 968
968

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








