什么是分页技术
分页,是一种将所有数据分段展示给用户的技术.用户每次看到的不是全部数据,而是其中的一部分,如果在其中没有找到自习自己想要的内容,用户可以通过制定页码或是翻页的方式转换可见内容,直到找到自己想要的内容为止.其实这和我们阅读书籍很类似。
分页的意义
分页确实有效,但它一定会加大系统的复杂度,但可否不分页呢?如果数据量少的话当然可以。但是对于企业信息系统来说数据量不会限制在一个小范围内。如果不顾一切的Select * from某个表,再将返回的数据一古脑的扔给客户,即使客户能够忍受成千上万足够让人眼花缭乱的表格式数据,繁忙的网络,紧张的服务器也会提出它们无声的抗议,甚至有时会以彻底的罢工作为终结。这个结局有点像古代为所欲为的暴君和他忍无可忍的臣民之间的故事。
程序员不是暴君,他希望程序使生活变得更好而不是更糟。考虑到企业信息系统多是三层甚至更多层架构的事实,程序员在向客户展示数据时都应该采取分页的形式。如果他不想被抱怨淹没或是半夜被电话惊醒的话。
相关算法
总行数(count): select count(1) from pet;
每页显示的行数: size
页数: countPage = (count-1)/size+1;
当前页号: currentPage
当前要显示的页面数据的起始行号和终止行号
startIdx: (currentPage-1)*size
如何显示从startIdx开始的size条记录
select * from pet limit startIdx, size
///////////////数据封装/////////////////
Map<String,Object> map;//封装表中的一行记录
map.put("id",1)
map.put("name","小黄");
map.put("color","黄色");
List<Map<String,Object>> datas; //封装整个表格
datas.add(map);
datas.add(map2);
Map<String,Object> result; //封装数据表 和 总页数 , 当前页码
//在dao中封装
result.put("datas",datas);
result.put("pageCount",pageCount);
//在servlet中封装
result.put("currentPage",currentPage);效果图:
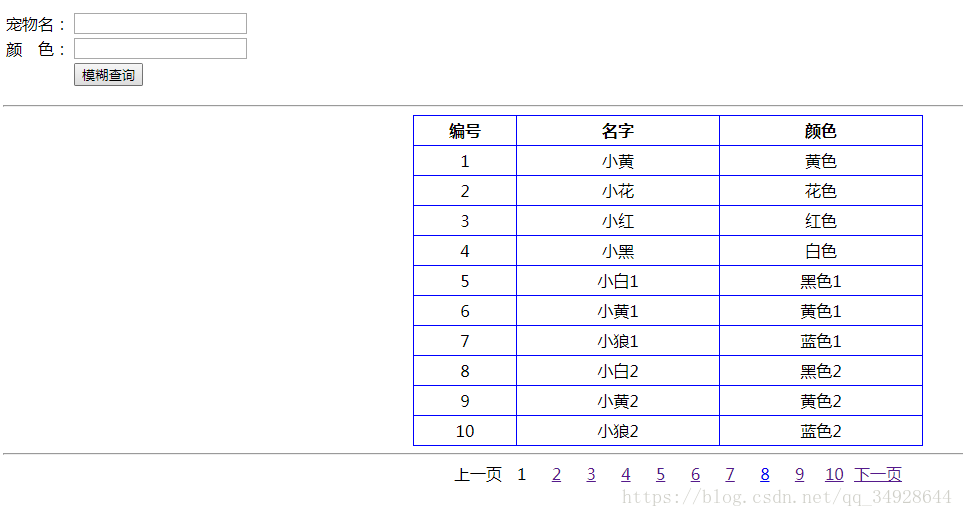
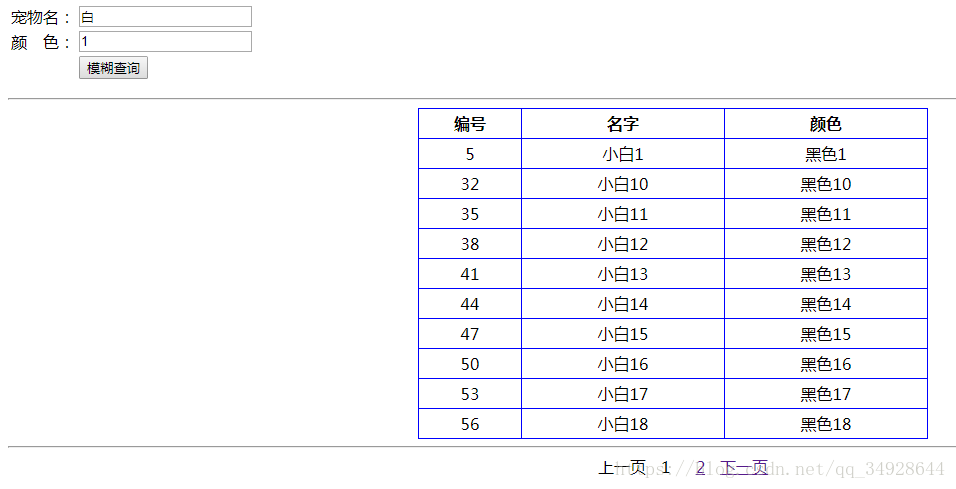
关键代码
前端页面
采用JSP+JSTL生成表格中的每一行记录。
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>宠物管理</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="<c:url value='/css/show.css'/>">
</head>
<body>
<h1>宠物信息查询</h1>
<a href="<c:url value='/PetServlet'/>">查看所有</a>
<br/>
<br/>
<form action="<c:url value='/PetServlet?action=likeQuery'/>" method="post">
<table>
<tr>
<td>宠物名:</td>
<td><input type="text" name='name' value="${pet.name}" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>颜 色:</td>
<td><input type="text" name='color' value="${pet.color}" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td><input type="submit" value='模糊查询' /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
<c:if test="${!empty queryString}">
<hr />
<table class="showTable">
<tr>
<td>编号</td>
<td>名字</td>
<td>颜色</td>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="${result.datas}" var="map">
<tr>
<td>${map.id}</td>
<td>${map.name}</td>
<td>${map.color}</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
<hr/>
<!-- 显示页码 -->
<div class="page">
<c:if test="${result.currentPage != 1}" var="boo">
<a href="<c:url value='/PetServlet?${queryString}currentPage=${result.currentPage-1}'/>">上一页</a>
</c:if>
<c:if test="${!boo}">
<span>上一页</span>
</c:if>
<c:forEach begin="${show.showStart}" end="${show.showEnd}" var="idx">
<c:if test="${result.currentPage==idx}" var="boo">
<span class="pageCode">${idx}</span>
</c:if>
<c:if test="${!boo}">
<span class="pageCode">
<a href="<c:url value='/PetServlet?${queryString}currentPage=${idx}'/>">${idx}</a>
</span>
</c:if>
</c:forEach>
<c:if test="${result.currentPage != result.countPage}" var="boo">
<a href="<c:url value='/PetServlet?${queryString}currentPage=${result.currentPage+1}'/>">下一页</a>
</c:if>
<c:if test="${!boo}">
<span>下一页</span>
</c:if>
</div>
</c:if>
</body>
</html>模糊查询的请求处理
当用户点击模糊查询按钮时,就会向服务器发生一个post请求,doPost()方法中根据类反射机制调用了likeQuery()方法进行相应的业务处理。
/**
* 模糊查询
*
* @param request
* 请求对象
* @param response
* 响应对象
* @throws ServletException
* @throws IOException
*/
public void likeQuery(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取用户所要查询的页
String strCurrentPage = request.getParameter("currentPage");
int currentPage = 1;
try {
currentPage = Integer.valueOf(strCurrentPage);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
// 这里能出异常一般是用户黑服务器
//e.printStackTrace();
}
//获取查询条件
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String color = request.getParameter("color");
Pet pet = new Pet();
pet.setName(name);
pet.setColor(color);
request.getSession().setAttribute("pet", pet);
try {
// 一页的记录数
int size = 10;
// 查询出 countPage 和 datas
Map<String, Object> result = service.likeQueryByCurrentPage(currentPage, size,pet);
// 获取总的页数
int countPage = (int) result.get("countPage");
// 需要显示的页码的个数
int showLen = 10;
// 获得起始页码,和结束页码
Map<String, Integer> show = getShowSatrAndShowEnd(currentPage, showLen, countPage);
// 把存放showStart和showEnd的 'Map' 放入 request 容器中
request.setAttribute("show", show);
// 再把当前页封装过去
result.put("currentPage", currentPage);
// 封装查询串并放入 request 容器中
String queryString = "action=likeQuery&name="+name+"&color="+color+"&";
request.setAttribute("queryString", queryString);
// 把结果放入 request 容器中
request.setAttribute("result", result);
// 请求转发
request.getRequestDispatcher("/index.jsp").forward(request, response);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 按理这样应该重定向到错误页面,这里就算了。
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}运算显示页码的起始位置和结束位置
提供当前页、要显示页码的个数、总的记录数,就可以算出起始页和结束页。
/**
* 获得显示页的起始,和显示页的结束
* @param currentPage 当前页
* @param showLen 显示页码的个数
* @param countPage 总的页数
* @return 封装了showStart和showEnd的Map集合
*/
private Map<String, Integer> getShowSatrAndShowEnd( int currentPage,int showLen,int countPage ){
HashMap<String, Integer> show = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
// 初始化起始页码,和结束页码
int showStart = 1;
int showEnd = 1;
// 当 '所需显示的页码个数' 大于等于 '总的页数' 时
if (showLen >= countPage) {
showStart = 1; // 起始页为1
showEnd = countPage; // 结束页为总的页数
} else {
// 当 '当前页' 小于等于 '所需显示的页码个数'的一半时
if (currentPage <= showLen / 2) {
showStart = 1; // 起始页为1
showEnd = showLen; // 结束页为 '所需显示的页码个数'
} else if (currentPage > countPage - showLen / 2) {
// 当 '当前页' 大于 '总的页数'-('所需显示的页码个数'的一半)时
showEnd = countPage;
showStart = countPage - showLen + 1;
} else {
showStart = currentPage - showLen / 2;
showEnd = showStart + showLen - 1;
}
}
show.put("showStart", showStart);
show.put("showEnd", showEnd);
return show;
}DAO数据查询并封装
Servlet调用service,service调用dao中的likeQueryByCurrentPage()方法,在SQL语句生成是采用了一个小技巧,不管查询条件有几个先给没有条件查询的sql语句后面拼接 'where 1=1 ' 如果后面有条件就直接 'and 条件 '。这样就可以通吃个数不确定的条件查询。封装具体的查询条件采用集合的方式,因为怕用户黑查询,所有采用dbutils工具的query方法所提供的可以通过带占位符的sql语句+可变参数去查询。dbutils工具基本使用方法快速通道:Apache公司的dbutils工具。
@Override
public Map<String, Object> likeQueryByCurrentPage(int currentPage, int size, Pet pet) throws SQLException {
HashMap<String, Object> result = new HashMap<String,Object>();
//获得数据库连接池
DataSource ds = C3p0Utils.getDataSource();
//获取 QueryRunner的实例
QueryRunner qr = new QueryRunner(ds);
////////拼装模糊查询语句和数据////////////
String sql1 = "select count(1) from pet where 1=1 ";
String sql2 = "select * from pet where 1=1 ";
List<Object> conditions = new ArrayList<Object>();
String name = pet.getName();
if( name != null && name.trim().length() != 0 ) {
sql1 += "and name like ? ";
sql2 += "and name like ? ";
conditions.add("%"+name+"%");
}
String color = pet.getColor();
if( color != null && color.trim().length() != 0 ) {
sql1 += "and color like ? ";
sql2 += "and color like ? ";
conditions.add("%"+color+"%");
}
sql2 += "limit ?,?"; //执行该sql语句前需要把额外条件封装进conditions中!!!
///////////////////////////////
//先查询总的记录数
Integer count = Integer.valueOf( ""+qr.query( sql1, new ScalarHandler(), conditions.toArray() ) );
//计算总的页数
int countPage = (count-1)/size+1;
result.put("countPage", countPage);
//查询当前页的记录
int startIdx = (currentPage-1)*size;
////////补充条件////////
conditions.add(startIdx); //起始位置
conditions.add(size); //查询的记录数量
/////////////////////
List<Map<String, Object>> datas = qr.query( sql2, new MapListHandler(), conditions.toArray() );
result.put("datas", datas);
return result;
}























 180
180

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








