一.流分类
1.按流方向:输入流(读) ,输出流(写)
2.按读取方式:字节流 , 字符流
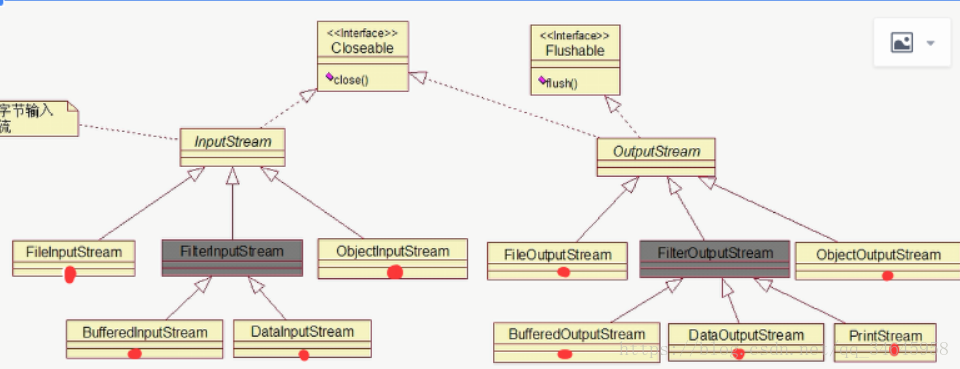
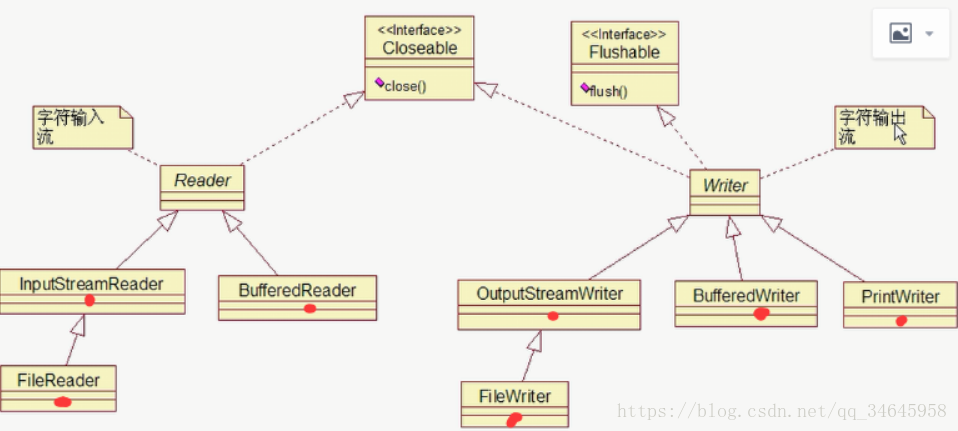
二.字节流
1.使用字节流实现文件的拷贝
public class Copy1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("E:/a.txt");
fos = new FileOutputStream("E:/b.txt", true);
//定义一个字节数组,减少IO次数
byte[] buff = new byte[1024];
//表示读取的字节数,如果未读到,返回-1
int len = 0;
while ((len = fis.read(buff)) != -1) {
fos.write(buff, 0, len);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
}
}
2.使用缓冲流包装字节流复制文件(缓冲流是一种包装流)
public class Copy1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
fis = new FileInputStream("E:/a.txt");
//使用缓冲流进行包装
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis, 10000);
fos = new FileOutputStream("E:/b.txt", true);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos, 10000);
//定义一个字节数组,减少IO次数
byte[] buff = new byte[1024];
//表示读取的字节数,如果未读到,返回-1
int len = 0;
while ((len = bis.read(buff)) != -1) {
bos.write(buff,0,len);
}
bis.close();
fis.close();
bos.close();
fos.close();
}
}二.字符流
使用字符流完成文件拷贝
public class Copy2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("E:/a.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("E:/b.txt"));
//临时字符数组
char[] buff = new char[512];
int len = 0;
while ((len = br.read(buff))!=-1){
bw.write(buff,0,len);
}
bw.flush();
br.close();
bw.close();
}
}三.转换流
1.转换流的作用:(1)将字节流转换为字符流(从而可以使用字符流的readLine等方法)
(2)设置编码
public class Trans {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("E:/a.txt"));
//只有转换流可以设置编码
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter
(new FileOutputStream("E:/b.txt"),"utf-8"));
String str = null;
while ((str = br.readLine())!=null){
bw.write(str+"\r\n");
}
bw.flush();
bw.close();
br.close();
}
}四.对象流(实现序列化和可序列化)
public class ObjectStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//序列化
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:/obj.object"));
oos.writeObject(new Person("王强", 18));
oos.close();
//反序列化
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:/obj.object"));
Person p = (Person) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(p.getName()+""+p.getAge());
}
}注意:使用transient修饰的变量不会被序列化
























 616
616

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








