1.关键字和新语法
1.1 auto关键字及用法
A.概念和一般用法
auto一般习惯称作自动类型推断。由其含义不难得出,凡是前面惯有auto的变量或者函数,其类型将会由编译器按照上下推断出来。对于变量,指定要声明的变量的类型讲自动从其初始化中推断出来。对于函数,指定返回类型为其返回值类型。
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
using namespace std;
//返回类型为numA + numB 即int
auto test(int numA,int numB)
{
return numA + numA;
}
int main()
{
int nNumA = 3,nNumB = 4;
//返回类型为int
auto nNumC = test(nNumA, nNumB);
cout << nNumC << " " << typeid(nNumC).name() << endl;
return 0;
}
从上面的例子我们可以出来,auto确实进行了自动类型推断的功能,并且实际类型正确无误。
B.注意事项
1.auto可以同时声明多个变量,但变量的类型必须一致。
2.在块作用域、命名空间范围、for循环的初始化语句中声明变量时,可以使用关键字AUTO作为类型说明符。
3.在不使用尾部返回类型语法的函数声明中,关键字AUTO表示将使用模板参数演绎规则从返回语句的操作数中推断返回类型。
4.在使用尾部返回类型语法的函数声明中,关键字AUTO不执行自动类型检测。它只作为语法的一部分。
C.提醒
直到C++ 11,Auto具有存储持续时间说明符的语义。
1.2 nullptr关键字及用法
A.nullptr的作用
测试如下代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void testA(int n)
{
cout << "testA" << endl;
}
void testA(int *n)
{
cout << "testB" << endl;
}
int main()
{
testA(nullptr);
testA(NULL);
return 0;
}
结构如下图所示
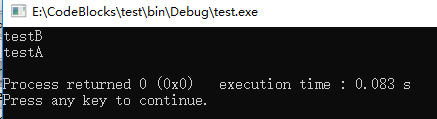
其实我们的本意都是想调用testA(int *n),但是测试程序给出的结果和我们的预期又不不同,因为编译将其解释为一个空值并不是空指针。
B.内部可能的实施
#define NULL 0
//since C++11
#define NULL nullptr
1.3 基于范围的循环
学习使用c++的时候,我们经常吐槽for循环没有python使用起来那么方便,每次必须必须至少写一个参数,但是c++新增基于范围循环的特性,我们可以按照下面的方法使用for循环。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n [] = {1,2,3,4,5};
for(auto i : n)
cout << i << endl;
return 0;
}
当然,基于范围的循环对于所有STl容器都是适应的。
2.STL容器
1.1 array
std::array是封装固定大小数组的容易。此容器是一个聚合类型,其语义等同于保有一个c风格数组T[N]作为其唯一费静态数据成员的结构体。
示例
#include <string>
#include <iterator>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <array>
int main()
{
// 用聚合初始化构造
std::array<int, 3> a1{ {1, 2, 3} }; // C++11 中要求双花括号
std::array<int, 3> a2 = {1, 2, 3}; // 决不要求在 = 后
std::array<std::string, 2> a3 = { std::string("a"), "b" };
// 支持容器操作
std::sort(a1.begin(), a1.end());
std::reverse_copy(a2.begin(), a2.end(),
std::ostream_iterator<int>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << '\n';
// 支持带范围 for 循环
for(const auto& s: a3)
std::cout << s << ' ';
}
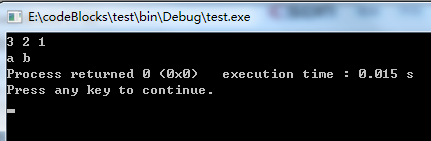
结果
1.2 std::forward_list
实现为单链表,且实质上与其在 C 中实现相比无任何开销。与 std::list相比,此容器提在不需要双向迭代时提供更有效地利用空间的存储。





















 11万+
11万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








