本文主要参考自:SQL简明数据分析教程 及 MySQL---数据库从入门走向大神系列(一)-基础入门
一 创建与检索
create database testbase character set utf8; 创建数据库
use testbase; 使用该数据库
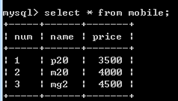
create table mobile(
num varchar(15) not null primary key,
name varchar(15) not null,
price int ); 创建表
insert into mobile(num, name, price) values('1','p20','3500'); 插入数据
insert into mobile values('2','m20','4000');
insert into mobile values('3','mg2','4500');
insert into tableA(columnA, columnB) select columnC, columnD from tableB;
插入检索出的数据:将表B的C D列数据复制到表A的 A B列
select * from mobile; 检索

select * from mobile order by name; 按name排序

select distinct name,price from mobile order by num desc; 降序desc,升序asc

select distinct num from mobile limit 1,2;
1表示取第2行(从0起),2表示共取2行

select * from mobile where num > '1' order by price desc limit 2;
取num>1中降序排列的前2行

select * from mobile where price between 4000 and 4500;
取price大于等于4000且小于等于4500
或:select * from mobile where price>=4000 and price<=4500;

select * from mobile where price in (4000 ,4500);
取price等于4000和 4500。 not in 指不等于
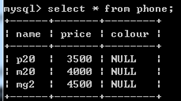
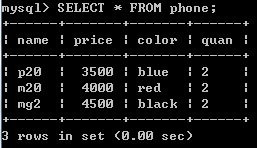
select * from phone where name like '%20';

模糊检索,'%20':以20结尾的; '20%':以20开头的; '%20%':含20的。
select * from phone where name like '_2_';
'_2_':3个字符,中间为2的。
二 增删与修改
alter table mobile rename phone; 改表名
alter table phone add column color varchar(10); 增加color列,column可以省略
alter table phone add column color varchar(10) after price;
after price表示加在price列后;用first表示加在第一列
alter table phone drop num; 删除num列
delete from phone where name='mg2'; 删除name列值为mg2的行
alter table phone change column color colour varchar(10); 改列名color为colour
 》》》》
》》》》 
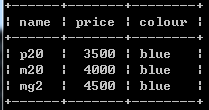
update phone set colour='blue' where colour is null;
替换:修改颜色为null的值为blue,null前用is
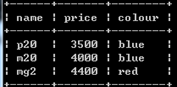
update phone set price=4400,colour='red' where name='mg2';
两表关联后修改字段值:
update 表1 a join 表2 b on a.xx=b.xx set a.xx1=b.xx1, a.xx2=b.xx2; (大表运行很慢)
update 表1 a , 表2 b set a.xx1=b.xx1 where a.xx=b.xx;
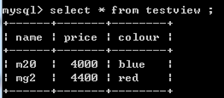
create view testview as select * from phone where price >=4000;
创建视图(需表),只存于内存。
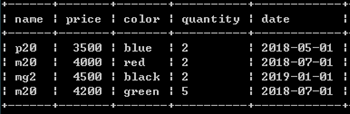
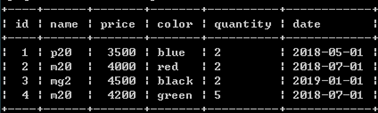
alter table mobile add id int primary key not null auto_increment first;
新增id列,实现自增。此处必须设为primary key
或: alter table phone add id int first;
select @rowid:=0;
update phone set id=(@rowid:=@rowid+1);
↓ ↓ ↓
三 函数
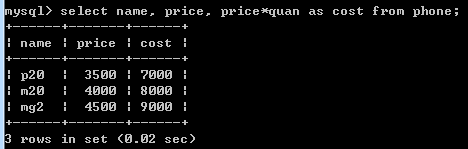
select name, price, price*quan as cost from phone;
取name,price,price*quan三列。可进行+, -, *, / 操作。
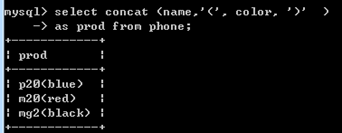
select concat (
name , '(' , color , ')'
) as prod from phone; 拼接字符串,例为 加上括号
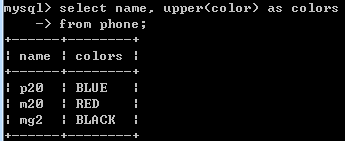
select name, upper(color) as colors from phone;
对color列的值转成大写。lower为转成小写。
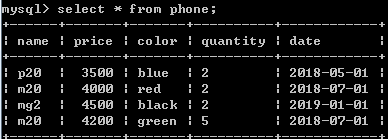
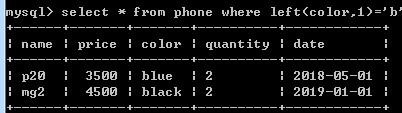
select * from phone where left(color,1)='b';
取color列字符串中,左起第1个字符为b的值。right为右起。
按日期筛选,可用date,month,year,日期格式必须为yyyy-mm-dd
select name, price from phone
where Date(date) between '2018-05-01' and '2018-06-01';
从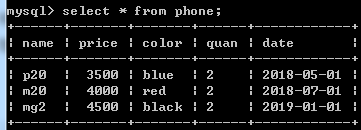 检索出:
检索出: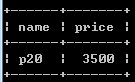
select name,date from phone where year(date)=2018;
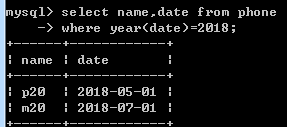
select count(*) as num from phone;
计算表中行数(包括null)。如需忽略null,则改*为列名
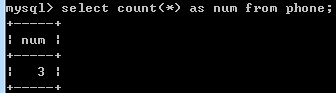
select sum(price) as cost from phone;
求和sum,平均avg,最大max,最小min,四舍五入round
括号里面加distinct表示去掉重复值,如sum(distinct price)
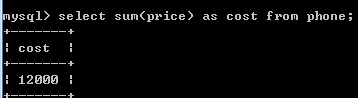
select name, price from phone
where price = (select max(distinct price) from phone );
存在判断:
1. in()适合B表比A表数据小的情况
2. exists()适合B表比A表数据大的情况
3. 当A表与B表数据一样大时,in与exists效率差不多,可任选一个使用。
select * from A
where id in(select id from B);
in()只执行一次,它查出B表中的所有id字段并缓存起来。之后,检查A表的id是否与B表中的id相等,即逐个A数据遍历B数据。所以B越小越好。
如:A表有10000条记录,B表有100000000条记录,那么最多有可能遍历10000*100000000次
再如:A表有10000条记录,B表有100条记录,那么最多有可能遍历10000*100次
select a.* from A a
where exists(select * from B b where a.id=b.id);
exists()会执行A.length次,它并不缓存exists()结果集,因为exists()结果集的内容并不重要,重要的是结果集中是否有记录,如果有则返回true,没有则返回false,即二选一。
如:A表有10000条记录,B表有100000000条记录,那么exists()执行10000次,因为它只执行A.length次
再如:A表有10000条记录,B表有100条记录,那么exists()还是执行10000次。
举例:
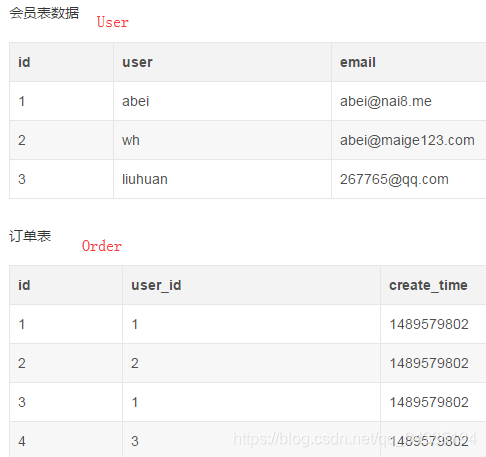
SELECT * FROM User
WHERE exists (SELECT * FROM Order WHERE user.id = order.user_id)
SELECT * FROM User
WHERE id in (SELECT user_id FROM Order)
四 分组
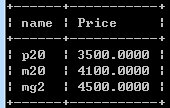
select name,avg(price) as Price from phone group by name order by Price;
按不同的name分组,同一组中取平均值Price,再按Price升序排列
 》》》
》》》
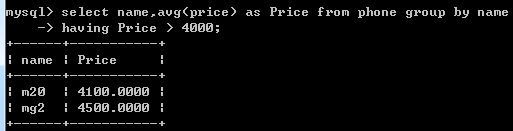
select name,avg(price) as Price from phone group by name having Price > 4000;
过滤功能:按不同的name分组,同一组取平均值Price,再取Price>4000的值
与where比较:WHERE过滤行,而HAVING过滤分组
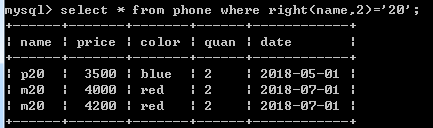
select * from phone where right(name,2)='20';
取符合name值右边两个字符为20的数据。左边用left
五 子查询
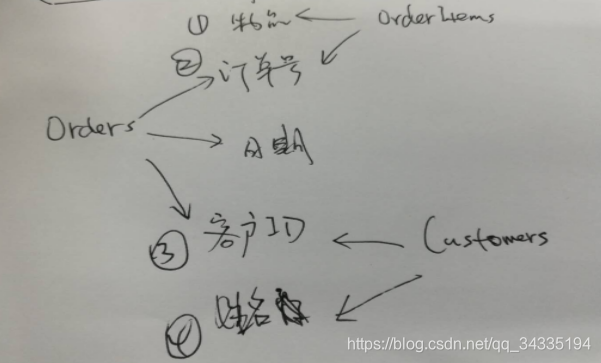
常用的数据库表都是关系表,若有如下3个表:
Orders表存储订单编号、客户ID、订单日期;
OrderItems表存储各订单内的具体物品;
Customers表存储顾客的客户ID、姓名。
现需要列出订购物品A的所有顾客的姓名,实现步骤如下:
1. 检索包含【1物品A】的所有【2订单编号】;
2. 检索前一步骤订单编号的对应的【3客户ID】;
3. 检索前一步骤的客户ID对应的【4客户姓名】。
SELECT cust_name
FROM Customers
WHERE cust_id IN (SELECT cust_id
FROM Orders
WHERE order_num IN (SELECT order_num
FROM OrderItems
WHERE prod_id = 'A' ) );
六 join与union连接
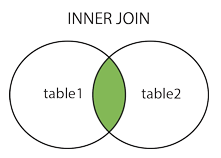
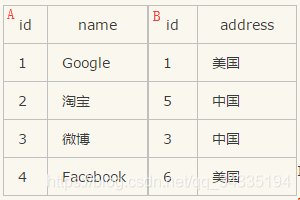
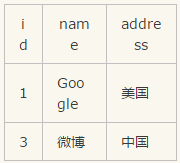
select * from Table A inner join Table B on Table A.id = Table B.id;
 》》》》
》》》》
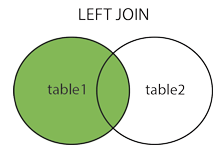
select * from Table A left join Table B
on Table A.id=Table B.id;
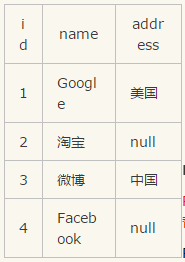
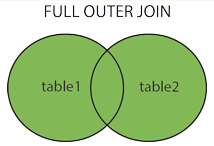
select * from Table A full join Table B
on Table A.id=Table B.id;
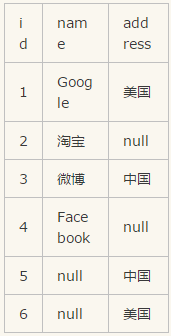
五中的子查询还可如下处理:
SELECT cust_name FROM Customers, Orders, OrderItems
WHERE Customers.cust_id = Orders.cust_id
AND OrderItems.order_num = Orders.order_num
AND prod_id = 'A';
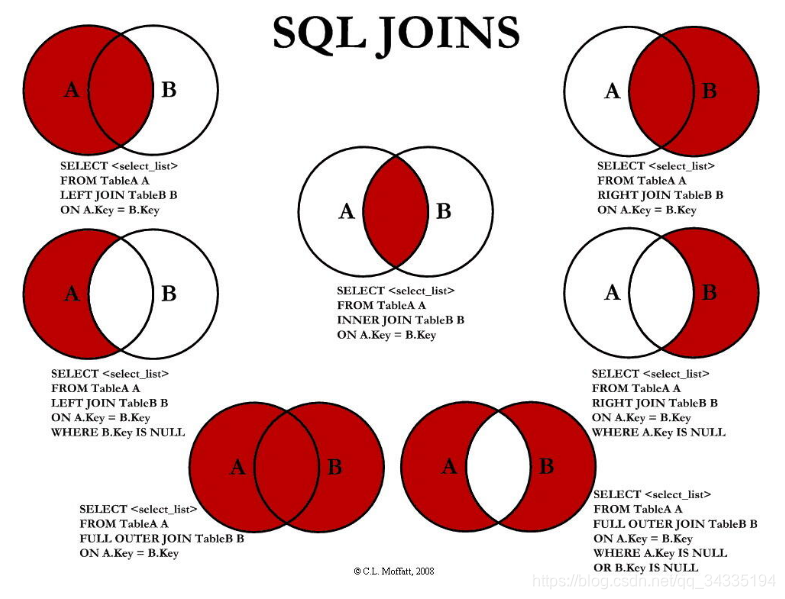
UNION 与 UNION ALL(union类似合并,join类似拼接)
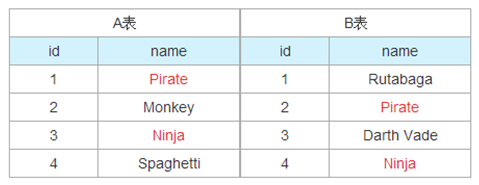
SELECT name FROM TableA
UNION SELECT name FROM TableB;
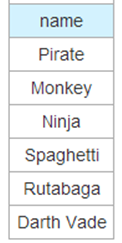
SELECT name FROM TableA
UNION ALL SELECT name FROM TableB;








 本文详细介绍了MySQL的基础操作,包括创建与检索数据库和表,增删改数据,使用函数,进行分组查询,子查询以及JOIN和UNION操作。涵盖了创建数据库、表,插入、更新和删除数据,以及各种查询技巧,如按条件筛选、排序、分页和聚合函数。
本文详细介绍了MySQL的基础操作,包括创建与检索数据库和表,增删改数据,使用函数,进行分组查询,子查询以及JOIN和UNION操作。涵盖了创建数据库、表,插入、更新和删除数据,以及各种查询技巧,如按条件筛选、排序、分页和聚合函数。
















 455
455

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








