题目描述
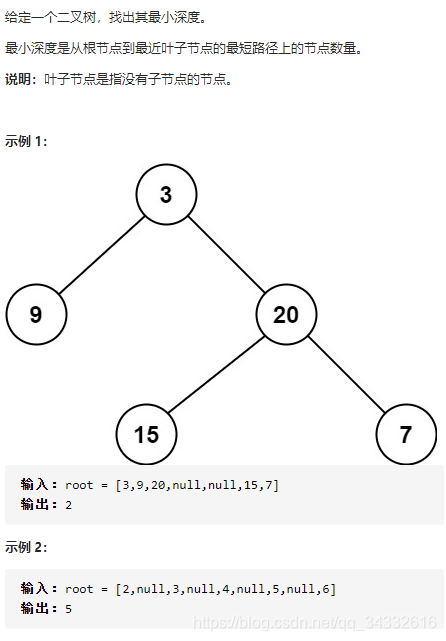
我的解法
思路
使用和求最大深度时类似的递归法,只不过将单层逻辑中的获取左右子树最大值变成过去左右子树最小值。但是出错了
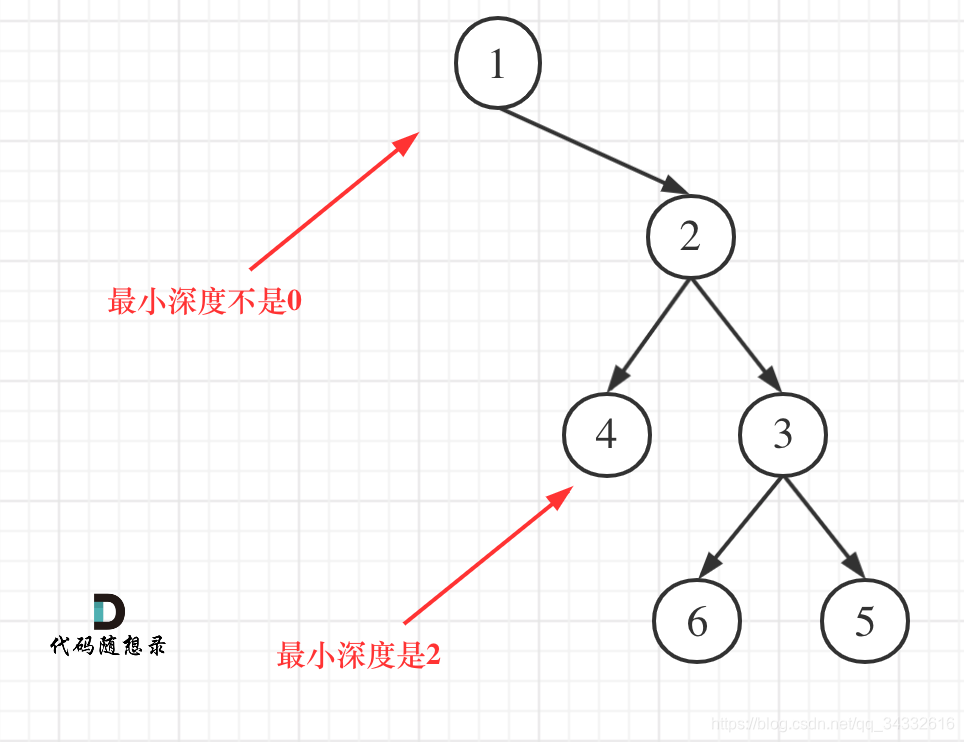
错误时的情况
下图来源于公众号代码随想录
出错的Java代码
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
return getMinDepth(root);
}
public int getMinDepth(TreeNode node){
if(node == null){return 0;}
int minLeftDepth = getMinDepth(node.left);
int minRightDepth = getMinDepth(node.right);
int depth = Math.min(minLeftDepth,minRightDepth) + 1;
return depth;
}
}
修改后的Java代码(递归法)

class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
return getMinDepth(root);
}
public int getMinDepth(TreeNode node){
if(node == null){return 0;}
int minLeftDepth = getMinDepth(node.left);
int minRightDepth = getMinDepth(node.right);
// 新增对子树为空时的处理
if(node.left == null && node.right != null) {
return minRightDepth + 1;
} else if(node.right == null && node.left != null){
return minLeftDepth + 1;
} else{
return Math.min(minLeftDepth,minRightDepth) + 1;
}
}
}
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n) 其中n是树的节点数,对每个节点访问一次
空间复杂度:O(h) 其中h是树的高度,空间复杂度主要取决于递归时栈空间的开销,最坏情况下,树呈链状,空间复杂度为O(n),平均情况下树的高度与节点数的对数正相关,空间复杂度为O(logn)
迭代法思路
和求最大深度一样使用层序遍历,不过这次要设置一个标记,当访问节点的左右节点都为空时就直接退出了
Java代码
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode> qu = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
if(root == null) {return 0;}
qu.offerLast(root);
int depth = 0;
while(!qu.isEmpty()){
int levelSize = qu.size();
depth++;
for(int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++){
TreeNode node = qu.pollFirst();
if(node.left == null && node.right == null){return depth;}
if(node.left != null){qu.offerLast(node.left);}
if(node.right != null){qu.offerLast(node.right);}
}
}
return depth;
}
}








 这篇博客探讨了在计算二叉树最小深度时可能出现的问题,通过实例展示了错误的Java代码,并提供了修正后的递归解决方案。博主分析了递归法的时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度在最坏情况下为O(n)。此外,还提出了迭代法思路来解决该问题。
这篇博客探讨了在计算二叉树最小深度时可能出现的问题,通过实例展示了错误的Java代码,并提供了修正后的递归解决方案。博主分析了递归法的时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度在最坏情况下为O(n)。此外,还提出了迭代法思路来解决该问题。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








