Python基本数据类型——字符串
字符串是字符的序列表示,可以由一对单引号(’),双引号(“)或三引号(’’’)构成。
其中单引号和双引号都可以表示单行字符串,两者作用相同。使用单引号时,双引号可以作为字符串的一部分,反之亦然。
三引号可以表示单行或多行字符串。
1、字符串实质上是字符的序列表示
2、按住鼠标左键再单击str可进入源码查看str拥有的函数方法按住鼠标左键再单击str可进入源码查看str拥有的函数方法
3、例如,查看到isalpha()方法的源码如下:
def isalpha(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Return True if the string is an alphabetic string, False otherwise.
A string is alphabetic if all characters in the string are alphabetic and there
is at least one character in the string.
"""
pass
- isalph()方法使用实例:
s1 = 'python'
s2 = '223'
print(s1.isalpha()) #True
print(s2.isalpha()) #False
- center()方法使用实例:
s1 = 'python'
s2 = '223'
print(s1.center(9))
print(s1.center(9, '='))
'''
运行结果:
python (注意,如果没有设置填充值,默认用空格填充)
==python=
'''
4、字符串—常用功能
| 方法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| strip() | 移除空白 |
| split() | 分割 |
| len() | 长度 |
| s[0], s[1] | 索引 |
| s[0: 2] | 切片 |
- strip()方法用于移除字符串两边空白:默认为移除两边的空白,但可选择移除左边或右边的空白
s = ' hello,python '
print(s.strip())
print(s.lstrip())
print(s.rstrip())
'''
运行结果:
hello,python
hello,python
hello,python
'''
strip()方法也可以用来移除特定的字符,但是要求开始时不能有空格
s1 = ' hello '
s2 = 'hello '
print(s1.strip('h')) # hello
print(s2.strip('h')) #ello
- split()方法用于分割字符串,使用split方法之后字符串会变成一个列表
s = 'hello,python'
print(s.split()) #['hello,python']
print(s.split(",")) #['hello', 'python']
print(s.split("l", 1)) #['he', 'lo,python']
print(s.split("l", 2)) #['he', '', 'o,python']
- len()方法用于查看字符串长度
s = 'hello,python'
print(len(s)) #12
- 索引
s = 'hello,python'
print(s[0]) #h
print(s[-12]) #h
- 切片:包前不包后,索引0可以不写
s = 'hello,python'
print(s[0:2]) #he
print(s[:2]) #he
print(s[0:-7]) #hello
print(s[:-7]) #hello
print(s[-6:]) #python
print(s[-6:-1]) #pytho (因为切片是包前不包后的)
split()方法的源码:
def split(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Return a list of the words in the string, using sep as the delimiter string.
sep
The delimiter according which to split the string.
None (the default value) means split according to any whitespace,
and discard empty strings from the result.
maxsplit
Maximum number of splits to do.
-1 (the default value) means no limit.
"""
pass
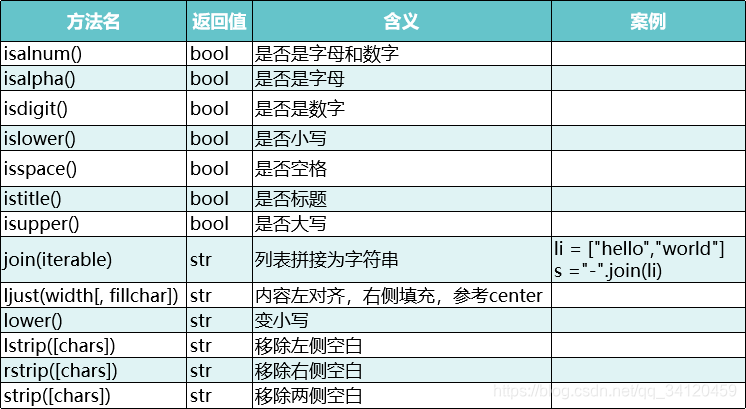
5、字符串功能一览表

6、练习
- 自定义一个字符串(eg:a = “hello,python!”),用切片的方式进行逆序。
- 有一个时间形式(eg: 1986年5月14日),要求从这个格式中得到年、月、日。
练习1答案:
s = 'hello,python'
print(s[::-1]) #nohtyp,olleh
练习2答案:
s = '1986年5月14日'
print(s[:5]) #1986年
print(s[5:7]) #5月
print(s[7:]) #14日
#方法二:
print(s[-10:-5]) #1986年
print(s[-5:-3]) #5月
print(s[-3:]) #14日








 这篇博客探讨了Python中的基本数据类型——字符串。字符串是字符的序列表示,可以用单引号、双引号或三引号定义。文章介绍了字符串的方法,如isalpha()、strip()、split()和len(),并提供了使用示例。同时,文章还提出了两个实践练习,包括字符串的切片逆序操作和从日期格式中提取年、月、日。
这篇博客探讨了Python中的基本数据类型——字符串。字符串是字符的序列表示,可以用单引号、双引号或三引号定义。文章介绍了字符串的方法,如isalpha()、strip()、split()和len(),并提供了使用示例。同时,文章还提出了两个实践练习,包括字符串的切片逆序操作和从日期格式中提取年、月、日。
















 669
669

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








