题目
给出 n 代表生成括号的对数,请你写出一个函数,使其能够生成所有可能的并且有效的括号组合。
例如,给出 n = 3,生成结果为:
[
“((()))”,
“(()())”,
“(())()”,
“()(())”,
“()()()”
]
算法1
public class P22_GenerateParentheses2 {
public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {
List<String> fl = new ArrayList<String>();
Map<String,String> smap = new HashMap<>();
if(n==1) {
fl.add("()");
}else if(n>1){
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
List<String> l = generateParenthesis(i);
List<String> r = generateParenthesis(n-i);
for(String sl : l){
for (String sr : r){
if(sl.equals("()")){
smap.put("("+sr+")","1");
}
smap.put(sl+sr,"1");
}
}
}
}
if(!smap.isEmpty()){
for(String key :smap.keySet()){
fl.add(key);
}
}
return fl;
}
}
思路:使用递归的方式暴力求解,用Hashmap来去重。
算法2
public class P22_GenerateParentheses3 {
public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<String>();
generate(res, "", 0, 0, n);
return res;
}
//count1统计“(”的个数,count2统计“)”的个数
public void generate(List<String> res , String ans, int count1, int count2, int n){
if(count1 > n || count2 > n) return;
if(count1 == n && count2 == n) res.add(ans);
if(count1 >= count2){
String ans1 = new String(ans);
generate(res, ans+"(", count1+1, count2, n);
generate(res, ans1+")", count1, count2+1, n);
}
}
}
思路:深度优先遍历,下图展示了遍历过程(n=2)
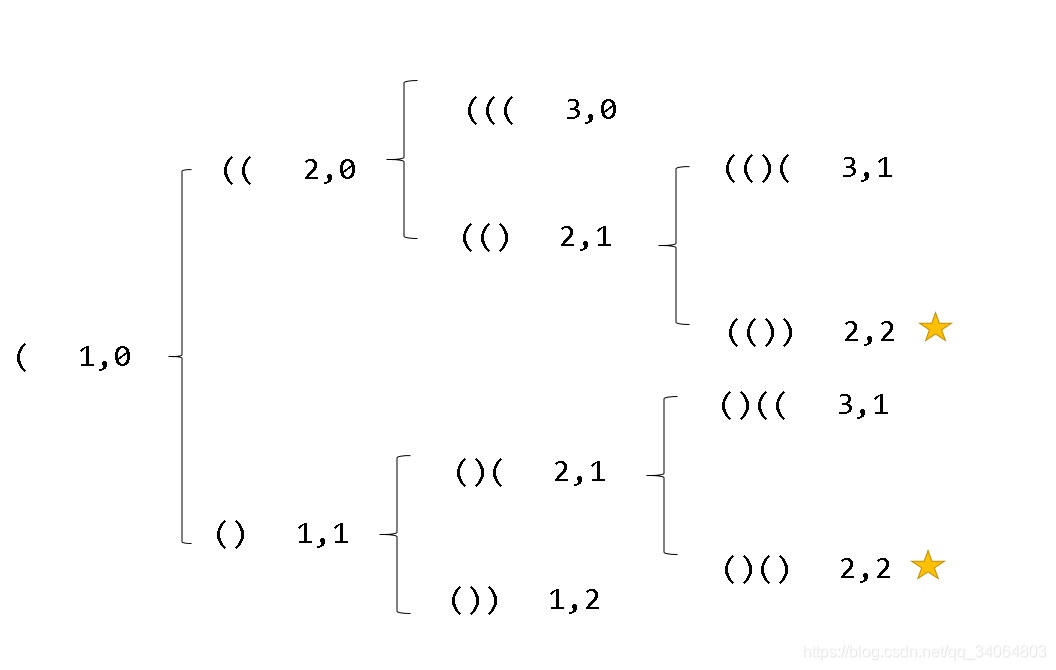
退出遍历条件:count1或count2大于n,count1 >= count2保证了括号表达式的正确性
























 4102
4102

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








