解码流程图:
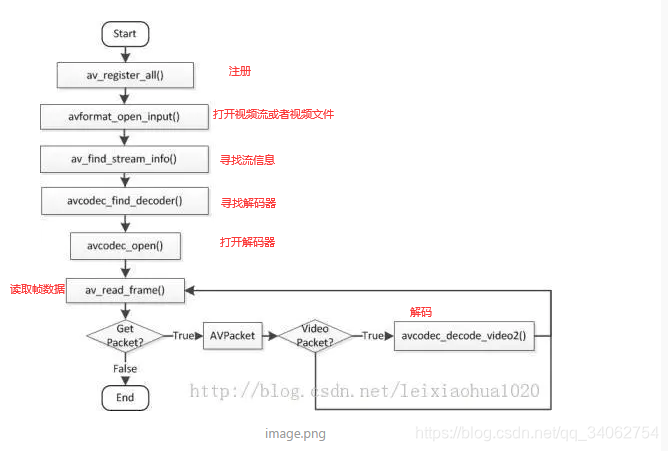
直接上代码,里面有每一步的解释
void CTestYUV::decode()
{
/*
av_register_all初始化所有组件,只有调用了该函数才能使用复用器和解码器。
*/
av_register_all();
avformat_network_init();
//AVFormatContext设备上下文
/*
*/
AVFormatContext* pFormatContext = NULL;
const char* path = "D://1.mp4";
//AVDictionary* opt = NULL;//设置选项
//av_dict_set(&opt, "rtsp_transport","tcp",0);
//av_dict_set(&opt,"max_delay","550",0);//设置延迟时间
int ret=avformat_open_input(&pFormatContext, path,NULL,NULL);//打开文件
//int ret=avformat_open_input(&pFormatContext, path,NULL,&opt);//打开网络流
if (ret)
{
//打开失败
return;
}
//打开成功
//寻找解码器信息,h264还是h265,
ret=avformat_find_stream_info(pFormatContext,NULL);
if (ret)
{
//寻找解码器失败
return;
}
int time = pFormatContext->duration;
int mbitime = (time / 1000000)/60;
cout << "时间" << mbitime;
//打印输出或者输入格式的详细信息,比如持续时间,比特率,编解码器,编码格式
av_dump_format(pFormatContext, NULL, path, 0);
//寻找流
int VideoStream = -1, AudioStream = -1;
VideoStream=av_find_best_stream(pFormatContext, AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO, -1, -1,NULL,0);
AVCodecContext* pCodecContext = NULL;
pCodecContext = avcodec_alloc_context3(NULL);
avcodec_parameters_to_context(pCodecContext, pFormatContext->streams[VideoStream]->codecpar);
//寻找一个解码器
AVCodec* cCodec=avcodec_find_decoder(pCodecContext->codec_id);
if (!cCodec)
{
return;//寻找器失败
}
//pFormatContext->streams[VideoStream]->codec已经被否决
ret=avcodec_open2(pCodecContext, cCodec,NULL);
//解码视频
AVFrame* frame = av_frame_alloc();//申请原始空间或者帧空间
AVFrame* frameYUV = av_frame_alloc();//创建yuv空间
int width= pCodecContext->width;
int height= pCodecContext->height;
int fmt = pCodecContext->pix_fmt;
//分配空间,进行图像转换
//int nSize=avpicture_get_size(AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, width,height);//已经被否决
int nSize = av_image_get_buffer_size(AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, width, height, 1);
uint8_t* buff = NULL;
buff=(uint8_t*)av_malloc(nSize);//分配空间
//一帧图像
//被否决avpicture_fill((AVPicture*)frameYUV, buff, AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, width, height);
av_image_fill_arrays(frameYUV->data, frameYUV->linesize, buff, AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, width, height, 1);
//av_malloc与c语言malloc等价
AVPacket* packet = (AVPacket*)av_malloc(sizeof(AVPacket));
//转换上下文
SwsContext* swsCtx = NULL;
swsCtx=sws_getContext(width, height, (AVPixelFormat)fmt,width,height, AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P,SWS_BICUBIC,NULL,NULL,NULL);
//读帧
int ss = 0;
int nFrameCount = 0;
//ss=av_read_frame(pFormatContext, packet);
while (av_read_frame(pFormatContext, packet)>=0)
{
if (packet->stream_index== VideoStream)
{
/*
//这个刚刚返回-1094995529,是解码器上下文不匹配,
packet->stream_index== VideoStream,没有进行筛选,有可能为音频,视频,字幕,需要用到对应的解码器
*/
ret = avcodec_send_packet(pCodecContext, packet);
if (ret < 0) {
}
while (ret >= 0) {
ret = avcodec_receive_frame(pCodecContext, frame);//这个返回-11,是因为刚刚av_packet_unref没有释放packet。
if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN) || ret == AVERROR_EOF) {
break;
}
else if (ret < 0) {
// goto end; //end处进行资源释放等善后处理
}
if (ret >= 0) {
sws_scale(swsCtx, (const uint8_t**)frame->data, frame->linesize, 0,
height, frameYUV->data, frameYUV->linesize);
nFrameCount++;
cout << "帧数:" << nFrameCount<<"\n"<<endl;
}
}
}
av_packet_unref(packet);
}
sws_freeContext(swsCtx);
av_frame_free(&frame);
av_frame_free(&frameYUV);
avcodec_close(pCodecContext);
avformat_close_input(&pFormatContext);
}





 博客给出了解码流程图相关代码,且代码中包含每一步的解释,聚焦信息技术领域的解码流程代码展示。
博客给出了解码流程图相关代码,且代码中包含每一步的解释,聚焦信息技术领域的解码流程代码展示。
















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








