C++如何获取当前路径下所有文件的文件名
今天我遇到了这样一个任务:要求编写一个程序,统计和这个程序在同一目录下(及其子目录)所有文件的单词数。统计单词数十分倒不是太难,倒是找出同一目录下的所有文件,是我从来没有接触过的。仔细分析,这个问题其实包含两个小问题:
1. 如何获取当前程序所在文件夹的路径
2. 如何给定一个路径,递归地找到其中(包括子目录)所有文件的文件名(相对路径)
那我们就依次解决这两个问题。
.
.
1. 如何获取当前程序所在文件夹的路径
.
.
解决这个问题只需要一个简单的函数即可(需要包含一个输入输出库):
#include <io.h>
char *getcwd( char *buffer, int maxlen );
这个函数能够获取当前的工作目录,具体来说,它会将当前工作目录的绝对路径复制到参数buffer所指的内存空间中,参数maxlen为buffer的空间大小。
.
我们可以写一个程序来测试一下。
#include<iostream>
#include<io.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_PATH 80
int main()
{
char buffer[MAX_PATH];
getcwd(buffer, MAX_PATH);
cout << buffer << endl;
return 0;
}

.
运行成功!
.
.
.
2. 如何给定一个路径,递归地找到其中(包括子目录)所有文件的文件名(相对路径)
.
.
这里我使用了网上现成的代码,先附上链接。
.
这里,他定义了一个函数(需要包含一个向量库,当然,还有我们在上一个问题里需要使用的输入输出库)
#include <io.h>
#include<vector>
void getFiles(string path, vector<string>& files);
它的用处是,给定一个文件目录path,然后找到其中所有(包括其子目录里)的文件,将文件名放入files中,files是一个字符串向量的引用类型。
.
具体的函数内容是这样的:
void getFiles( string path, vector<string>& files )
{
long hFile = 0;
struct _finddata_t fileinfo;
string p;
if((hFile = _findfirst(p.assign(path).append("\\*").c_str(),&fileinfo)) != -1)
{
do
{
if((fileinfo.attrib & _A_SUBDIR))
{
if(strcmp(fileinfo.name,".") != 0 && strcmp(fileinfo.name,"..") != 0)
getFiles( p.assign(path).append("\\").append(fileinfo.name), files );
}
else
{
files.push_back(p.assign(path).append("\\").append(fileinfo.name) );
}
}while(_findnext(hFile, &fileinfo) == 0);
_findclose(hFile);
}
}
.
下面给出一个运用这个函数的例子:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<io.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_PATH 80
void getFiles( string path, vector<string>& files );
int main()
{
vector<string> files;
char * filePath = “C:\Users\Star\Desktop\SoftTest”;
getFiles(filePath, files);
char str[30];
int size = files.size();
for (int i = 0;i < size;i++)
{
cout<<files[i].c_str()<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

运行成功!
.
.
.
3. 组合以后的完整代码
.
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<io.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_PATH 80
void getFiles( string path, vector<string>& files );
int main()
{
vector<string> files;
char buffer[MAX_PATH];
getcwd(buffer, MAX_PATH);
char * filePath = buffer;
getFiles(filePath, files );
char str[30];
int size = files.size();
for (int i = 0;i < size;i++)
{
cout<<files[i].c_str()<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
void getFiles( string path, vector<string>& files )
{
long hFile = 0;
struct _finddata_t fileinfo;
string p;
if((hFile = _findfirst(p.assign(path).append("\*").c_str(),&fileinfo)) != -1)
{
do
{
if((fileinfo.attrib & _A_SUBDIR))
{
if(strcmp(fileinfo.name,".") != 0 && strcmp(fileinfo.name,"…") != 0)
getFiles( p.assign(path).append("\").append(fileinfo.name), files );
}
else
{
files.push_back(p.assign(path).append("\").append(fileinfo.name) );
}
}while(_findnext(hFile, &fileinfo) == 0);
_findclose(hFile);
}
}
.
这段代码的运行结果和上面的运行结果相同,我就不给出运行结果了。
.
.
.
4.返回相对路径
.
之前的那种方法很好,不过唯一的缺点是,函数返回的都是绝对路径,如果想要改成相对路径,该怎么办呢?
.
.
我将代码进行了修改,具体做法是在getFile()函数中加入了一个path2参数,改进后的代码如下:
.
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<io.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_PATH 80
void getFiles( string path, string path2, vector<string>& files );
int main(){
vector<string> files;
char buffer[MAX_PATH];
getcwd(buffer, MAX_PATH);
string filePath;
filePath.assign(buffer).append("\");
getFiles(filePath,"", files );
char str[30];
int size = files.size();
for (int i = 0;i < size;i++)
{
cout<<files[i].c_str()<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
void getFiles( string path, string path2, vector<string>& files )
{
long hFile = 0;
struct _finddata_t fileinfo;
string p,p2;
if((hFile = _findfirst(p.assign(path).append(path2).append("*").c_str(),&fileinfo)) != -1)
{
do
{
if((fileinfo.attrib & _A_SUBDIR))
{
if(strcmp(fileinfo.name,".") != 0 && strcmp(fileinfo.name,"…") != 0)
getFiles( p.assign(path).append("\"),p2.assign(fileinfo.name).append("\"), files );
}
else
{
files.push_back(p.assign(path2).append(fileinfo.name) );
}
}while(_findnext(hFile, &fileinfo) == 0);
_findclose(hFile);
}
}
.
运行结果:

成功地给出了相对路径!!
.
.
也可以给出文件名:
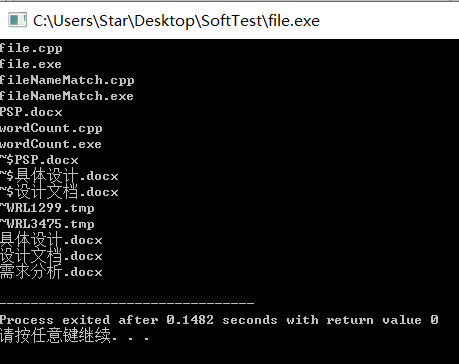
.
.
.





 本文介绍如何使用C++获取当前程序所在文件夹的路径,并递归地找到指定目录下及其子目录中所有文件的文件名。通过具体代码示例,展示了获取绝对路径和相对路径的方法。
本文介绍如何使用C++获取当前程序所在文件夹的路径,并递归地找到指定目录下及其子目录中所有文件的文件名。通过具体代码示例,展示了获取绝对路径和相对路径的方法。




















 2265
2265

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








