在很多时候,当我们要处理⼀个应⽤程序的业务逻辑时,数据校验是必须要考虑和⾯对的事情。应⽤程序必须通过某种⼿段来确保输⼊进来的数据从语义上来讲是正确的。在 Java 应⽤程序中,必须要对输⼊进来的数据从语义上分析是有效的,也就是数据校验。
输⼊验证是最重要的 Web 开发任务之⼀,在 Spring MVC 中有两种⽅式可以验证输⼊:
⼀种是 Spring ⾃带的验证框架,另外⼀种是利⽤ JSR 实现。
JSR 是⼀个规范⽂档,指定了⼀整套 API,通过标注给对象属性添加约束。 Hibernate Validator 就是 JSR 规范的具体实现, Hibernate Validator 提供了 JSR 规范中所有内置约束注解的实现,以及⼀些附加的约束注解,除此之外⽤户还可以⾃定义约束注解。
Spring Boot 的参数校验依赖于 hibernate-validator 来进⾏。使⽤ Hibernate Validator 校验数据,需要定义⼀个接收的数据模型,使⽤注解的形式描述字段校验的规则,以 User 对象为例为⼤家演示如何使⽤。
一、在src/java/的dao层编写用户类User.java
package com.example.demo.model;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Length;
import javax.validation.constraints.Max;
import javax.validation.constraints.Min;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotEmpty;
public class User {
@NotEmpty(message = "姓名不能为空")
private String name;
@Max(value = 100,message = "年龄不能大于100岁")
@Min(value=18,message = "年龄不能少于18岁")
private int age;
@NotEmpty(message = "密码不能为空")
@Length(min = 6,max = 10,message = "密码长度在6-10之间")
private String pass;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setPass(String pass) {
this.pass = pass;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getPass() {
return pass;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "name="+name+",age="+age+",pass="+pass;
}
}
message=“xxx”,是自定义返回的报错信息
Hibernate Validator 基本上包含了常⽤的数据校验,包括校验属性是否为空、⻓度、⼤⼩、特定格式等,注解列表如下:
| 注解 | 适用的数据类型 | 说明 |
| @AssertFalse | Boolean, boolean | 验证注解的元素值是 false |
| @AssertTrue | Boolean, boolean | 验证注解的元素值是 true |
| @DecimalMax(value=x) | BigDecimal, BigInteger, String, byte,short, int, long and the respective wrappers of the primitive types. Additionally supported by HV: any sub-type of Number andCharSequence. | 验证注解的元素值小于等于 @ DecimalMax 指定的 value 值 |
| @DecimalMin(value=x) | BigDecimal, BigInteger, String, byte,short, int, long and the respective wrappers of the primitive types. Additionally supported by HV: any sub-type of Number andCharSequence. | 验证注解的元素值小于等于 @ DecimalMin 指定的 value 值 |
| @Digits(integer= 整数位数,fraction = 小数位数) | BigDecimal, BigInteger, String, byte,short, int, long and the respective wrappers of the primitive types. Additionally supported by HV: any sub-type of Number andCharSequence. | 验证注解的元素值的整数位数和小数位数上限 |
| @Future | java.util.Date, java.util.Calendar; Additionally supported by HV, if theJoda Time date/time API is on the class path: any implementations ofReadablePartial andReadableInstant. | 验证注解的元素值(日期类型)比当前时间晚 |
| @Max(value=x) | BigDecimal, BigInteger, byte, short,int, long and the respective wrappers of the primitive types. Additionally supported by HV: any sub-type ofCharSequence (the numeric value represented by the character sequence is evaluated), any sub-type of Number. | 验证注解的元素值小于等于 @Max 指定的 value 值 |
| @Min(value=x) | BigDecimal, BigInteger, byte, short,int, long and the respective wrappers of the primitive types. Additionally supported by HV: any sub-type of CharSequence (the numeric value represented by the char sequence is evaluated), any sub-type of Number. | 验证注解的元素值大于等于 @Min 指定的 value 值 |
| @NotNull | Any type | 验证注解的元素值不是 null |
| @Null | Any type | 验证注解的元素值是 null |
| @Past | java.util.Date, java.util.Calendar; Additionally supported by HV, if theJoda Time date/time API is on the class path: any implementations ofReadablePartial andReadableInstant. | 验证注解的元素值(日期类型)比当前时间早 |
| @Pattern(regex= 正则表达式,flag=) | String. Additionally supported by HV: any sub-type of CharSequence. | 验证注解的元素值与指定的正则表达式匹配 |
| @Size(min= 最小值,max = 最大值) | String, Collection, Map and arrays. Additionally supported by HV: any sub-type of CharSequence. | 验证注解的元素值的在 min 和 max(包含)指定区间之内,如字符长度、集合大小 |
| @Valid | Any non-primitive type(引用类型) | 验证关联的对象,如账户对象里有一个订单对象,指定验证订单对象 |
| @NotEmpty |
| 验证注解的元素值不为 null 且不为空(字符串长度不为 0、集合大小不为 0) |
| @Range(min= 最小值,max = 最大值) |
| 验证注解的元素值在最小值和最大值之间 |
| @NotBlank |
| 验证注解的元素值不为空(不为 null、去除首位空格后长度为 0),不同于 @NotEmpty,@NotBlank 只应用于字符串且在比较时会去除字符串的空格 |
| @Length(min= 下限,max = 上限) |
| 验证注解的元素值长度在 min 和 max 区间内 |
| |
| 验证注解的元素值是 Email,也可以通过正则表达式和 flag 指定自定义的 email 格式 |
二、在controller层创建userController.java
@RestController
public class userController {
@RequestMapping("/saveUser")
public void saveUser(@Valid User user, BindingResult bindingResult){
System.out.println("user:"+user);
if(bindingResult.hasErrors()){
List<ObjectError> list = bindingResult.getAllErrors();
for(ObjectError error : list){
System.out.println(error.getCode()+"-"+error.getDefaultMessage());
}
}
}
}
- @Valid 参数前⾯添加 @Valid 注解,代表此对象使⽤了参数校验;
- BindingResult 参数校验的结果会存储在此对象中,可以根据属性判断是否校验通过,校验不通过可以将错误信息打印出来。
三、添加测试⽅法,对属性校验进⾏测试
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class vaildTest {
private MockMvc mvc;
@Before
public void setup() throws Exception{
mvc = MockMvcBuilders.standaloneSetup(new webController()).build();
}
@Test
public void webVaildTest() throws Exception{
mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders
.post("/saveUser")
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8)
.param("pass","123456")
.param("age","20")
.param("name","xsj"));
//param方法,第一个参数是key,后面的是value列表
}
}
测试结果:
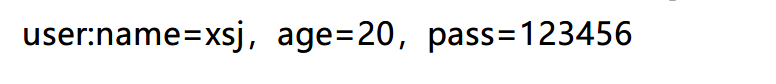












 本文介绍了在Spring Boot中进行数据校验的方法,主要使用了Hibernate Validator,这是一种基于JSR规范的实现。通过在User类中定义数据模型并添加校验规则注解,然后在controller层使用@Valid进行参数校验,结合BindingResult获取并处理校验结果。文章详细讲解了如何在DAO层编写用户类,controller层创建控制器以及设置测试用例进行校验测试。
本文介绍了在Spring Boot中进行数据校验的方法,主要使用了Hibernate Validator,这是一种基于JSR规范的实现。通过在User类中定义数据模型并添加校验规则注解,然后在controller层使用@Valid进行参数校验,结合BindingResult获取并处理校验结果。文章详细讲解了如何在DAO层编写用户类,controller层创建控制器以及设置测试用例进行校验测试。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










