一、树的概念
N个节点构成的有限集合
——树中有一个称为“根”的特殊节点
——其余节点可分为若干个互不相交的树,称为原来节点的子树

其常用基本术语:
| 基本术语 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| 节点的度 | 节点的子树个数 (如图其A节点的度为3) |
| 树的度 | 树中所有节点中最大的度(A/D节点的度都是3) |
| 叶节点 | 度为0的节点(叶节点有EKGLIJ) |
| 父节点 | 有子树的节点是其子树的根节点的父节点 |
| 子节点 | 若A是B的父节点,B就是A的子节点 |

判断是否为树结构的几大准则:
——子树是不相交的
——除了根节点外,每个节点有且只有一个父节点
——N个节点的树有且只有N-1条边
二、二叉树
2.1 概念
- 度为2的树
- 子树有左右顺序之分
2.2 编码问题案例
- 等长ASCII码
- 等长3位编码
- 不等长编码?
- ——二叉树解决编码问题(0/ 1 / 10 /11)
- ——如何避免二义性:字符只在叶节点上
编码问题案例最优解决方法引入哈夫曼树
三、哈夫曼树
3.1 概念
该树的带权路径长度达到最小,称为最优二叉树,即哈夫曼树
3.2 构造方式
每次把权值最小的两棵二叉树合并
左节点权值比右节点权值小




所以由以上分析,2.2编码问题的答案是:

3.3 代码实现哈夫曼树
package com.enjoy.tree;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 哈夫曼树
*/
public class HuffmanTree {
//节点
public static class Node<E> {
E data; //数据
int weight; //权重
Node leftChild; //左子节点
Node rightChild;//右子节点
public Node(E data, int weight) {
super();
this.data = data;
this.weight = weight;
}
public String toString() {
return "Node[" + weight + ",data=" + data + "]";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<Node>();
//把节点加入至list中
nodes.add(new Node("a", 10));
nodes.add(new Node("b", 15));
nodes.add(new Node("c", 12));
nodes.add(new Node("d", 3));
nodes.add(new Node("e", 4));
nodes.add(new Node("f", 13));
nodes.add(new Node("g", 1));
//进行哈夫曼树的构造
Node root = HuffmanTree.createTree(nodes);
//打印哈夫曼树
printTree(root);
}
/**
* 构造哈夫曼树
* @param nodes 节点集合
* @return 构造出来的哈夫曼树的根节点
*/
private static Node createTree(List<Node> nodes) {
//如果节点node列表中海油2个和2个以上的节点
while(nodes.size()>1){
//什么是最小的,list表进行排序,增序的方式, 0,1,
sort(nodes);//排序方式是增序的
Node left = nodes.get(0);//权重最小的
Node right = nodes.get(1);//权重第二小的
//生成一个新的节点(父节点),父节点的权重为两个子节点的之和
Node parent = new Node(null,left.weight+right.weight);
//树的连接,让子节点与父节点进行连接
parent.leftChild = left;
parent.rightChild = right;
nodes.remove(0);//删除最小的
nodes.remove(0);//删除第二小的。
nodes.add(parent);
}
return nodes.get(0); //返回根节点
}
/**
* 冒泡排序,用于对节点进行排序(增序排序)
*
* @param nodes
*/
public static void sort(List<Node> nodes) {
if (nodes.size() <= 1)
return ;
/*循环数组长度的次数*/
for (int i = 0; i < nodes.size(); i++){
/*从第0个元素开始,依次和后面的元素进行比较
* j < array.length - 1 - i表示第[array.length - 1 - i]
* 个元素已经冒泡到了合适的位置,无需进行比较,可以减少比较次数*/
for (int j = 0; j < nodes.size() - 1 - i; j++){
/*如果第j个节点比后面的第j+1节点权重大,交换两者的位置*/
if (nodes.get(j + 1).weight < nodes.get(j).weight) {
Node temp = nodes.get(j + 1);
nodes.set(j+1,nodes.get(j));
nodes.set(j,temp);
}
}
}
return ;
}
/*
* 递归打印哈夫曼树(先左子树,后右子树打印)
*/
public static void printTree(Node root) {
System.out.println(root.toString());
if(root.leftChild !=null){
System.out.print("left:");
printTree(root.leftChild);
}
if(root.rightChild !=null){
System.out.print("right:");
printTree(root.rightChild);
}
}
}
四、二叉排序树
4.1 概念
- 左子树的所有值小于根节点的值
- 右子树的所有值大于根节点的值
- 左右子树满足以上两点
4.2 二叉排序树的查找操作
从根节点开始查找值X:
- 如果X小于根节点值,则在左子树中继续查找;
- 如果X大于根节点值,则在右子树中继续查找;
- 如果X值等于根节点值,则返回该节点;
- 如果都查不到,则返回空Null;
==》查找的效率取决于树的高度,最大元素一定是在树的最右分支的节点上,最小元素一定是在树的最左分支的节点上
4.3 二叉排序树的插入操作
从根节点开始查找插入的值X:
- X值小于该节点值,在左子树中继续;
- X值大于该节点值,在右子树中继续;
- 如果节点是叶节点,X值小于该节点值则插入左子节点,否则插入右节点;
4.4 二叉排序树的删除操作
从根节点开始查找删除值X:
- 如果节点的值等于X,则删除;
- X值小于该节点值,在左子树中继续;
- X值大于该节点值,在右子树中继续;
五、平衡二叉树
5.1 概念
其也是一棵二叉排序树,只是它的左右两个子树的高度差(平衡因子)的绝对值不超过1,且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树
目的:使得树的高度最低,因为树查找的概率决定于树的高度
5.2 平衡二叉树的调整
如果A是一颗平衡二叉树,如果新插入一个元素,会有两个结果
——平衡没有被打破,不用调整
——平衡被打破,需要调整
调整原则:根据插入节点与失衡结点的位置关系来划分
LL旋转:插入节点在失衡结点的左子树的左边,只需要经过一次左旋即可达到平衡

RR旋转:插入节点在失衡结点的右子树的右边,只需要经过一次右旋即可达到平衡

LR旋转:插入节点在失衡结点的左子树的右边,失衡结点的左子树先做RR旋转,失衡结点再做LL旋转也可达到平衡

RL旋转:插入节点在失衡结点的右子树的左边,失衡结点的右子树先做LL旋转,失衡结点再做RR旋转也可达到平衡
5.3 代码实现平衡二叉树
package com.enjoy.tree;
/**
* 二叉平衡树,AVL树
*/
public class AVLTree {
//节点
public static class Node {
int data; //数据
Node leftChild; //左子节点
Node rightChild;//右子节点
int height; // 记录该节点所在的高度
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
//获取节点的高度
public static int getHeight(Node p){
return p == null ? -1 : p.height; // 空树的高度为-1
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node root = null;
root = insert(root,30);
root = insert(root,20);
root = insert(root,40);
root = insert(root,10);
root = insert(root,25);
//插入节点在失衡结点的左子树的左边
root = insert(root,5);
//打印树,按照先打印左子树,再打印右子树的方式
printTree(root);
}
public static void printTree(Node root) {
System.out.println(root.data);
if(root.leftChild !=null){
System.out.print("left:");
printTree(root.leftChild);
}
if(root.rightChild !=null){
System.out.print("right:");
printTree(root.rightChild);
}
}
// AVL树的插入方法
public static Node insert(Node root, int data) {
if (root == null) {
root = new Node(data);
return root;
}
if (data <= root.data) { // 插入到其左子树上
root.leftChild = insert(root.leftChild, data);
//平衡调整
if (getHeight(root.leftChild) - getHeight(root.rightChild) > 1) {
if (data <= root.leftChild.data) { // 插入节点在失衡结点的左子树的左边
System.out.println("LL旋转");
root = LLRotate(root); // LL旋转调整
}else{ // 插入节点在失衡结点的左子树的右边
System.out.println("LR旋转");
root = LRRotate(root);
}
}
}else{ // 插入到其右子树上
root.rightChild = insert(root.rightChild, data);
//平衡调整
if(getHeight(root.rightChild) - getHeight(root.leftChild) > 1){
if(data <= root.rightChild.data){//插入节点在失衡结点的右子树的左边
System.out.println("RL旋转");
root = RLRotate(root);
}else{
System.out.println("RR旋转");//插入节点在失衡结点的右子树的右边
root = RRRotate(root);
}
}
}
//重新调整root节点的高度值
root.height = Math.max(getHeight(root.leftChild), getHeight(root.rightChild)) + 1;
return root;
}
// LR旋转
public static Node LRRotate(Node p){
p.leftChild = RRRotate(p.leftChild); // 先将失衡点p的左子树进行RR旋转
return LLRotate(p); // 再将失衡点p进行LL平衡旋转并返回新节点代替原失衡点p
}
// RL平衡旋转
public static Node RLRotate(Node p){
p.rightChild = LLRotate(p.rightChild); // 先将失衡点p的右子树进行LL平衡旋转
return RRRotate(p); // 再将失衡点p进行RR平衡旋转并返回新节点代替原失衡点p
}
/*
* LL旋转
* 左旋示意图(对结点20进行左旋)
* 30 20
* / \ / \
* 20 40 10 30
* / \ --LL旋转- / / \
* 10 25 5 25 40
* /
* 5
*
*/
public static Node LLRotate(Node p){ // 30为失衡点
Node lsubtree = p.leftChild; //失衡点的左子树的根结点20作为新的结点
p.leftChild = lsubtree.rightChild; //将新节点的右子树25成为失衡点30的左子树
lsubtree.rightChild = p; // 将失衡点30作为新结点的右子树
// 重新设置失衡点30和新节点20的高度
p.height = Math.max(getHeight(p.leftChild), getHeight(p.rightChild)) + 1;
lsubtree.height = Math.max(getHeight(lsubtree.leftChild), p.height) + 1;
return lsubtree; // 新的根节点取代原失衡点的位置
}
/*
* RR旋转
* 右旋示意图(对结点30进行左旋)
* 20 30
* / \ / \
* 10 30 20 40
* / \ --RR旋转- / \ \
* 25 40 10 25 50
* \
* 50
*
*/
// RR旋转
public static Node RRRotate(Node p){ // 20为失衡点
Node rsubtree = p.rightChild; //失衡点的右子树的根结点30作为新的结点
p.rightChild = rsubtree.leftChild; //将新节点的左子树25成为失衡点20的右子树
rsubtree.leftChild = p; // 将失衡点20作为新结点的左子树
// 重新设置失衡点20和新节点30的高度
p.height = Math.max(getHeight(p.leftChild), getHeight(p.rightChild)) + 1;
rsubtree.height = Math.max(getHeight(rsubtree.leftChild), getHeight(rsubtree.rightChild)) + 1;
return rsubtree; // 新的根节点取代原失衡点的位置
}
}
六、红黑树
6.1 概念及特征
一棵特殊的二叉查找树,具备以下特征:
- 1 节点非红即黑
- 2 根节点是黑色
- 3 所有NUll节点称为叶子节点,且认为颜色为黑
- 4 所有红色节点的子节点都为黑色
- 5 从任一节点到其叶子节点的所有路径上都包含相同数目的黑节点
==》从根到叶子的最长的路径不多于最短的可能路径的两倍长

6.2 红黑树的插入操作
插入原则:因为插入节点的颜色如果为黑肯定破坏红黑树性质5,所以每次插入的点首先都是红结点
情况1:插入的新节点N位于树的根上、插入的新节点的父节点是黑色

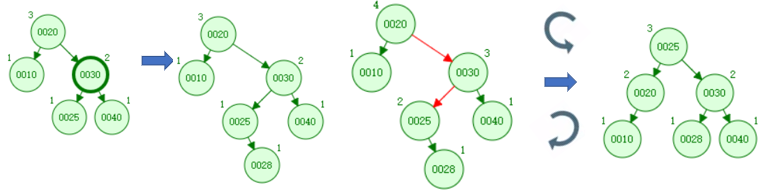
6.3 红黑树插入后的操作——变色
叔父节点来指新节点的父节点的兄弟节点、祖父节点新节点的父节点的父节点
情况2:如果新节点的父节点(0008)和叔父节点(0017)都是红色节点,先插入新节点(红色),(变色)新节点的父节点、叔父节点、祖父节点都需要变色

6.4 红黑树插入后的操作——单次旋转
情况3:如果新节点的父节点是红色同时叔父节点都是黑色,同时新节点是其父节点的左子节点而父节点又是其父节点的左子节点。进行一次右旋转调换新节点和其父节点的角色(以父节点为轴)
情况4:如果新节点的父节点是红色同时叔父节点都是黑色,同时新节点是其父节点的右子节点而父节点又是其父节点的右子节点。对祖父节点进行一次左旋转调换新节点和其父节点的角色(以父节点为轴)

6.5 红黑树插入后的操作——两次旋转
情况5:如果新节点的父节点是红色同时叔父节点都是黑色,同时新节点是其父节点的右子节点而父节点又是其父节点的左子节点。们进行一次左旋转调换新节点和其父节点的角色(第一次旋转),同时发现节点(0008)符合情况3,再进行一次右旋转(第二次旋转)

情况6:如果新节点的父节点是红色同时叔父节点都是黑色,同时新节点是其父节点的左子节点而父节点又是其父节点的右子节点。进行一次右旋转调换新节点和其父节点的角色(第一次旋转),同时发现节点(0017)符合情况4,再进行一次左旋转(第二次旋转)

6.6 代码实现红黑树
package com.enjoy.tree;
/**
* 红黑树
*/
public class RBTree<T extends Comparable<T>> {
private RBTNode<T> mRoot; // 根结点
private static final boolean RED = false;//红色是false
private static final boolean BLACK = true;//黑色是true
public class RBTNode<T extends Comparable<T>> {
boolean color; // 颜色
T key; // 关键字(键值)
RBTNode<T> left; // 左孩子
RBTNode<T> right; // 右孩子
RBTNode<T> parent; // 父结点
public RBTNode(T key, boolean color, RBTNode<T> parent, RBTNode<T> left, RBTNode<T> right) {
this.key = key;
this.color = color;
this.parent = parent;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
public T getKey() {
return key;
}
public String toString() {
return ""+key+(this.color==RED?"(R)":"B");
}
}
public RBTree() {
mRoot=null;
}
private RBTNode<T> parentOf(RBTNode<T> node) {
return node!=null ? node.parent : null;
}
private boolean colorOf(RBTNode<T> node) {
return node!=null ? node.color : BLACK;
}
private boolean isRed(RBTNode<T> node) {
return ((node!=null)&&(node.color==RED)) ? true : false;
}
private boolean isBlack(RBTNode<T> node) {
return !isRed(node);
}
private void setBlack(RBTNode<T> node) {
if (node!=null)
node.color = BLACK;
}
private void setRed(RBTNode<T> node) {
if (node!=null)
node.color = RED;
}
private void setParent(RBTNode<T> node, RBTNode<T> parent) {
if (node!=null)
node.parent = parent;
}
private void setColor(RBTNode<T> node, boolean color) {
if (node!=null)
node.color = color;
}
/*
* (递归实现)查找"红黑树x"中键值为key的节点
*/
private RBTNode<T> search(RBTNode<T> x, T key) {
if (x==null)
return x;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0)
return search(x.left, key);
else if (cmp > 0)
return search(x.right, key);
else
return x;
}
public RBTNode<T> search(T key) {
return search(mRoot, key);
}
/*
* (非递归实现)查找"红黑树x"中键值为key的节点
*/
private RBTNode<T> iterativeSearch(RBTNode<T> x, T key) {
while (x!=null) {
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0)
x = x.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
x = x.right;
else
return x;
}
return x;
}
public RBTNode<T> iterativeSearch(T key) {
return iterativeSearch(mRoot, key);
}
/*
* 查找最小结点:返回tree为根结点的红黑树的最小结点。
*/
private RBTNode<T> minimum(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree == null)
return null;
while(tree.left != null)
tree = tree.left;
return tree;
}
public T minimum() {
RBTNode<T> p = minimum(mRoot);
if (p != null)
return p.key;
return null;
}
/*
* 查找最大结点:返回tree为根结点的红黑树的最大结点。
*/
private RBTNode<T> maximum(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree == null)
return null;
while(tree.right != null)
tree = tree.right;
return tree;
}
public T maximum() {
RBTNode<T> p = maximum(mRoot);
if (p != null)
return p.key;
return null;
}
/*
* 找结点(x)的后继结点。即,查找"红黑树中数据值大于该结点"的"最小结点"。
*/
public RBTNode<T> successor(RBTNode<T> x) {
// 如果x存在右孩子,则"x的后继结点"为 "以其右孩子为根的子树的最小结点"。
if (x.right != null)
return minimum(x.right);
// 如果x没有右孩子。则x有以下两种可能:
// (01) x是"一个左孩子",则"x的后继结点"为 "它的父结点"。
// (02) x是"一个右孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有左孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的后继结点"。
RBTNode<T> y = x.parent;
while ((y!=null) && (x==y.right)) {
x = y;
y = y.parent;
}
return y;
}
/*
* 找结点(x)的前驱结点。即,查找"红黑树中数据值小于该结点"的"最大结点"。
*/
public RBTNode<T> predecessor(RBTNode<T> x) {
// 如果x存在左孩子,则"x的前驱结点"为 "以其左孩子为根的子树的最大结点"。
if (x.left != null)
return maximum(x.left);
// 如果x没有左孩子。则x有以下两种可能:
// (01) x是"一个右孩子",则"x的前驱结点"为 "它的父结点"。
// (01) x是"一个左孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有右孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的前驱结点"。
RBTNode<T> y = x.parent;
while ((y!=null) && (x==y.left)) {
x = y;
y = y.parent;
}
return y;
}
/*
* 对红黑树的节点(x)进行左旋转
*
* 左旋示意图(对节点x进行左旋):
* 13 17
* / \ / \
* nul 17 13 27
* / \ --(左旋)-. / \ / \
* nul 27 nul nul nul nul
* / \
* nul nul
*
*
*/
private void leftRotate(RBTNode<T> x) {
// 设置x的右孩子为y
RBTNode<T> y = x.right;
// 将 “y的左孩子” 设为 “x的右孩子”;
// 如果y的左孩子非空,将 “x” 设为 “y的左孩子的父亲”
x.right = y.left;
if (y.left != null)
y.left.parent = x;
// 将 “x的父亲” 设为 “y的父亲”
y.parent = x.parent;
if (x.parent == null) {
this.mRoot = y; // 如果 “x的父亲” 是空节点,则将y设为根节点
} else {
if (x.parent.left == x)
x.parent.left = y; // 如果 x是它父节点的左孩子,则将y设为“x的父节点的左孩子”
else
x.parent.right = y; // 如果 x是它父节点的左孩子,则将y设为“x的父节点的左孩子”
}
// 将 “x” 设为 “y的左孩子”
y.left = x;
// 将 “x的父节点” 设为 “y”
x.parent = y;
}
/*
* 对红黑树的节点(8)进行右旋转
*
* 右旋示意图(对节点8进行右旋):
* 13 8
* / \ / \
* 8 nul 1 13
* / \ --(右旋)- / \ / \
* 1 nul nul nul nul nul
* / \
* nul nul
*
*/
private void rightRotate(RBTNode<T> y) {
// 设置x是当前节点的左孩子。
RBTNode<T> x = y.left;
// 将 “x的右孩子” 设为 “y的左孩子”;
// 如果"x的右孩子"不为空的话,将 “y” 设为 “x的右孩子的父亲”
y.left = x.right;
if (x.right != null)
x.right.parent = y;
// 将 “y的父亲” 设为 “x的父亲”
x.parent = y.parent;
if (y.parent == null) {
this.mRoot = x; // 如果 “y的父亲” 是空节点,则将x设为根节点
} else {
if (y == y.parent.right)
y.parent.right = x; // 如果 y是它父节点的右孩子,则将x设为“y的父节点的右孩子”
else
y.parent.left = x; // (y是它父节点的左孩子) 将x设为“x的父节点的左孩子”
}
// 将 “y” 设为 “x的右孩子”
x.right = y;
// 将 “y的父节点” 设为 “x”
y.parent = x;
}
/*
* 红黑树插入修正函数
*
* 在向红黑树中插入节点之后(失去平衡),再调用该函数;
* 目的是将它重新塑造成一颗红黑树。
*
* 参数说明:
* node 插入的结点 // 对应《算法导论》中的z
*/
private void insertFixUp(RBTNode<T> node) {
RBTNode<T> parent, gparent;
// 若“父节点存在,并且父节点的颜色是红色”
while (((parent = parentOf(node))!=null) && isRed(parent)) {
gparent = parentOf(parent);//祖父节点
//若“父节点”是“祖父节点的左孩子”
if (parent == gparent.left) {
RBTNode<T> uncle = gparent.right;
if ((uncle!=null) && isRed(uncle)) { // 情况2:叔叔节点是红色
setBlack(uncle);
setBlack(parent);
setRed(gparent);
node = gparent;
continue;
}
// 情况5:叔叔是黑色,且当前节点是右孩子(两次旋转,先左后右)
if (parent.right == node) {
RBTNode<T> tmp;
leftRotate(parent); //左旋转
tmp = parent;
parent = node;
node = tmp;
}
// 情况3:叔叔是黑色,且当前节点是左孩子。(一次右旋转)
setBlack(parent);
setRed(gparent);
rightRotate(gparent);
} else { //若“父节点”是“祖父节点的右孩子”
RBTNode<T> uncle = gparent.left;
if ((uncle!=null) && isRed(uncle)) { // 情况2:叔叔节点是红色
setBlack(uncle);
setBlack(parent);
setRed(gparent);
node = gparent;
continue;
}
// 情况6:叔叔是黑色,且当前节点是左孩子(两次旋转,先右后左)
if (parent.left == node) {
RBTNode<T> tmp;
rightRotate(parent);
tmp = parent;
parent = node;
node = tmp;
}
// 情况4:叔叔是黑色,且当前节点是右孩子。(一次左旋转)
setBlack(parent);
setRed(gparent);
leftRotate(gparent);
}
}
// 将根节点设为黑色
setBlack(this.mRoot);
}
/*
* 将结点插入到红黑树中
*
* 参数说明:
* node 插入的结点
*/
private void insert(RBTNode<T> node) {
int cmp;
RBTNode<T> y = null;
RBTNode<T> x = this.mRoot;
// 1. 将红黑树当作一颗二叉查找树,将节点添加到二叉查找树中。
while (x != null) {
y = x;
cmp = node.key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0)
x = x.left;
else
x = x.right;
}
node.parent = y;
if (y!=null) {
cmp = node.key.compareTo(y.key);
if (cmp < 0)
y.left = node;
else
y.right = node;
} else {
this.mRoot = node;
}
// 2. 设置节点的颜色为红色
node.color = RED;
// 3. 将它重新修正为一颗二叉查找树
insertFixUp(node);
}
/*
* 新建结点(key),并将其插入到红黑树中
*
* 参数说明:
* key 插入结点的键值
*/
public void insert(T key) {
RBTNode<T> node=new RBTNode<T>(key,BLACK,null,null,null);
// 如果新建结点失败,则返回。
if (node != null)
insert(node);
}
/*
* 红黑树删除修正函数
*
* 在从红黑树中删除插入节点之后(红黑树失去平衡),再调用该函数;
* 目的是将它重新塑造成一颗红黑树。
*
* 参数说明:
* node 待修正的节点
*/
private void removeFixUp(RBTNode<T> node, RBTNode<T> parent) {
RBTNode<T> other;
while ((node==null || isBlack(node)) && (node != this.mRoot)) {
if (parent.left == node) {
other = parent.right;
if (isRed(other)) {
// Case 1: x的兄弟w是红色的
setBlack(other);
setRed(parent);
leftRotate(parent);
other = parent.right;
}
if ((other.left==null || isBlack(other.left)) &&
(other.right==null || isBlack(other.right))) {
// Case 2: x的兄弟w是黑色,且w的俩个孩子也都是黑色的
setRed(other);
node = parent;
parent = parentOf(node);
} else {
if (other.right==null || isBlack(other.right)) {
// Case 3: x的兄弟w是黑色的,并且w的左孩子是红色,右孩子为黑色。
setBlack(other.left);
setRed(other);
rightRotate(other);
other = parent.right;
}
// Case 4: x的兄弟w是黑色的;并且w的右孩子是红色的,左孩子任意颜色。
setColor(other, colorOf(parent));
setBlack(parent);
setBlack(other.right);
leftRotate(parent);
node = this.mRoot;
break;
}
} else {
other = parent.left;
if (isRed(other)) {
// Case 1: x的兄弟w是红色的
setBlack(other);
setRed(parent);
rightRotate(parent);
other = parent.left;
}
if ((other.left==null || isBlack(other.left)) &&
(other.right==null || isBlack(other.right))) {
// Case 2: x的兄弟w是黑色,且w的俩个孩子也都是黑色的
setRed(other);
node = parent;
parent = parentOf(node);
} else {
if (other.left==null || isBlack(other.left)) {
// Case 3: x的兄弟w是黑色的,并且w的左孩子是红色,右孩子为黑色。
setBlack(other.right);
setRed(other);
leftRotate(other);
other = parent.left;
}
// Case 4: x的兄弟w是黑色的;并且w的右孩子是红色的,左孩子任意颜色。
setColor(other, colorOf(parent));
setBlack(parent);
setBlack(other.left);
rightRotate(parent);
node = this.mRoot;
break;
}
}
}
if (node!=null)
setBlack(node);
}
/*
* 删除结点(node),并返回被删除的结点
*
* 参数说明:
* node 删除的结点
*/
private void remove(RBTNode<T> node) {
RBTNode<T> child, parent;
boolean color;
// 被删除节点的"左右孩子都不为空"的情况。
if ( (node.left!=null) && (node.right!=null) ) {
// 被删节点的后继节点。(称为"取代节点")
// 用它来取代"被删节点"的位置,然后再将"被删节点"去掉。
RBTNode<T> replace = node;
// 获取后继节点
replace = replace.right;
while (replace.left != null)
replace = replace.left;
// "node节点"不是根节点(只有根节点不存在父节点)
if (parentOf(node)!=null) {
if (parentOf(node).left == node)
parentOf(node).left = replace;
else
parentOf(node).right = replace;
} else {
// "node节点"是根节点,更新根节点。
this.mRoot = replace;
}
// child是"取代节点"的右孩子,也是需要"调整的节点"。
// "取代节点"肯定不存在左孩子!因为它是一个后继节点。
child = replace.right;
parent = parentOf(replace);
// 保存"取代节点"的颜色
color = colorOf(replace);
// "被删除节点"是"它的后继节点的父节点"
if (parent == node) {
parent = replace;
} else {
// child不为空
if (child!=null)
setParent(child, parent);
parent.left = child;
replace.right = node.right;
setParent(node.right, replace);
}
replace.parent = node.parent;
replace.color = node.color;
replace.left = node.left;
node.left.parent = replace;
if (color == BLACK)
removeFixUp(child, parent);
node = null;
return ;
}
if (node.left !=null) {
child = node.left;
} else {
child = node.right;
}
parent = node.parent;
// 保存"取代节点"的颜色
color = node.color;
if (child!=null)
child.parent = parent;
// "node节点"不是根节点
if (parent!=null) {
if (parent.left == node)
parent.left = child;
else
parent.right = child;
} else {
this.mRoot = child;
}
if (color == BLACK)
removeFixUp(child, parent);
node = null;
}
/*
* 删除结点(z),并返回被删除的结点
*
* 参数说明:
* tree 红黑树的根结点
* z 删除的结点
*/
public void remove(T key) {
RBTNode<T> node;
if ((node = search(mRoot, key)) != null)
remove(node);
}
/*
* 销毁红黑树
*/
private void destroy(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree==null)
return ;
if (tree.left != null)
destroy(tree.left);
if (tree.right != null)
destroy(tree.right);
tree=null;
}
public void clear() {
destroy(mRoot);
mRoot = null;
}
/*
* 打印"红黑树"
*
* key -- 节点的键值
* direction -- 0,表示该节点是根节点;
* -1,表示该节点是它的父结点的左孩子;
* 1,表示该节点是它的父结点的右孩子。
*/
private void print(RBTNode<T> tree, T key, int direction) {
if(tree != null) {
if(direction==0) // tree是根节点
System.out.printf("%2d(B) is root\n", tree.key);
else // tree是分支节点
System.out.printf("%2d(%s) is %2d's %6s child\n", tree.key, isRed(tree)?"R":"B", key, direction==1?"right" : "left");
print(tree.left, tree.key, -1);
print(tree.right,tree.key, 1);
}
}
public void print() {
if (mRoot != null)
print(mRoot, mRoot.key, 0);
}
/*
* 前序遍历"红黑树"
*/
private void preOrder(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if(tree != null) {
System.out.print(tree.key+" ");
preOrder(tree.left);
preOrder(tree.right);
}
}
public void preOrder() {
preOrder(mRoot);
}
/*
* 中序遍历"红黑树"
*/
private void inOrder(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if(tree != null) {
inOrder(tree.left);
System.out.print(tree.key+" ");
inOrder(tree.right);
}
}
public void inOrder() {
inOrder(mRoot);
}
/*
* 后序遍历"红黑树"
*/
private void postOrder(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if(tree != null)
{
postOrder(tree.left);
postOrder(tree.right);
System.out.print(tree.key+" ");
}
}
public void postOrder() {
postOrder(mRoot);
}
}

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








