普通方法:
CommonDao.java
public class CommonDao {
/**
* 此方法是公共方法,专门获取数据库连接
* @return
*/
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection con=null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testdb","root","0118");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return con;
}
/**
* 此方法是公共方法,专门用来关闭数据库资源
* @param rs
* @param pstmt
* @param con
*/
public static void closeAll(ResultSet rs,PreparedStatement pstmt,Connection con){
try {
if(rs!=null){
rs.close();
}if(pstmt!=null){
pstmt.close();
}if(con!=null){
con.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}UserDao.java
public class UserDao implements UserDao{
@Override
public User login(String userName, String userPassword) throws SQLException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
User user = null;
Connection con = CommonDao.getConnection();
String sql="select id from t_user where username=? and password=?";
PreparedStatement pstmt=con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, userName);
pstmt.setString(2,userPassword);
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
if(rs.next()){
user = new User();
user.setUserId(rs.getInt("user_id"));
user.setUserName(rs.getString("user_name"));
user.setUserPassword(rs.getString("user_password"));
}
CommonDao.closeAll(rs, pstmt, con);
return user;
}
@Override
public int addUser(User user) throws SQLException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int rowAffect = 0;
Connection con = CommonDao.getConnection();
String sql="insert into t_user(username,password) values(?,?)";
PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, user.getUserName());
pstmt.setString(2, user.getUserPassword());
rowAffect = pstmt.executeUpdate(sql);
CommonDao.closeAll(null, pstmt, con);
return rowAffect ;
}优化:策略模式
UserDao中存在大量的重复代码,比如数据库的连接与关闭,PrepareStatement的数据填充操作,不同的是sql语句和对ResultSet结果集的操作,所以可以使用策略模式对代码进行优化
策略模式:http://www.runoob.com/design-pattern/strategy-pattern.html
RowMapper.java
public interface RowMapper<T> {
public T mapRow(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException;
}CommonDao.java
public class CommonDao {
/**
* 此方法是公共方法,专门获取数据库连接
* @return
*/
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection con=null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testdb","root","0118");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return con;
}
/**
* 此方法是公共方法,专门用来关闭数据库资源
* @param rs
* @param pstmt
* @param con
*/
public static void closeAll(ResultSet rs,PreparedStatement pstmt,Connection con){
try {
if(rs!=null){
rs.close();
}if(pstmt!=null){
pstmt.close();
}if(con!=null){
con.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
/**
* 通用更新
* @param sql DML语句
* @param params 参数
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static int executeUpdate(String sql,Object...params) throws SQLException{
int rowAffect = 0;
Connection con = getConnection();
PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
if(params!=null){
for(int i=0;i<params.length;i++){
pstmt.setObject(i+1, params[i]);
}
}
rowAffect = pstmt.executeUpdate();
closeAll(null, pstmt, con);
return rowAffect;
}
/**
* 通用查询
* @param sql
* @param params
* @param rm
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static <T> List<T> executeQuery(String sql,RowMapper<T> rm,Object...params) throws SQLException{
List<T> list = new ArrayList<T>();
Connection con = getConnection();
PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
if(params!=null){
for(int i=0;i<params.length;i++){
pstmt.setObject(i+1, params[i]);
}
}
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
T mapRow = rm.mapRow(rs);
list.add(mapRow);
}
closeAll(rs, pstmt, con);
return list;
}
}UserDao.java
public class UserMysql implements UserDao{
@Override
public User login(String userName, String userPassword) throws SQLException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
User user = null;
String sql="select user_id from t_user where user_name=? and user_password=?";
RowMapper<User> rm = new RowMapper<User>() {
@Override
public User mapRow(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
User user = new User();
user.setUserId(rs.getInt("user_id"));
user.setUserName(rs.getString("user_name"));
user.setUserPassword(rs.getString("user_password"));
return user;
}
};
Object[] params = {userName,userPassword};
user = CommonDao.executeQuery(sql, rm, params).get(0);
return user;
}
@Override
public int addUser(User user) throws SQLException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int rowAffect = 0;
String sql="insert into t_user(user_name,user_password) values(?,?)";
rowAffect = CommonDao.executeUpdate(sql, user.getUserName(),user.getUserPassword());
return rowAffect;
}
}优化:反射1.0
对于通用查询,虽然策略模式可以节省很多工作,但是每次都要去写不同实现,还是比较费事,通过观察可以发现,从数据库中取出的结果集是和User实体类一 一对应的,所以可以使用反射对代码再一次进行优化
CommonDao.java
public class CommonDao {
/**
* 此方法是公共方法,专门获取数据库连接
* @return
*/
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection con=null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testdb","root","0118");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return con;
}
/**
* 此方法是公共方法,专门用来关闭数据库资源
* @param rs
* @param pstmt
* @param con
*/
public static void closeAll(ResultSet rs,PreparedStatement pstmt,Connection con){
try {
if(rs!=null){
rs.close();
}if(pstmt!=null){
pstmt.close();
}if(con!=null){
con.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
/**
* 通用更新
* @param sql DML语句
* @param params 参数
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static int executeUpdate(String sql,Object...params) throws SQLException{
int rowAffect = 0;
Connection con = getConnection();
PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
if(params!=null){
for(int i=0;i<params.length;i++){
pstmt.setObject(i+1, params[i]);
}
}
rowAffect = pstmt.executeUpdate();
closeAll(null, pstmt, con);
return rowAffect;
}
/**
* 通用DQL,,反射版本
* @param sql 只能是DQL语句
* @param params 占位符的值
* @param class 实体对象,对象存储的是数据库的数据
* @return
* @throws SQLException
* @throws IllegalAccessException
* @throws InstantiationException
*/
public static <T> List<T> executeQuery(String sql,Class<T> clazz,Object...params) throws Exception{
List<T> list = new ArrayList<T>();
Connection con = getConnection();
PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
if(params!=null){
for(int i=0;i<params.length;i++){
pstmt.setObject(i+1, params[i]);
}
}
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
//获取结果集的元数据
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
//从结果的元数据中获取结果集的元数据,元数据就是结果集的列信息
List<String> columnNames = new ArrayList<String>();//存储结果的列头的名字
for(int i=0;i<rsmd.getColumnCount();i++){
columnNames.add(rsmd.getColumnLabel(i+1));
}
while(rs.next()){
//实例化T类型的实体对象
T t = clazz.newInstance();
//用反射调用t中的set方法
for(String columnName:columnNames){
//类似于setId setUserName setUserPassword
String setterName = "set"+columnName.substring(0,1).toUpperCase()+columnName.substring(1);
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method m:methods){
m.invoke(t, value);
}
}
}
list.add(t);
}
closeAll(rs, pstmt, con);
return list;
}
}UserDao.java
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{
@Override
public int login(String userName, String userPassword) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
User user = null;
String sql="select user_id as userId from t_user where username=? and password=?";
Object[] params = new Object[] {userName,userPassword};
List<User> list = CommonDao.executeQuery(sql, User.class, params);
user = list.get(0);
return user;
}
@Override
public int addUser(User user) throws SQLException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int rowAffect = 0;
String sql="insert into t_user(user_name,user_password) values(?,?)";
rowAffect = CommonDao.executeUpdate(sql,user.getUserName(),user.getUserPassword());
return rowAffect;
}
这样一来,UserDao中方法的代码又少了很多,但是上面反射有一个问题就是,每次获取方法名时都要将columnNames遍历一遍,这样的话对于资源的消耗会比较大,所以。。。。
优化:反射2.0
Class中还有一个方法就是 Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes),可以直接通过方法名获取类的方法,那么问题来了,getDeclaredMethod方法还需要查找方法参数的类类型,这个。。。
解决:ResultSetMetaData这个对象有两个方法 int getColumnType(int column) 和 String getColumnType(int column)
方法
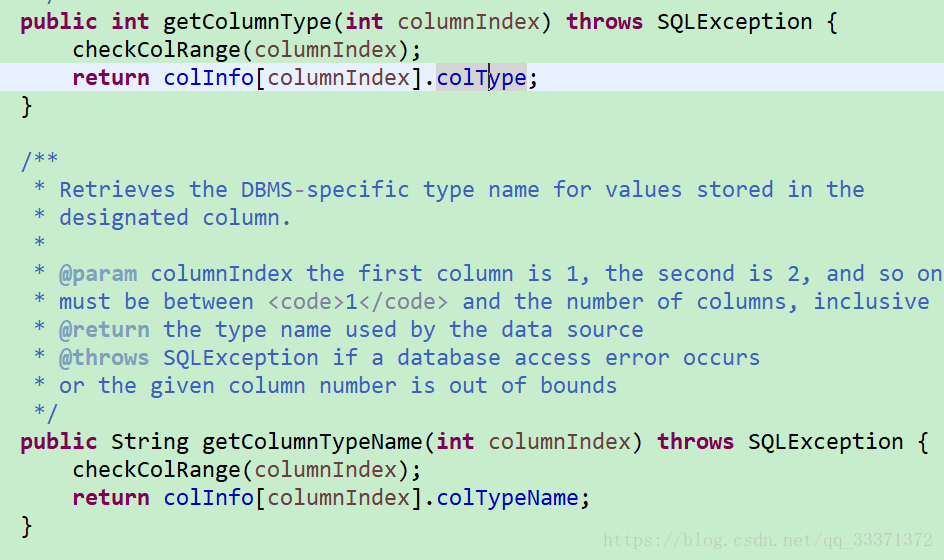
查看colType和colTypeName

注释大概意思是colType是java.sql.Type中的类型,colTypeName是数据源的类型名称
如果想让程序有更好的兼容性,那么colTypeName肯定是不行的,因为不同的数据库字段的类型名称也不同,但是java.sql.Types就不一样了,这是jdk定义的类型,属于java的十三种规范之一JDBC,不同的数据库厂商都会按照这个标准去做数据库驱动
java.sql.Types的源码
/*
* Copyright (c) 1996, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
*
*/
package java.sql;
/**
* <P>The class that defines the constants that are used to identify generic
* SQL types, called JDBC types.
* <p>
* This class is never instantiated.
*/
public class Types {
/**
* <P>The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred
* to as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>BIT</code>.
*/
public final static int BIT = -7;
/**
* <P>The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred
* to as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>TINYINT</code>.
*/
public final static int TINYINT = -6;
/**
* <P>The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred
* to as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>SMALLINT</code>.
*/
public final static int SMALLINT = 5;
/**
* <P>The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred
* to as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>INTEGER</code>.
*/
public final static int INTEGER = 4;
/**
* <P>The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred
* to as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>BIGINT</code>.
*/
public final static int BIGINT = -5;
/**
* <P>The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred
* to as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>FLOAT</code>.
*/
public final static int FLOAT = 6;
/**
* <P>The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred
* to as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>REAL</code>.
*/
public final static int REAL = 7;
/**
* <P>The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred
* to as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>DOUBLE</code>.
*/
public final static int DOUBLE = 8;
/**
* <P>The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred
* to as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>NUMERIC</code>.
*/
public final static int NUMERIC = 2;
/**
* <P>The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred
* to as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>DECIMAL</code>.
*/
public final static int DECIMAL = 3;
/**
* <P>The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred
* to as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>CHAR</code>.
*/
public final static int CHAR = 1;
/**
* <P>The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred
* to as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>VARCHAR</code>.
*/
public final static int VARCHAR = 12;
/**
* <P>The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred
* to as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>LONGVARCHAR</code>.
*/
public final static int LONGVARCHAR = -1;
/**
* <P>The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred
* to as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>DATE</code>.
*/
public final static int DATE = 91;
/**
* <P>The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred
* to as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>TIME</code>.
*/
public final static int TIME = 92;
/**
* <P>The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred
* to as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>TIMESTAMP</code>.
*/
public final static int TIMESTAMP = 93;
/**
* <P>The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred
* to as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>BINARY</code>.
*/
public final static int BINARY = -2;
/**
* <P>The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred
* to as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>VARBINARY</code>.
*/
public final static int VARBINARY = -3;
/**
* <P>The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred
* to as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>LONGVARBINARY</code>.
*/
public final static int LONGVARBINARY = -4;
/**
* <P>The constant in the Java programming language
* that identifies the generic SQL value
* <code>NULL</code>.
*/
public final static int NULL = 0;
/**
* The constant in the Java programming language that indicates
* that the SQL type is database-specific and
* gets mapped to a Java object that can be accessed via
* the methods <code>getObject</code> and <code>setObject</code>.
*/
public final static int OTHER = 1111;
/**
* The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred to
* as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>JAVA_OBJECT</code>.
* @since 1.2
*/
public final static int JAVA_OBJECT = 2000;
/**
* The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred to
* as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>DISTINCT</code>.
* @since 1.2
*/
public final static int DISTINCT = 2001;
/**
* The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred to
* as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>STRUCT</code>.
* @since 1.2
*/
public final static int STRUCT = 2002;
/**
* The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred to
* as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>ARRAY</code>.
* @since 1.2
*/
public final static int ARRAY = 2003;
/**
* The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred to
* as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>BLOB</code>.
* @since 1.2
*/
public final static int BLOB = 2004;
/**
* The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred to
* as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>CLOB</code>.
* @since 1.2
*/
public final static int CLOB = 2005;
/**
* The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred to
* as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* <code>REF</code>.
* @since 1.2
*/
public final static int REF = 2006;
/**
* The constant in the Java programming language, somtimes referred to
* as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type <code>DATALINK</code>.
*
* @since 1.4
*/
public final static int DATALINK = 70;
/**
* The constant in the Java programming language, somtimes referred to
* as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type <code>BOOLEAN</code>.
*
* @since 1.4
*/
public final static int BOOLEAN = 16;
//------------------------- JDBC 4.0 -----------------------------------
/**
* The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred to
* as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type <code>ROWID</code>
*
* @since 1.6
*
*/
public final static int ROWID = -8;
/**
* The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred to
* as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type <code>NCHAR</code>
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public static final int NCHAR = -15;
/**
* The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred to
* as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type <code>NVARCHAR</code>.
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public static final int NVARCHAR = -9;
/**
* The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred to
* as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type <code>LONGNVARCHAR</code>.
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public static final int LONGNVARCHAR = -16;
/**
* The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred to
* as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type <code>NCLOB</code>.
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public static final int NCLOB = 2011;
/**
* The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred to
* as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type <code>XML</code>.
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public static final int SQLXML = 2009;
//--------------------------JDBC 4.2 -----------------------------
/**
* The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred to
* as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type {@code REF CURSOR}.
*
* @since 1.8
*/
public static final int REF_CURSOR = 2012;
/**
* The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred to
* as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* {@code TIME WITH TIMEZONE}.
*
* @since 1.8
*/
public static final int TIME_WITH_TIMEZONE = 2013;
/**
* The constant in the Java programming language, sometimes referred to
* as a type code, that identifies the generic SQL type
* {@code TIMESTAMP WITH TIMEZONE}.
*
* @since 1.8
*/
public static final int TIMESTAMP_WITH_TIMEZONE = 2014;
// Prevent instantiation
private Types() {}
}
其中不同的数字对应了不同的数据类型
如果还不太清楚的话可以参照 Java数据类型和MySql数据类型对应

那么
CommonDao.java
/**
* 通用查询
* @param sql
* @param clazz
* @param params
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static <T> List<T> executeQuery(String sql,Class<T> clazz,Object...params)throws Exception{
Connection con = getConnection();
PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
List<T> list = new ArrayList<T>();
if(params!=null){
for(int i=0;i<params.length;i++){
pstmt.setObject(i+1, params[i]);
}
}
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
//获取结果集元数据
ResultSetMetaData metaData = rs.getMetaData();
while(rs.next()){
T t = clazz.newInstance();
for(int i=1;i<=metaData.getColumnCount();i++){
String columnName = metaData.getColumnLabel(i);
String methodName = "set"+columnName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase()+columnName.substring(1);
Class<?> paramType = null;
if(metaData.getColumnType(i)==4){
paramType=Integer.class;
}else if(metaData.getColumnType(i)==12){
paramType=String.class;
}
Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod(methodName, new Class[]{paramType});
method.invoke(t, rs.getObject(columnName));
}
list.add(t);
}
return list;
} 在这个Demo中我只使用了两种数据类型,所以并没有写过多的代码,当然,也可以根据自己的需要,将类型的判断写成一个方法,去进行类型的选择








 本文介绍了如何使用策略模式优化JDBC中的CommonDao,减少UserDao中的重复代码。接着通过反射1.0版本进一步简化通用查询,然后针对反射1.0存在的资源消耗问题,提出反射2.0版本,利用java.sql.Types增强兼容性和效率。
本文介绍了如何使用策略模式优化JDBC中的CommonDao,减少UserDao中的重复代码。接着通过反射1.0版本进一步简化通用查询,然后针对反射1.0存在的资源消耗问题,提出反射2.0版本,利用java.sql.Types增强兼容性和效率。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








