服务定位器模式
服务定位器模式充分利用了缓存技术。在首次请求某个服务时,服务定位器在 JNDI 中查找服务,并缓存该服务对象。当再次请求相同的服务时,服务定位器会在它的缓存中查找,这样可以在很大程度上提高应用程序的性能。
以下是这种设计模式的实体。
1、服务(Service) - 实际处理请求的服务。对这种服务的引用可以在 JNDI 服务器中查找到。
2、Context / 初始的 Context - JNDI Context 带有对要查找的服务的引用。
3、服务定位器(Service Locator) - 服务定位器是通过 JNDI 查找和缓存服务来获取服务的单点接触。
4、缓存(Cache) - 缓存存储服务的引用,以便复用它们。
5、客户端(Client) - Client 是通过 ServiceLocator 调用服务的对象。
采用菜鸟教程的例子,这里用C++实现
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
//创建服务抽象接口类Service
class Service
{
public:
Service() {};
virtual ~Service() {};
virtual string getName()=0;
virtual void execute()=0;
};
//创建服务实体类Service1
class Service1 :public Service
{
public:
Service1() {};
~Service1() {};
string getName();
void execute();
};
string Service1::getName()
{
return "service1";
}
void Service1::execute()
{
cout << "execute Service1" << endl;
}
//创建服务实体类Service2
class Service2 :public Service
{
public:
Service2() {};
~Service2() {};
string getName();
void execute();
};
string Service2::getName()
{
return "service2";
}
void Service2::execute()
{
cout << "execute Service2" << endl;
}
//为 JNDI 查询创建 InitialContext。主要是负责对服务实体对象的管理
class InitialContext
{
public:
InitialContext() {};
~InitialContext() {};
Service *lookup(string tname);
};
Service *InitialContext::lookup(string tname)
{
if ("service1" == tname)
{
cout << "Looking up and creating a new Service1 object" << endl;
return new Service1();
}
else if ("service2" == tname)
{
cout << "Looking up and creating a new Service2 object" << endl;
return new Service2();
}
else
{
return NULL;
}
}
//创建缓存类Cache
class Cache
{
public:
Cache() {};
~Cache();
Service* getService(string serviceName);
void addService(Service *newService);
private:
list<Service*> services;
};
Cache::~Cache()
{
list<Service*>::iterator it;
for (it = this->services.begin(); it != this->services.end(); ++it)
{
delete (*it);
(*it) = NULL;
}
}
Service* Cache::getService(string serviceName)
{
list<Service*>::iterator it;
for (it = this->services.begin(); it != this->services.end(); ++it)
{
if ((*it)->getName() == serviceName)
{
cout << "Returning cached: " << serviceName << " Object" << endl;
return (*it);
}
}
return NULL;
}
void Cache::addService(Service *newService)
{
bool exits=false;
list<Service*>::iterator it;
for (it = this->services.begin(); it != this->services.end(); ++it)
{
if ((*it)->getName() == newService->getName())
{
exits = true;
}
}
if (!exits)
{
this->services.push_back(newService);
}
}
//创建服务定位器类ServiceLocator,获取具体的服务
class ServiceLocator
{
public:
ServiceLocator() {};
~ServiceLocator() {};
static Service* getService(string sername);
private:
static Cache tcache;
static InitialContext inicontext;
};
Cache ServiceLocator::tcache;
InitialContext ServiceLocator::inicontext;
Service* ServiceLocator::getService(string sername)
{
if (NULL != ServiceLocator::tcache.getService(sername))
{
return ServiceLocator::tcache.getService(sername);
}
else
{
ServiceLocator::tcache.addService(ServiceLocator::inicontext.lookup(sername));
return ServiceLocator::inicontext.lookup(sername);
}
}
int main()
{
Service *service = ServiceLocator::getService("service1");
service->execute();
service = ServiceLocator::getService("service2");
service->execute();
service = ServiceLocator::getService("service1");
service->execute();
service = ServiceLocator::getService("service2");
service->execute();
delete service;
service = NULL;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
在visual studio 2015上运行结果:
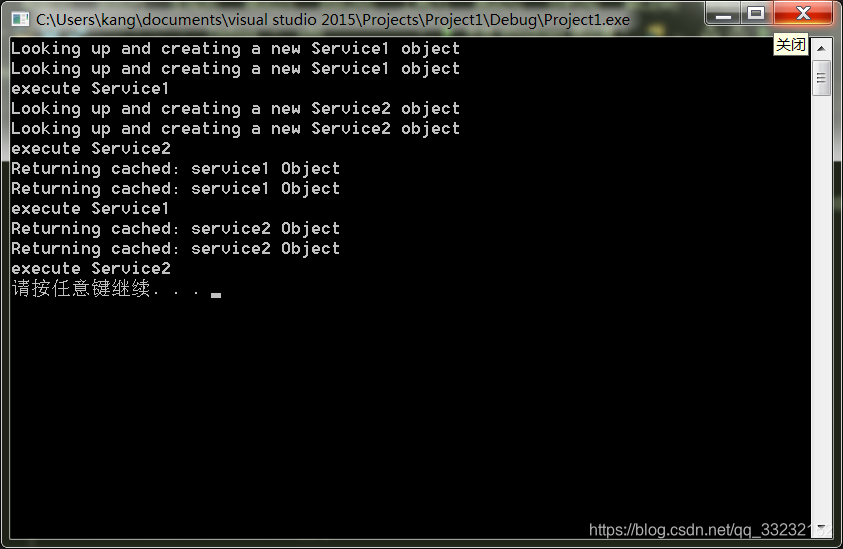





 本文深入探讨了服务定位器模式,一种利用缓存技术提升应用性能的设计模式。通过C++实现示例,详细介绍了模式中的关键实体,包括服务、上下文、服务定位器、缓存和客户端,以及它们之间的交互过程。
本文深入探讨了服务定位器模式,一种利用缓存技术提升应用性能的设计模式。通过C++实现示例,详细介绍了模式中的关键实体,包括服务、上下文、服务定位器、缓存和客户端,以及它们之间的交互过程。
















 1561
1561

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








