#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
map<int, string> map1;
//map插入元素
//方法1
pair<map<int,string>::iterator,bool> myPair1 = map1.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "teacher01"));
if (myPair1.second)
{
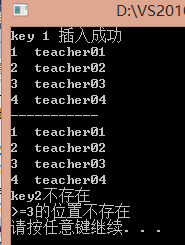
cout << "key 1 插入成功" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << myPair1.first->first << " " << myPair1.first->second << endl;
}
//方法2
map1.insert(make_pair(2, "teacher02"));
//方法3
map1.insert(map<int, string>::value_type(3, "teacher03"));
//方法4
map1[4] = "teacher04";
//插入的前三种方法返回值为pair<iterator,bool>,若key已经存在则报错,第四种方法若key已经存在,则替换value
//遍历
for (map<int,string>::iterator it=map1.begin();it!=map1.end();it++)
{
cout << it->first << " " << it->second << endl;
}
cout << "-----------" << endl;
//删除
while (!map1.empty())
{
map<int, string>::iterator it = map1.begin();
cout << it->first << " " << it->second << endl;
map1.erase(it);
}
//map的查找
map<int, string>::iterator it2 = map1.find(2);//若存在则返回该键的元素的迭代器,若不存在,则返回map.end()
if (it2 == map1.end())
{
cout << "key2不存在" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << it2->first << " " << it2->second << endl;
}
//equal_range(a)返回两个迭代器,第一个迭代器是>=a的位置,第二个是=a的位置
//equal_range相当于lower_bound()+upper_bound()
pair<map<int, string>::iterator, map<int, string>::iterator> myPair2 = map1.equal_range(3);
//使用第一个迭代器
if (myPair2.first == map1.end())
{
cout << ">=3的位置不存在" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << myPair2.first->first << " " << myPair2.first->second << endl;
}
system("pause");
}运行结果:
swap:两个容器交换;
Map中的元素是自动按key升序排序,所以不能对map用sort函数
begin() 返回指向map头部的迭代器
clear() 删除所有元素
count() 返回指定元素出现的次数
empty() 如果map为空则返回true
end() 返回指向map末尾的迭代器
equal_range() 返回特殊条目的迭代器对
erase() 删除一个元素
find() 查找一个元素
get_allocator() 返回map的配置器
insert() 插入元素
key_comp() 返回比较元素key的函数
lower_bound() 返回键值>=给定元素的第一个位置
max_size() 返回可以容纳的最大元素个数
rbegin() 返回一个指向map尾部的逆向迭代器
rend() 返回一个指向map头部的逆向迭代器
size() 返回map中元素的个数
swap() 交换两个map
upper_bound() 返回键值>给定元素的第一个位置
value_comp() 返回比较元素value的函数
还有一些基本操作可以看看这篇文章:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_40914533/article/details/81981467
multimap与map基本相同,不同的是multimap的key可以重复,以下是一个multimap的应用实例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
string name;
int age;
string tel;
double saly;
};
void fun()
{
Person p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6;
p1.name = "张1";
p1.age = 30;
p2.name = "张2";
p2.age = 31;
p3.name = "张3";
p3.age = 32;
p4.name = "张4";
p4.age = 33;
p5.name = "张5";
p5.age = 34;
p6.name = "张6";
p6.age = 35;
//multimap,key可重复
multimap<string, Person> map1;
//sale部门
map1.insert(make_pair("sale",p1));
map1.insert(make_pair("sale", p2));
//development部门
map1.insert(make_pair("development", p3));
map1.insert(make_pair("development", p4));
//financial部门
map1.insert(make_pair("financial", p5));
map1.insert(make_pair("financial", p6));
//遍历
for (multimap<string,Person>::iterator it = map1.begin(); it != map1.end(); it++)
{
//将年龄=33的人的name换为33
if (it->second.age == 33)
{
it->second.name = "33";
}
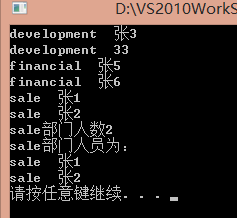
cout << it->first << " " << it->second.name << endl;
}
int num = map1.count("sale");
cout << "sale部门人数" << num << endl;
cout << "sale部门人员为:" << endl;
multimap<string,Person>::iterator it2 = map1.find("sale");
int tag = 0;
while (it2 != map1.end() && tag < num)
{
cout << it2->first << " " << it2->second.name << endl;
it2++;
tag++;
}
}
void main()
{
fun();
system("pause");
}运行结果:








 本文介绍了Map的相关操作,如swap可交换两个容器,Map元素按key升序排序不能用sort函数,还列举了begin、clear等多种操作函数。同时提到multimap与map基本相同,不同之处在于multimap的key可以重复,并给出了应用实例。
本文介绍了Map的相关操作,如swap可交换两个容器,Map元素按key升序排序不能用sort函数,还列举了begin、clear等多种操作函数。同时提到multimap与map基本相同,不同之处在于multimap的key可以重复,并给出了应用实例。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








