阅读源码方法及要素:
- 先梳理脉络,再扣细节。(防止看到方法就点)
- 不要忽略注释,包含非常多的关键信息
- 见名知意
- 大胆猜测,小心验证
- (最重要)坚持!
脉络梳理:
1.什么是容器:
存放对象的水桶,从对象的创建到对象的使用, 到对象的销毁,全部交给容器进行管理。
2.告诉容器我要怎么使用:
通常我们有多种方式来告诉spring容器怎么做:
- XML 配置文件
- properties 配置文件
- yaml配置文件
- 注解
3.从配置文件—>对象
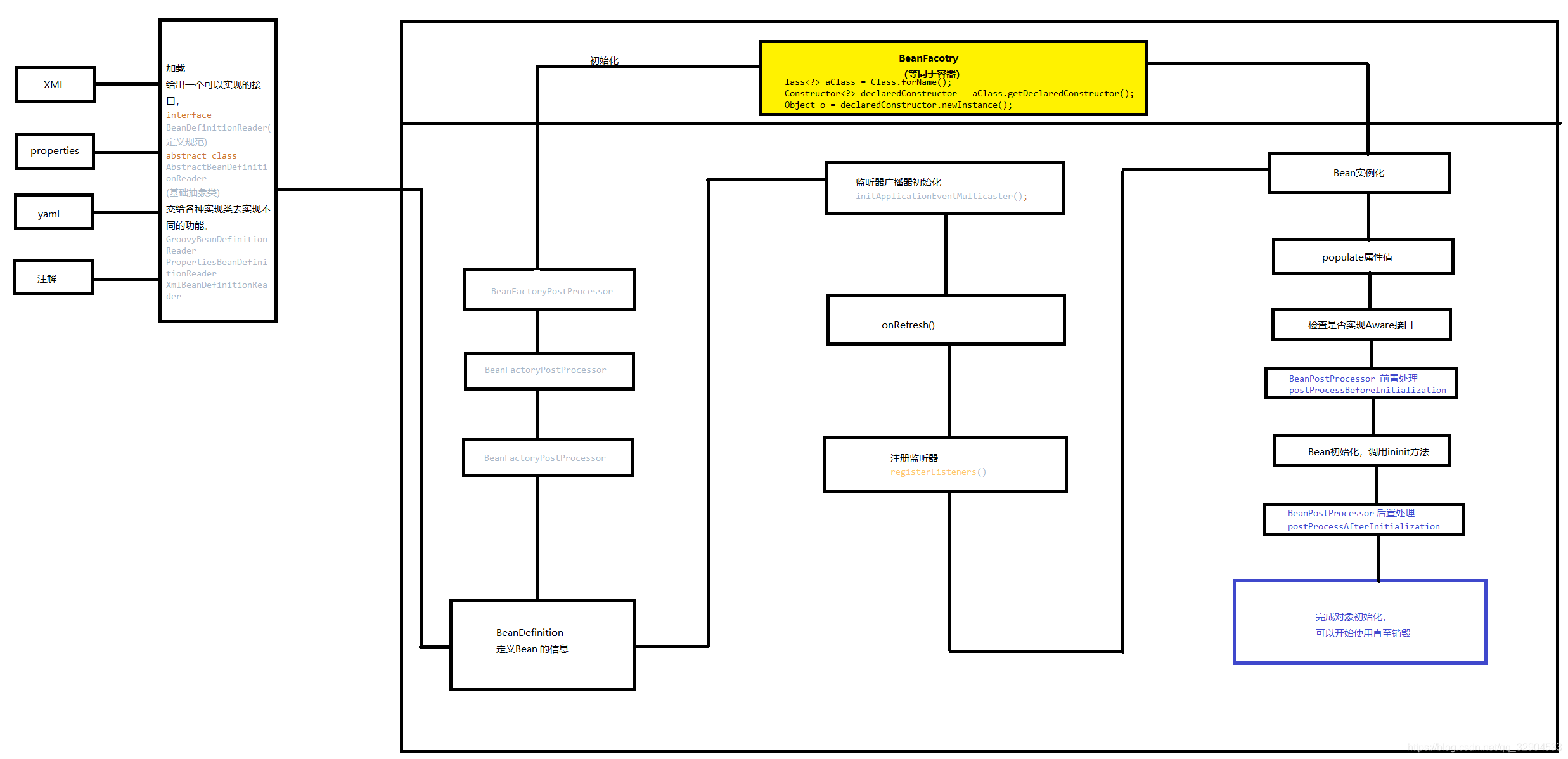
根据上图的思路来一步一步了解整体脉络
源码探究:
启动Spring
接下来我们就以ClassPathXmlApplicationContext作为切入点,开始对整体功能进行分析。首先看下其构造函数:
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext classPathXmlApplicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application-spring-config.xml");
/**
* Create a new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext with the given parent,
* loading the definitions from the given XML files.
* @param configLocations array of resource locations
* @param refresh whether to automatically refresh the context,
* loading all bean definitions and creating all singletons.
* Alternatively, call refresh manually after further configuring the context.
* @param parent the parent context
* @throws BeansException if context creation failed
* @see #refresh()
*/
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext中可以将配置文件路径以数组的方式传入,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext可以对数组进行解析并进行加载。而对于解析及功能实现都在refresh()中实现。
设置配置路径
在ClassPathXmlApplicationContext中支持多个配置文件以数组方式同时传入,以下是设置配置路径方法代码,同时会在resolvePath方法中初始化enviroment并对一些占位符进行替换。
/**
* Set the config locations for this application context.
* 设置此应用程序上下文的配置位置。
* <p>If not set, the implementation may use a default as appropriate.
* 如果未设置,则实现可酌情使用默认值。
*/
public void setConfigLocations(@Nullable String... locations) {
if (locations != null) {
Assert.noNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null");
this.configLocations = new String[locations.length];
for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) {
this.configLocations[i] = resolvePath(locations[i]).trim();
}
}
else {
this.configLocations = null;
}
}
Spring核心功能
AbstractApplicationContext是所有context的抽象类,各种applicationContext都是基于这个类扩展,AbstractApplicationContext.refresh函数中包含了几乎ApplicationContext中提供的全部功能,而且此函数中逻辑非常清晰明了,使我们很容易分析对应的层次及逻辑.
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
//准备刷新的上下文 环境
prepareRefresh();
//通知子类初始化或刷新自己内部的BeanFactory,并进行XML文件读取
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
//对beanFactory进行各种功能填充
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
//子类覆盖方法做额外处理
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard
* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans
* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for registering special
* BeanPostProcessors etc in certain ApplicationContext implementations.
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
*/
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//调用在context中注册过的 BeanFactoryPostProcessors 类
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//注册拦截Bean创建的Bean处理器,这里只是注册,真正的调用实在getBean时候
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//为上下文初始化Message源,即不同语言的消息体,国际化处理
initMessageSource();
//初始化应用消息广播器,并放入“applicationEventMulticaster”bean中
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
//留给子类来初始化其它的Bean
onRefresh();
//在所有注册的bean中查找Listener bean,注册到消息广播器中
registerListeners();
//初始化剩下的(非懒加载的)单例类
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
//完成刷新过程,通知生命周期处理器lifecycleProcessor刷新过程,同时发出ContextRefreshEvent通知别人
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
destroyBeans();
cancelRefresh(ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








