水平有限,静待各位大佬提出的宝贵的建议。
接上篇 自己动手写aop(一),这里通过注解方式切入。
1.定义自己的注解
package com.iflytek.edu;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
}
2.在实现方法上标上注解,say方法上标上@MyAnnotation注解了
package com.iflytek.edu;
public class ManSayHello implements SayHello{
private String name ;
@Override
@MyAnnotation
public String say(String name) {
System.out.println(name+" say : Hello world!");
return name+" is the speaker's name";
}
@Override
public void hello() {
System.out.println("hello");
}
@Override
public void hi() {
System.out.println("hi");
}
}顺便附上接口SayHello
public interface SayHello {
String say(String name);
void hello();
void hi();
}3.AopHandle的修改,主要增加了注解集合
package com.iflytek.edu;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 此处用到静态代理模式 Object obj 为真实角色(被代理角色);AOPHandle 创建的对象为代理角色
*/
public class AOPHandle implements InvocationHandler {
private Object obj;
List<String> methodNameList;
private List<String> annotationList;
AOPHandle(Object obj,List<String> methodNameList,List<String> annotationList){
this.obj = obj;
this.setMethodNameList(methodNameList);
this.setAnnotationList(annotationList);
}
AOPHandle(Object obj){
this.obj = obj;
this.setMethodNameList(methodNameList);
}
public List<String> getAnnotationList() {
return annotationList;
}
public void setAnnotationList(List<String> annotationList) {
this.annotationList = annotationList;
}
public List<String> getMethodNameList() {
return methodNameList;
}
public void setMethodNameList(List<String> methodNameList) {
this.methodNameList = methodNameList;
}
private Object executeProxy(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
//方法返回值
System.out.println("前置代理");
//反射调用方法
Object ret = method.invoke(obj, args);
//声明结束
System.out.println("后置代理");
//返回反射调用方法的返回值
return ret;
}
@Override
/**
*
*/
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// //methodNameList里面定义所有可以切入的方法
//
// if(methodNameList!=null&&methodNameList.size()>0){
// int i=0;
// while (i < methodNameList.size()){
// if(method.getName().equals(methodNameList.get(i++))){
// return executeProxy(proxy,method,args);
// }
// }
// Object ret=method.invoke(obj, args);
// return ret;
// }
//注解的方式
if(annotationList!=null&&annotationList.size()>0){
//获取该方法的所有注解
Annotation methodAnnotations[] = obj.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(method.getName(),method.getParameterTypes()).getAnnotations();
for(int i = 0;i < methodAnnotations.length ; i++){
//该注解是否在annotationList里面,若在,表示其可以被切入
String annotation = methodAnnotations[i].annotationType().getName();
if(annotationList.contains(annotation)){
return executeProxy(proxy,method,args);
}
}
Object ret=method.invoke(obj, args);
return ret;
}
else {
return executeProxy(proxy,method,args); //如果methodName为空 则给所有方法代理
}
}
}
4.Main里增加需要切入的注解是集合。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
ManSayHello manSayHello = new ManSayHello();
List<String> methodName = new ArrayList<String>();
//methodName.add("say");//此处定义需要被切入的方法
List<String> annotations = new ArrayList<String>();//此处定义需要切入的方法的注解
annotations.add(MyAnnotation.class.getName());
//下面这段代码实际上生成了一个新的接口实现类的所有方法
SayHello sayHello = (SayHello) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
SayHello.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { SayHello.class },
new AOPHandle(manSayHello,methodName,annotations));
String rs = sayHello.say("Linda");
System.out.println(rs);
sayHello.hello();
sayHello.hi();
}
}5.效果如下:
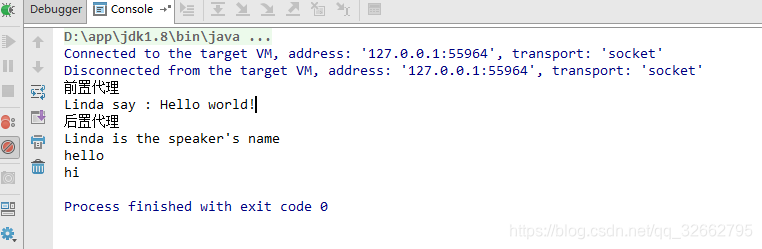
6.通过注解的方式切入就介绍到这里了。
放一个可爱的微笑(* ̄︶ ̄)。
























 800
800

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








