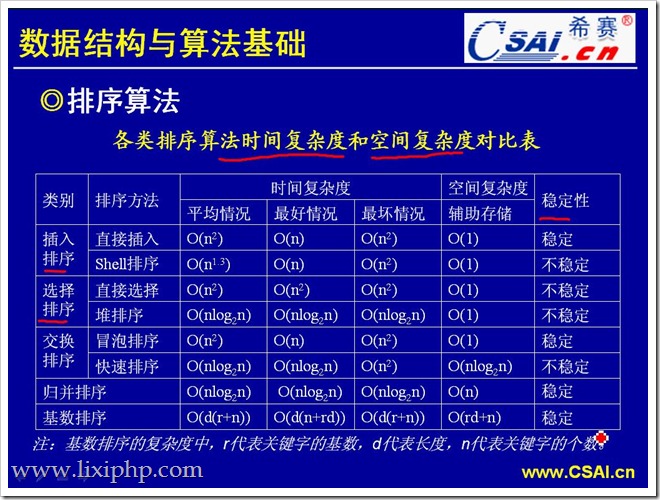
1直接插入排序
- void Insertsort2(int a[], int n)
- {
- int i, j;
- for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
- if (a[i] < a[i - 1])
- {
- int temp = a[i];
- for (j = i - 1; j >= 0 && a[j] > temp; j--)
- a[j + 1] = a[j];
- a[j + 1] = temp;
- }
- }
时间复杂度为O(n的平方)
2希尔排序
1 public void sort(int[] arr) { 2 // i表示希尔排序中的第n/2+1个元素(或者n/4+1) 3 // j表示希尔排序中从0到n/2的元素(n/4) 4 // r表示希尔排序中n/2+1或者n/4+1的值 5 int i, j, r, tmp; 6 // 划组排序 7 for(r = arr.length / 2; r >= 1; r = r / 2) { 8 for(i = r; i < arr.length; i++) { 9 tmp = arr[i]; 10 j = i - r; 11 // 一轮排序 12 while(j >= 0 && tmp < arr[j]) { 13 arr[j+r] = arr[j]; 14 j -= r; 15 } 16 arr[j+r] = tmp; 17 } 18 System.out.println(i + ":" + Arrays.toString(arr)); 19 } 20 }
希尔排序并不稳定,O(1)的额外空间,时间复杂度为O(N*(logN)^2)。
3冒泡排序
public class BubbleSort {
public static void bubbleSort(int[] a) {
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length - 1; ++i) {
for (int j = a.length - 1; j > i; --j) {
if (a[j] < a[j - 1]) {
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j - 1];
a[j - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[] = { 49,38,65,97,76,13,27,49};
bubbleSort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
} 4,快速排序
快速排序是我们之前学习的冒泡排序的升级,他们都属于交换类排序,都是采用不断的比较和移动来实现排序的。快速排序是一种非常高效的排序算法,它的实现,增大了记录的比较和移动的距离,将关键字较大的记录从前面直接移动到后面,关键字较小的记录从后面直接移动到前面,从而减少了总的比较次数和移动次数。同时采用“分而治之”的思想,把大的拆分为小的,小的拆分为更小的,其原理如下:对于给定的一组记录,选择一个基准元素,通常选择第一个元素或者最后一个元素,通过一趟扫描,将待排序列分成两部分,一部分比基准元素小,一部分大于等于基准元素,此时基准元素在其排好序后的正确位置,然后再用同样的方法递归地排序划分的两部分,直到序列中的所有记录均有序为止。
public class QuickSort { public static void sort(int a[], int low, int hight) { int i, j, index; if (low > hight) { return; } i = low; j = hight; index = a[i]; // 用子表的第一个记录做基准 while (i < j) { // 从表的两端交替向中间扫描 while (i < j && a[j] >= index) j--; if (i < j) a[i++] = a[j];// 用比基准小的记录替换低位记录 while (i < j && a[i] < index) i++; if (i < j) // 用比基准大的记录替换高位记录 a[j--] = a[i]; } a[i] = index;// 将基准数值替换回 a[i] sort(a, low, i - 1); // 对低子表进行递归排序 sort(a, i + 1, hight); // 对高子表进行递归排序 } public static void quickSort(int a[]) { sort(a, 0, a.length - 1); } public static void main(String[] args) { int a[] = { 49, 38, 65, 97, 76, 13, 27, 49 }; quickSort(a); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); } }
5选择排序
选择排序是一种简单直观的排序算法,其基本原理如下:对于给定的一组记录,经过第一轮比较后得到最小的记录,然后将该记录的位置与第一个记录的位置交换;接着对不包括第一个记录以外的其他记录进行第二次比较,得到最小记录并与第二个位置记录交换;重复该过程,知道进行比较的记录只剩下一个为止。
public class SelectSort { public static void selectSort(int[] a) { if (a == null || a.length <= 0) { return; } for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { int temp = a[i]; int flag = i; // 将当前下标定义为最小值下标 for (int j = i + 1; j < a.length; j++) { if (a[j] < temp) {// a[j] < temp 从小到大排序;a[j] > temp 从大到小排序 temp = a[j]; flag = j; // 如果有小于当前最小值的关键字将此关键字的下标赋值给flag } } if (flag != i) { a[flag] = a[i]; a[i] = temp; } } } public static void main(String[] args) { int a[] = { 49,38,65,97,76,13,27,49 }; selectSort(a); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); } }
6.堆排序
堆排序适合于数据量非常大的场合(百万数据)。
堆排序不需要大量的递归或者多维的暂存数组。这对于数据量非常巨大的序列是合适的。比如超过数百万条记录,因为快速排序,归并排序都使用递归来设计算法,在数据量非常大的时候,可能会发生堆栈溢出错误。
堆排序会将所有的数据建成一个堆,最大的数据在堆顶,然后将堆顶数据和序列的最后一个数据交换。接下来再次重建堆,交换数据,依次下去,就可以排序所有的数据。
堆排序就是利用堆(假设利用大顶堆)进行排序的方法。它的基本思想是,将待排序的序列构造成一个大顶堆。此时,整个序列的最大值就是堆顶的根节点。将它移走(其实就是将其与堆数组的末尾元素交换,此时末尾元素就是最大值),然后将剩余的 n-1 个序列重新构造成一个堆,这样就会得到 n 个元素中次大的值。如此反复执行,便能得到一个有序序列了。
堆排序的实现需要解决的两个关键问题:
(1)将一个无序序列构成一个堆。
(2)输出堆顶元素后,调整剩余元素成为一个新堆。
public class HeapSort { /** * 构建大顶堆 */ public static void adjustHeap(int[] a, int i, int len) { int temp, j; temp = a[i]; for (j = 2 * i; j < len; j *= 2) {// 沿关键字较大的孩子结点向下筛选 if (j < len && a[j] < a[j + 1]) ++j; // j为关键字中较大记录的下标 if (temp >= a[j]) break; a[i] = a[j]; i = j; } a[i] = temp; } public static void heapSort(int[] a) { int i; for (i = a.length / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {// 构建一个大顶堆 adjustHeap(a, i, a.length - 1); } for (i = a.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {// 将堆顶记录和当前未经排序子序列的最后一个记录交换 int temp = a[0]; a[0] = a[i]; a[i] = temp; adjustHeap(a, 0, i - 1);// 将a中前i-1个记录重新调整为大顶堆 } } public static void main(String[] args) { int a[] = { 51, 46, 20, 18, 65, 97, 82, 30, 77, 50 }; heapSort(a); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); } }
7,归并排序
归并排序就是利用归并的思想实现的排序方法。而且充分利用了完全二叉树的深度是
经过第一轮比较后得到最小的记录,然后将该记录的位置与第一个记录的位置交换;接着对不包括第一个记录以外的其他记录进行第二次比较,得到最小记录并与第二个位置记录交换;重复该过程,知道进行比较的记录只剩下一个为止。
工作原理:
(1)申请空间,使其大小为两个已经排序序列之和,该空间用来存放合并后的序列
(2)设定两个指针,最初位置分别为两个已经排序序列的起始位置
(3)比较两个指针所指向的元素,选择相对小的元素放入到合并空间,并移动指针到下一位置
(4)重复步骤3直到某一指针达到序列尾
(5)将另一序列剩下的所有元素直接复制到合并序列尾
public class MergeSort { public static void merge(int[] a, int low, int mid, int high) { int[] temp = new int[high - low + 1]; int i = low;// 左指针 int j = mid + 1;// 右指针 int k = 0; // 把较小的数先移到新数组中 while (i <= mid && j <= high) { if (a[i] < a[j]) { temp[k++] = a[i++]; } else { temp[k++] = a[j++]; } } // 把左边剩余的数移入数组 while (i <= mid) { temp[k++] = a[i++]; } // 把右边边剩余的数移入数组 while (j <= high) { temp[k++] = a[j++]; } // 把新数组中的数覆盖nums数组 for (int k2 = 0; k2 < temp.length; k2++) { a[k2 + low] = temp[k2]; } } public static void mergeSort(int[] a, int low, int high) { int mid = (low + high) / 2; if (low < high) { // 左边 mergeSort(a, low, mid); // 右边 mergeSort(a, mid + 1, high); // 左右归并 merge(a, low, mid, high); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); } } public static void main(String[] args) { int a[] = { 51, 46, 20, 18, 65, 97, 82, 30, 77, 50 }; mergeSort(a, 0, a.length - 1); System.out.println("排序结果:" + Arrays.toString(a)); } }


























 30万+
30万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








