1.孩子们的游戏(圆圈中最后剩下的数)
两种方法,第一种:模拟链表.
class Solution {
public:
int LastRemaining_Solution(int n, int m)
{
if(n==0 || m == 0)return -1;
list<int> p;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
p.push_back(i);
}
int move=0;
while(p.size()>1){
move = (move+m-1)% p.size();
auto it = p.begin();
advance(it,move);
p.erase(it);
}
return p.back();
}
};2.约瑟夫环
主要是记住公式: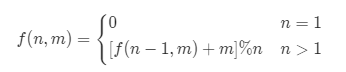
class Solution {
public:
int LastRemaining_Solution(int n, int m)
{
if(n <=0 || m<=0)return -1;
int f = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
f = (f + m) % i;
}
return f;
}
};2.删除链表中重复的结点
和LeetCode的某一道题很类似:83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
给定一个排序链表,删除所有重复的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次。
可以用一个指针,如果这个指针下一个元素等于该指针的值,那么p->next = p->next->next。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL) return NULL;
auto p = head,p1 = head;
while(p && p->next){
if(p->val == p->next->val){
p->next = p->next->next;
}else{
p = p->next;
}
}
return head;
}
};本题不保留重复的元素:
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplication(ListNode* pHead)
{
if(pHead == NULL) return NULL;
auto p = new ListNode(-1);
p->next = pHead;
auto p1 = p,p2 = p;
while(p2){
while(p2->next && p2->val == p2->next->val){
p2 = p2->next;
}
//找到p2不重复的值
p2 = p2->next;
//判断是不是1-2-2-3-3-4中3的情况
if(p2 && p2->next && p2->val == p2->next->val){
continue;
}
p1->next=p2;
p1 = p1->next;
}
return p->next;
}
};
3.从尾到头打印链表
第一个想法是reverse
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) :
* val(x), next(NULL) {
* }
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode* head) {
auto p = head;
vector<int> res;
while(p){
res.push_back(p->val);
p = p->next;
}
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
return res;
}
};2.可以先翻转链表,然后push_back()
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) :
* val(x), next(NULL) {
* }
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode* head) {
//if(head == NULL) return NULL;
ListNode* pre=nullptr;ListNode* cur=head;
while(cur){
ListNode* t = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = t;
}
vector<int> res;
while(pre){
res.push_back(pre->val);
pre=pre->next;
}
return res;
}
};3.用栈(我真是菜鸡,这都没想到)
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) :
* val(x), next(NULL) {
* }
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode* head) {
stack<int> res;
auto p = head;
while(p){
res.push(p->val);
p = p->next;
}
vector<int> ret;
while(!res.empty()){
ret.push_back(res.top());
res.pop();
}
return ret;
}
};所有的链表都已经完结,总结:就是双指针、快慢指针来来回回的用。
下面开始栈、队列、数组的章节
4.用两个栈实现队列
push操作就直接往stack1中push, pop操作需要分类一下:如果stack2为空,那么需要将stack1中的数据转移到stack2中,然后在对stack2进行pop,如果stack2不为空,直接pop就ok。
class Solution
{
public:
void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node);
}
int pop() {
if(stack2.empty()){
while(!stack1.empty()){
stack2.push(stack1.top());
stack1.pop();
}
}
int res=stack2.top();
stack2.pop();
return res;
}
private:
stack<int> stack1;
stack<int> stack2;
};5.斐波那契数列
最基本的动态规划,当然有其他解法
class Solution {
public:
int Fibonacci(int n) {
if(n == 0)return 0;
if(n == 1)return 1;
vector<int> dp(n+1, 0);
dp[0]=0;dp[1]=1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
dp[i]=dp[i-1]+dp[i-2];
}
return dp[n];
}
};6.调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
这道题,LeetCode上题目不需要相对位置不变,所以可以采用荷兰国旗的想法:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> exchange(vector<int>& nums) {
int p1=-1,p2=nums.size(),i=0;
while(i<p2){
if(nums[i]%2!=0){
swap(nums[++p1],nums[i++]);
}else {
swap(nums[--p2],nums[i]);
}
}
return nums;
}
};或者双路快排的想法:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> exchange(vector<int>& nums) {
int p1=0,p2=nums.size()-1;
while(p1 < p2){
while(p1 < p2 && nums[p1] % 2 != 0)p1++;
while(p1 < p2 && nums[p2] % 2 == 0)p2--;
swap(nums[p1],nums[p2]);
}
return nums;
}
};牛客上的题目要求需要相对位置不改变,所以需要借助vector:
class Solution {
public:
void reOrderArray(vector<int> &array) {
vector <int> res;
for(auto c : array){
if(c % 2 != 0) res.push_back(c);
}
for(auto c : array){
if(c % 2 == 0) res.push_back(c);
}
copy(res.begin(), res.end(), array.begin());
}
};
7.二维数组中的查找
从左下角开始查找。
class Solution {
public:
bool Find(int target, vector<vector<int> > array) {
int n = array.size()-1;
int m = array[0].size()-1;
int i=n,j=0;
while(i>=0 && j<=m){
if(target < array[i][j])i--;
else if(target > array[i][j])j++;
else return true;
}
return false;
}
};8.顺时针打印矩阵
这道题就是扣边界……将螺旋矩阵当作一个框,规定上下左右边界:
上:0
下:m.size()-1
左:0
右:m[0].size()-1
返回条件:上边界>下边界 || 左边界>右边界
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printMatrix(vector<vector<int> > matrix) {
int l=0,r=matrix[0].size()-1,u=0,d=matrix.size()-1;
vector<int> res;
while(true){
for(int i=l;i<=r;i++)res.push_back(matrix[u][i]);
u++;
if(u > d)break;
for(int i=u;i<=d;i++)res.push_back(matrix[i][r]);
r--;
if(l > r)break;
for(int i=r;i>=l;i--)res.push_back(matrix[d][i]);
d--;
if(u > d)break;
for(int i=d;i>=u;i--)res.push_back(matrix[i][l]);
l++;
if(l > r)break;
}
return res;
}
};
9.最小的k个数
第一个想法就是:sort
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(vector<int> input, int k) {
vector<int> p;
if(input.size() == 0 || k > input.size())return p;
sort(input.begin(), input.end());
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
p.push_back(input[i]);
}
return p;
}
};第二个想法就是用堆
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(vector<int> input, int k) {
vector<int> res;
if (k==0 || k > input.size()) return res;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, less<int>> p;
for(int i=0; i < input.size();i++){
if(p.size()<k){
p.push(input[i]);
}else{
if(input[i] < p.top()){
p.pop();
p.push(input[i]);
}
}
}
while(!p.empty()){
res.push_back(p.top());
p.pop();
}
return res;
}
};
10.把数组排成最小的数
定义比较器,需要注意的是to_string。发现牛客上题意总是写的比较模糊……
class Solution {
public:
string PrintMinNumber(vector<int> numbers) {
if(numbers.size()<=0)
return "";
sort(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), cmp);
string s;
for(int i=0;i<numbers.size();i++){
s+=to_string(numbers[i]);
}
return s;
}
static bool cmp(int n1,int n2){
string A=to_string(n1)+to_string(n2);
string B=to_string(n2)+to_string(n1);
return A<B;
}
};也可以先把数转为string再比较,最后输出:
class Solution {
public:
string minNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
string s[nums.size()],str;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
s[i]=to_string(nums[i]);
}
sort(s,s+nums.size(),cmp);
for(auto c:s){
str+=c;
}
return str;
}
static bool cmp(string n1,string n2){
return n1+n2<n2+n1;
}
};





 本文深入解析了包括链表、栈、队列、数组在内的多种数据结构的经典算法题,如约瑟夫环、链表去重、矩阵打印等,并提供多种解法,如双指针、快慢指针技巧及动态规划。
本文深入解析了包括链表、栈、队列、数组在内的多种数据结构的经典算法题,如约瑟夫环、链表去重、矩阵打印等,并提供多种解法,如双指针、快慢指针技巧及动态规划。
















 1092
1092

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








