原文链接
获得深度图像数据,转成cv::Mat格式
cv::Mat depthMat(depthi->getHeight(), depthi->getWidth (), CV_16UC1, depth_map);清除1米外的数据
int nr = depthMat.rows; // number of rows
int nc = depthMat.cols; // number of columns
for (int i = 0; i<nr; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j<nc; j++) {
if (depthMat.at<ushort>(i, j)>1000){
depthMat.at<ushort>(i, j) = 0;
}
}
}将像素16U数据转成8U数据
depthMat.convertTo(depthMat, CV_8UC1, 1.0 / 16);正常来说因子应该为 256/65536=1/256。16表示16×256=4096,可测障碍最远为4.096米,而1米外的障碍已清除,图像像素最大深度肯定小于1000,因此因子为1/16可将图像上的所有障碍保留下来。
用阈值函数将图像中的障碍显示到一个平面中
cv::Mat threshold_output;
cv::threshold(depthMat, threshold_output, 20, 255, CV_THRESH_BINARY);
像素数值大于20的都认为是障碍,但这里的20实际代表20×16=320mm距离远的部分。
在Mat中找到障碍的轮廓
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point> > contours;
std::vector<cv::Vec4i> hierarchy;
cv::findContours(threshold_output, contours, hierarchy, CV_RETR_TREE, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, cv::Point(0, 0));找到障碍轮廓的凸形外廓
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point> >hull(contours.size());
for (int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++)
{
cv::convexHull(cv::Mat(contours[i]), hull[i], false);
}将面积小于100mm平方的凸形外廓当成噪点屏蔽
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point> > result;
for (int i = 0; i< contours.size(); i++)
{
if (cv::contourArea(contours[i]) < 100)
{
continue;
}
result.push_back(hull[i]);
}绘制障碍轮廓
cv::RNG rng(12345);
cv::Mat drawing = cv::Mat::zeros(threshold_output.size(), CV_8UC3);
for (int i = 0; i< contours.size(); i++)
{
cv::Scalar color = cv::Scalar(rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0, 255));
cv::drawContours(drawing, contours, i, color, 1, 8, std::vector<cv::Vec4i>(), 0, cv::Point());
cv::drawContours(drawing, hull, i, color, 1, 8, std::vector<cv::Vec4i>(), 0, cv::Point());
}显示障碍
cv::imshow("contours", drawing);
cv::waitKey(30);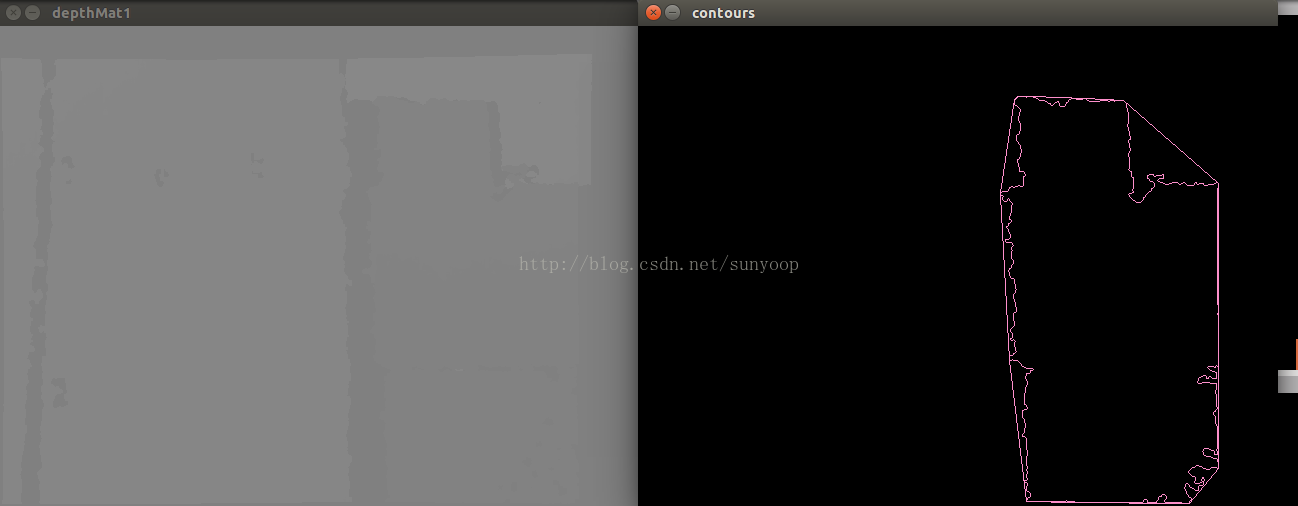
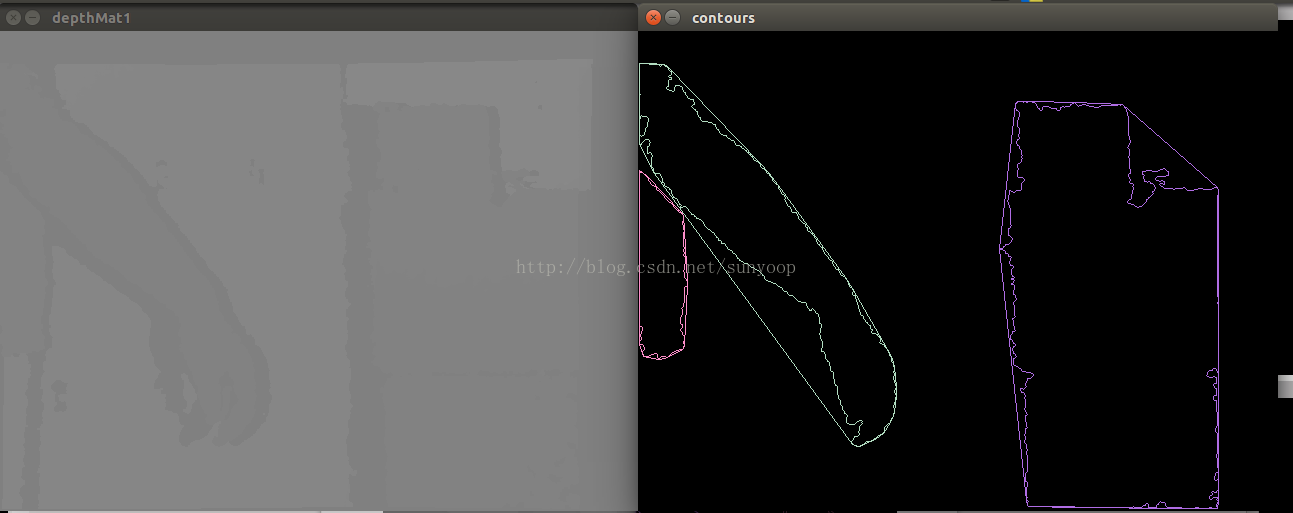







 本文介绍如何从深度图像数据中检测并清除1米外的障碍物,通过阈值处理和轮廓分析,实现对近处障碍物的有效识别与可视化。详细步骤包括:数据格式转换、深度阈值设定、障碍物轮廓提取及噪声过滤。
本文介绍如何从深度图像数据中检测并清除1米外的障碍物,通过阈值处理和轮廓分析,实现对近处障碍物的有效识别与可视化。详细步骤包括:数据格式转换、深度阈值设定、障碍物轮廓提取及噪声过滤。
















 3546
3546

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








