目录
3、_invocation_counter和_backedge_counter
二、InterpreterGenerator::generate_counter_incr
三、InterpreterGenerator::generate_counter_overflow
在上一篇《Hotspot 字节码执行与栈顶缓存实现 源码解析》中分析InterpreterGenerator::generate_normal_entry方法的实现时提到了用于增加方法调用计数的InterpreterGenerator::generate_counter_incr方法和在方法调用计数达到阈值后自动触发方法编译的InterpreterGenerator::generate_counter_overflow方法,本篇就详细探讨这两个方法的实现为线索研究热点代码编译的实现。热点代码编译实际是有两个场景的,一种是正常的方法调用,调用次数超过阈值形成热点,一种是通过for循环执行一段代码,for循环的次数超过阈值形成热点,这两种情形都会触发方法的编译,不同的是前者是提交一个编译任务给后台编译线程,编译完成后通过适配器将对原来字节码的调用转换成对本地代码的调用,后者是尽可能的立即完成编译,并且在完成必要的栈帧迁移转换后立即执行编译后的本地代码,即完成栈上替换。
一、InvocationCounter
1、定义
InvocationCounter表示一个调用计数器,可以在初始化时为不同状态下的InvocationCounter定义对应的阈值和触发的动作,当计数超过阈值时自动执行初始化时指定的触发动作。为了节省内存空间,InvocationCounter的状态和计数被编码在一个int数据(4字节,32位,对应_counter属性)中,各部分占的位数如下图,其中carry相当于一个分隔符,只占1位。
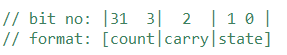
InvocationCounter定义的状态枚举State如下:
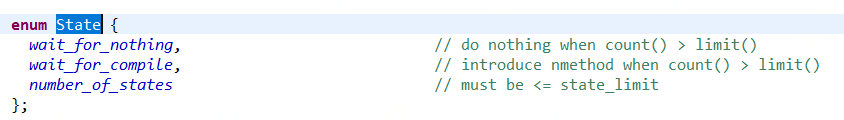
即实际的有效状态只有前面两种。
InvocationCounter定义的私有属性如下,注意除第一个外,其他的都是静态属性
- _counter:unsigned int,保存调用计数,state。
- _init:int [number_of_states],不同State下的阈值
- _action:Action [number_of_states],不同State下的达到阈值执行的动作
- InterpreterInvocationLimit:int,执行方法编译的阈值
- InterpreterBackwardBranchLimit:int,执行栈上替换的阈值
- InterpreterProfileLimit:int,收集解释器执行性能数据的阈值
其中Action的定义如下:
![]()
InvocationCounter定义的方法主要是属性操作相关的方法,重点关注其init方法和reinitialize方法的实现。
2、init方法
init方法用于初始化计数器相关属性的,源码说明如下:
void InvocationCounter::init() {
_counter = 0; //所有的位都初始化成0
reset();
}
void InvocationCounter::reset() {
// Only reset the state and don't make the method look like it's never
// been executed
set_state(wait_for_compile);
}
void InvocationCounter::set_state(State state) {
//校验state的合法性
assert(0 <= state && state < number_of_states, "illegal state");
//获取该state下的调用计数,初始为0
int init = _init[state];
// prevent from going to zero, to distinguish from never-executed methods
//初始状态下count()返回0,init也是0
//当运行一段时间发生状态切换后,count()返回值大于0,如果此时init==0说明是第一次执行此状态下的调用,将init初始化为1
if (init == 0 && count() > 0) init = 1;
int carry = (_counter & carry_mask); // the carry bit is sticky
初始化counter
_counter = (init << number_of_noncount_bits) | carry | state;
}
//返回总的调用计数
int count() const { return _counter >> number_of_noncount_bits; }其中init方法的调用链如下:
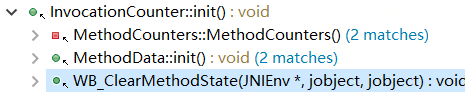
MethodCounters用于热点代码跟踪中的方法调用计数,其中MethodData用于保存JIT编译器为了优化代码而收集的方法执行性能相关数据,初始化为null。两者都定义了两个InvocationCounter的属性,且属性名一样,以MethodCounters为例,如下:
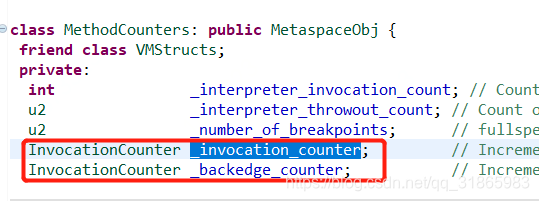
上述调用链就是初始化各自的 InvocationCounter的属性。
3、_invocation_counter和_backedge_counter
其中_invocation_counter记录方法调用的次数,_backedge_counter记录循环跳转的次数,可以用如下测试用例说明:
import java.lang.management.ManagementFactory;
import java.lang.management.RuntimeMXBean;
public class HSDBTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
forTest();
while (true){
try {
System.out.println(getProcessID());
Thread.sleep(600*1000);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
public static void forTest(){
int a=0;
for (int i=0;i<10000;i++){
a++;
}
System.out.println(a);
}
public static final int getProcessID() {
RuntimeMXBean runtimeMXBean = ManagementFactory.getRuntimeMXBean();
System.out.println(runtimeMXBean.getName());
return Integer.valueOf(runtimeMXBean.getName().split("@")[0])
.intValue();
}
}
运行起来后通过HSDB查看forTest方法对应的Method实例的相关属性,结果如下:
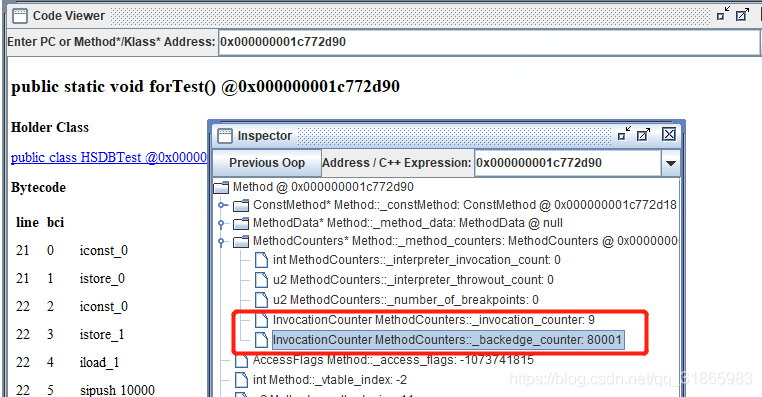
这里的9和80001都是 _counter的值,实际的调用计数需要将其右移三位计算,如

结果如下:
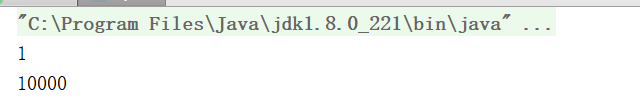
与forTest中循环了10000次,forTest本身只调用了一次完全一致。
4、reinitialize
reinitialize方法主要用于初始化InvocationCounter的静态属性,其源码实现如下:
void InvocationCounter::reinitialize(bool delay_overflow) {
//确保number_of_states小于等于4
guarantee((int)number_of_states <= (int)state_limit, "adjust number_of_state_bits");
//设置两种状态下的触发动作
def(wait_for_nothing, 0, do_nothing);
//如果延迟处理,delay_overflow肯定是true,所以不会走到dummy_invocation_counter_overflow,该方法是空实现
if (delay_overflow) {
def(wait_for_compile, 0, do_decay);
} else {
def(wait_for_compile, 0, dummy_invocation_counter_overflow);
}
//计算InterpreterInvocationLimit等阈值
InterpreterInvocationLimit = CompileThreshold << number_of_noncount_bits;
InterpreterProfileLimit = ((CompileThreshold * InterpreterProfilePercentage) / 100)<< number_of_noncount_bits;
if (ProfileInterpreter) {
InterpreterBackwardBranchLimit = (CompileThreshold * (OnStackReplacePercentage - InterpreterProfilePercentage)) / 100;
} else {
InterpreterBackwardBranchLimit = ((CompileThreshold * OnStackReplacePercentage) / 100) << number_of_noncount_bits;
}
//校验计算结果的合法性
assert(0 <= InterpreterBackwardBranchLimit,
"OSR threshold should be non-negative");
assert(0 <= InterpreterProfileLimit &&
InterpreterProfileLimit <= InterpreterInvocationLimit,
"profile threshold should be less than the compilation threshold "
"and non-negative");
}
static address do_nothing(methodHandle method, TRAPS) {
//获取并校验目标方法的MethodCounters
MethodCounters* mcs = method->method_counters();
assert(mcs != NULL, "");
//重置调用计数为CompileThreshold的一般
mcs->invocation_counter()->set_carry();
//显示的将状态置为wait_for_nothing
mcs->invocation_counter()->set_state(InvocationCounter::wait_for_nothing);
return NULL;
}
void InvocationCounter::set_carry() {
//执行set_carry_flag后,_counter会变得很大
set_carry_flag();
int old_count = count();
//new_count的值一般情况下取后者
int new_co







 本文深入探讨Hotspot虚拟机的热点代码编译,包括InvocationCounter的实现,如方法调用计数阈值、触发编译的动作。分析了 InterpreterGenerator 的 generate_counter_incr 和 generate_counter_overflow 方法,讲解了正常方法调用和循环执行超过阈值时的编译过程。栈上替换在循环次数超过阈值时发生,编译后立即执行本地代码,实现快速优化。
本文深入探讨Hotspot虚拟机的热点代码编译,包括InvocationCounter的实现,如方法调用计数阈值、触发编译的动作。分析了 InterpreterGenerator 的 generate_counter_incr 和 generate_counter_overflow 方法,讲解了正常方法调用和循环执行超过阈值时的编译过程。栈上替换在循环次数超过阈值时发生,编译后立即执行本地代码,实现快速优化。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 2172
2172

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








