import time ''' 时间戳转换成日期格式 1)将时间时间戳转换成时间元组 2)通过strftime()将时间元组转换成格式化时间 ''' def timestamp_to_format(timestamp=None,format = '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'): # try: if timestamp: time_tuple = time.localtime(timestamp) print('time_tuple:',time_tuple) #print('type(time_tuple):',type(time_tuple)) res = time.strftime(format,time_tuple) else: res = time.strftime(format) return res # except: # print('error') print('时间戳1234567转换成日期格式为:',timestamp_to_format(1234567))
运行结果:
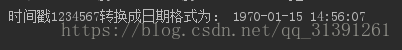
1)time.localtime(seconds=Noe) 作用:将时间戳转换成一个时间元组,包括年,月,天,小时,分钟,秒,当月的第N周,当前年的第M天 如果没有参数传入,那么就转换当前时间的时间戳 def localtime(seconds=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ localtime([seconds]) -> (tm_year,tm_mon,tm_mday,tm_hour,tm_min, tm_sec,tm_wday,tm_yday,tm_isdst) Convert seconds since the Epoch to a time tuple expressing local time. When 'seconds' is not passed in, convert the current time instead. """ pass 函数运行结果:
2)time.strftime(format,p_tuple=None) 作用:根据设定好的格式将时间元组转换成字符串 如果时间元组缺省,那么将当前时间转换成设定格式的日期 def strftime(format, p_tuple=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ strftime(format[, tuple]) -> string Convert a time tuple to a string according to a format specification. See the library reference manual for formatting codes. When the time tuple is not present, current time as returned by localtime() is used. Commonly used format codes: %Y Year with century as a decimal number. %m Month as a decimal number [01,12]. %d Day of the month as a decimal number [01,31]. %H Hour (24-hour clock) as a decimal number [00,23]. %M Minute as a decimal number [00,59]. %S Second as a decimal number [00,61]. %z Time zone offset from UTC. %a Locale's abbreviated weekday name. %A Locale's full weekday name. %b Locale's abbreviated month name. %B Locale's full month name. %c Locale's appropriate date and time representation. %I Hour (12-hour clock) as a decimal number [01,12]. %p Locale's equivalent of either AM or PM. Other codes may be available on your platform. See documentation for the C library strftime function. """ return "" 运行结果:
|
二:日期格式转换成时间戳
''' 将格式化时间转换为时间戳 1)将日期转换成时间元组 2)转换成时间戳 ''' def timeformat_to_timestamp(timeformat=None,format = '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'): # try: if timeformat: time_tuple = time.strptime(timeformat,format) res = time.mktime(time_tuple) #转成时间戳 else: res = time.time() #获取当前时间戳 return int(res) print("timeformat_to_timestamp('2018-04-12 09:09:45')的时间戳:",timeformat_to_timestamp('2018-04-12 09:09:45'))
运行结果:
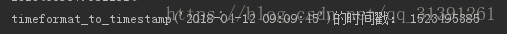
1)time.strptime() 作用:将format格式的时间字符串解析成一个时间元组 def strptime(string, format): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ strptime(string, format) -> struct_time Parse a string to a time tuple according to a format specification. See the library reference manual for formatting codes (same as strftime()). Commonly used format codes: %Y Year with century as a decimal number. %m Month as a decimal number [01,12]. %d Day of the month as a decimal number [01,31]. %H Hour (24-hour clock) as a decimal number [00,23]. %M Minute as a decimal number [00,59]. %S Second as a decimal number [00,61]. %z Time zone offset from UTC. %a Locale's abbreviated weekday name. %A Locale's full weekday name. %b Locale's abbreviated month name. %B Locale's full month name. %c Locale's appropriate date and time representation. %I Hour (12-hour clock) as a decimal number [01,12]. %p Locale's equivalent of either AM or PM. Other codes may be available on your platform. See documentation for the C library strftime function. """ return struct_time 2)time.mktime(p_tuple) 作用:将时间元组转换成时间戳 def mktime(p_tuple): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ mktime(tuple) -> floating point number Convert a time tuple in local time to seconds since the Epoch. Note that mktime(gmtime(0)) will not generally return zero for most time zones; instead the returned value will either be equal to that of the timezone or altzone attributes on the time module. """ return 0.0 |








 本文介绍了如何在Python中实现时间戳与日期格式之间的相互转换,包括使用time模块中的函数如localtime、strftime、strptime及mktime等来完成转换过程。
本文介绍了如何在Python中实现时间戳与日期格式之间的相互转换,包括使用time模块中的函数如localtime、strftime、strptime及mktime等来完成转换过程。

















 1255
1255

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








