目录
EL表达式
一、什么是 EL 表达式,EL 表达式的作用?
2.EL 表达式的作用:EL 表达式主要是代替 jsp 页面中的表达式脚本在 jsp 页面中进行数据的输出。 因为 EL 表达式在输出数据的时候,要比 jsp 的表达式脚本要简洁很多。
3.示例代码
<body>
<%
request.setAttribute("key","值");
%>
表达式脚本输出的key值是:<%=request.getAttribute("key")%><br/>
EL表达式输出的key值是:${key}<br/>
表达式脚本输出的key值是:<%=request.getAttribute("key1")%><br/>
EL表达式输出的key值是:${key1}<br/>
</body>
补充说明:
EL表达式的格式是:${表达式}
EL表达式在输出null值的时候,输出的是空串。但是jsp表达式脚本输出的是null字符串
二.EL表达式搜索域数据的顺序
1.EL表达式主要是在jsp页面中输出域对象中的数据
补充:jsp的四大域对象和九大内置对象


2.EL表达式的输出顺序:
当四个域中都有相同的 key 的数据的时候,EL 表达式会按照四个域的从小到大的顺序去进行搜索,找到就输出。
示例代码:
<body> <%
//往四个域中都保存了相同的 key 的数据。
request.setAttribute("key", "request");
session.setAttribute("key", "session");
application.setAttribute("key", "application");
pageContext.setAttribute("key", "pageContext");
%>
${ key }
</body>
3.EL 表达式输出 Bean 的普通属性,数组属性。List 集 合属性,map 集合属性
示例代码:
<body>
<%
Person person = new Person();
person.setAge(20);
person.setPhones(new String[]{"18888888888","199999999","20000000000"});
List<String> cities = new ArrayList<>();
cities.add("北京");
cities.add("上海");
cities.add("成都");
person.setCities(cities);
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("key1","value1");
map.put("key2","value2");
map.put("key3","value3");
person.setMap(map);
pageContext.setAttribute("p",person);
%>
输出Person:${p}<br/>
输出Person的age属性:${p.age}<br/>
输出Person的phone属性:${p.phones[2]}<br/>
输出Person的cities属性:${p.cities}<br/>
输出Person的List的个别元素属性:${p.cities[2]}<br/>
输出Person的Map属性:${p.map}<br/>
输出Person的Map属性中某个key的值:${p.map.key2}<br/>
</body>
注:输出的属性是根据的JavaBean里面的get方法输出的,如果没有get方法就会报错
三、EL 表达式——运算
1.数学运算:
2.比较运算:> gt < lt >= ge <= le == eq != !=
3.逻辑运算: && || !
4.empty 运算:
可以判断一个数据是否为空,如果为空,则输出 true,不为空输出 false。
5. “.”点运算 和 [] 中括号运算符
<body>
<%
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("a.a.a", "aaaValue");
map.put("b+b+b", "bbbValue");
map.put("c-c-c", "cccValue");
request.setAttribute("map", map);
%>
${ map['a.a.a'] } <br>
${ map["b+b+b"] } <br>
${ map['c-c-c'] } <br>
</body>
四、EL 表达式的 11 个隐含对象
1.EL 个达式中 11 个隐含对象,是 EL 表达式中自己定义的,可以直接使用。
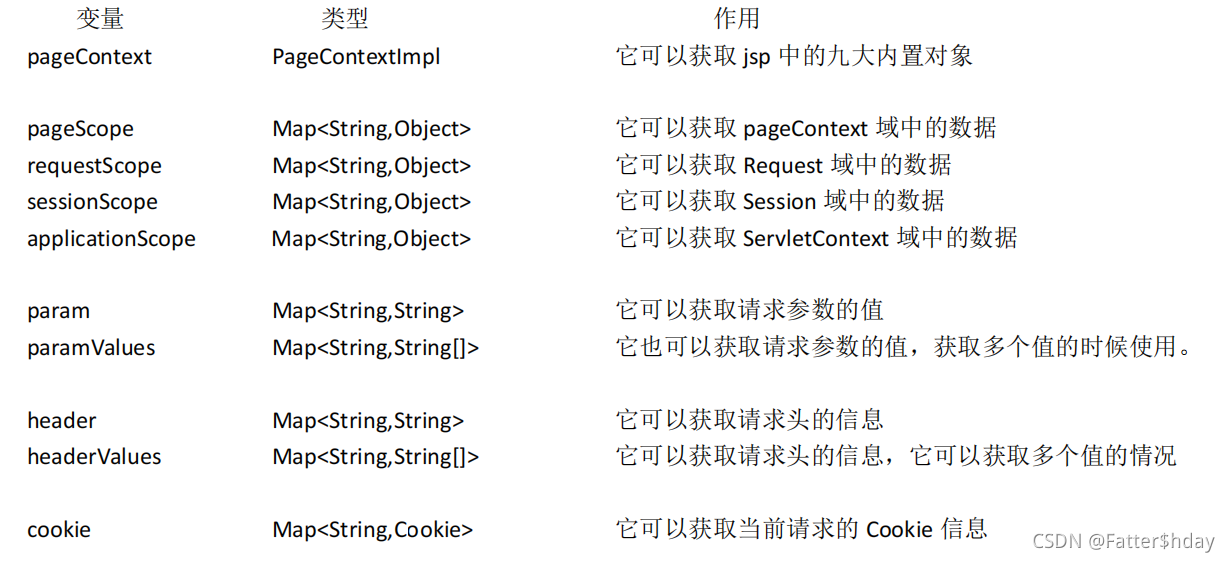
2. EL 获取四个特定域中的属性

<body>
<%
//往四个域中都保存了相同的key的数据
pageContext.setAttribute("key","pageContext");
request.setAttribute("key","request");
session.setAttribute("key","session");
application.setAttribute("key"," application");
%>
${pageScope.key};<br/>
${requestScope.key};<br/>
${sessionScope.key};<br/>
${applicationScope.key};<br/>
</body>
3.pageContext 对象的使用
示例代码:
<% pageContext.setAttribute("req", request);
%>
1.协议: ${ req.scheme }<br>
2.服务器 ip:${ pageContext.request.serverName }<br>
3.服务器端口:${ pageContext.request.serverPort }<br>
4.获取工程路径:${ pageContext.request.contextPath }<br>
5.获取请求方法:${ pageContext.request.method }<br>
6.获取客户端 ip 地址:${ pageContext.request.remoteHost }<br> 7.获取会话的 id
编号:${ pageContext.session.id }<br>
</body>
4.EL 表达式其他隐含对象的使用




示例代码:
web.xml 中的配置:
<context-param>
<param-name>username</param-name>
<param-value>root</param-value>
</context-param>
<context-param>
<param-name>url</param-name>
<param-value>jdbc:mysql:///test</param-value>
</context-param>示例代码:
<body>
输出请求参数 username 的值:${ param.username } <br>
输出请求参数 password 的值:${ param.password } <br>
输出请求参数 username 的值:${ paramValues.username[1] } <br>
输出请求参数 hobby 的值:${ paramValues.hobby[0] } <br>
输出请求参数 hobby 的值:${ paramValues.hobby[1] } <br>
输出请求头【User-Agent】的值:${ header['User-Agent'] } <br>
输出请求头【Connection】的值:${ header.Connection } <br>
输出请求头【User-Agent】的值:${ headerValues['User-Agent'][0] } <br>
获取 Cookie 的名称:${ cookie.JSESSIONID.name } <br> 获取 Cookie 的值:${ cookie.JSESSIONID.value } <br>
输出<Context-param>username 的值:${ initParam.username } <br>
输出<Context-param>url 的值:${ initParam.url } <br>
</body>
JSTL标签库
一、什么是 JSTL标签库,JSTL标签库的作用?
2.JSTL标签库的作用:EL 表达式主要是为了替换 jsp 中的表达式脚本,而标签库则是为了替换代码脚本。这样使得整个 jsp 页面 变得更佳简洁。
3.JSTL 由五个不同功能的标签库组成。

二.JSTL 标签库的使用步骤
1.JSTL 标签库的使用步骤:
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>三.core 核心库使用
1.<c:set />、<c:if />、<c:choose> <c:when> <c:otherwise>的使用
示例代码:
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%--
i.<c:set /> 作用:set 标签可以往域中保存数据域对象.setAttribute(key,value);
scope 属性设置保存到哪个域 :
page 表示 PageContext域(默认值)
request 表示 Request域
session 表示 Session域
application 表示 ServletContext域 var 属性设置 key 是多少 value 属性设置值
--%>
保存之前:${ sessionScope.abc } <br>
<c:set scope="session" var="abc" value="abcValue"/>
保存之后:${ sessionScope.abc } <br>
<%--
ii.<c:if /> if 标签用来做 if 判断。
test 属性表示判断的条件(使用 EL 表达式输出)
没有if else功能
--%>
<c:if test="${ 12 == 12 }">
<h1>12 等于 12</h1>
</c:if>
<%--
iii.<c:choose> <c:when> <c:otherwise>标签
作用:多路判断。跟 switch ... case .... default 非常接近
choose 标签开始选择判断
when 标签表示每一种判断情况
test 属性表示当前这种判断情况的值
otherwise 标签表示剩下的情况
<c:choose> <c:when> <c:otherwise>
标签使用时需要注意的点:
1、标签里不能使用 html 注释,要使用 jsp 注释
2、when 标签的父标签一定要是 choose 标签
--%>
<% request.setAttribute("height", 159); %>
<c:choose>
<%-- 这是 html 注释 --%>
<c:when test="${ requestScope.height > 190 }">
<h2>小巨人</h2>
</c:when>
<c:when test="${ requestScope.height > 180 }">
<h2>很高</h2>
</c:when>
<c:when test="${ requestScope.height > 170 }">
<h2>还可以</h2>
</c:when>
<c:otherwise>
<c:choose>
<c:when test="${requestScope.height > 160}">
<h3>大于 160</h3>
</c:when>
<c:when test="${requestScope.height > 150}">
<h3>大于 150</h3></c:when>
<c:when test="${requestScope.height > 140}">
<h3>大于 140</h3>
</c:when>
<c:otherwise>其他小于 140 </c:otherwise>
</c:choose>
</c:otherwise>
</c:choose>
</body>
</html>
2.<c:forEach /> 的使用
<%@ page import="java.util.HashMap" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.Map" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: MateBook
Date: 2021/10/27
Time: 19:56
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%--
1.遍历 1 到 10,输出
begin 属性设置开始的索引
end 属性设置结束的索引
var 属性表示循环的变量(也是当前正在遍历到的数据)
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
--%>
<table border="1">
<c:forEach begin="1" end="10" var="i">
<tr>
<td>第${i}行</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
<br>
<br>
<%--
2.1遍历 Object 数组
for (Object item: arr)
items表示遍历的数据源(遍历的集合)
var 表示当前遍历到的数据
--%>
<% request.setAttribute("arr", new String[]{"18610541354", "18688886666", "18699998888"}); %>
<c:forEach items="${ requestScope.arr }" var="item">
${ item }
</c:forEach>
<%--
2.2遍历Map集合
for (Object item: arr)
items表示遍历的数据源(遍历的集合)
var 表示当前遍历到的数据
--%>
<% Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("key1", "value1");
map.put("key2", "value2");
map.put("key3", "value3");
request.setAttribute("map", map); %>
<c:forEach items="${ requestScope.map }" var="entry">
<h1>${entry.key} = ${entry.value}</h1>
</c:forEach>
</body>
</html>








 本文深入解析了EL表达式的基础知识及应用技巧,包括其搜索域数据的顺序、运算规则以及11个隐含对象的使用方法,并详细介绍了JSTL标签库的使用步骤和核心标签的功能。
本文深入解析了EL表达式的基础知识及应用技巧,包括其搜索域数据的顺序、运算规则以及11个隐含对象的使用方法,并详细介绍了JSTL标签库的使用步骤和核心标签的功能。
















 841
841

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








