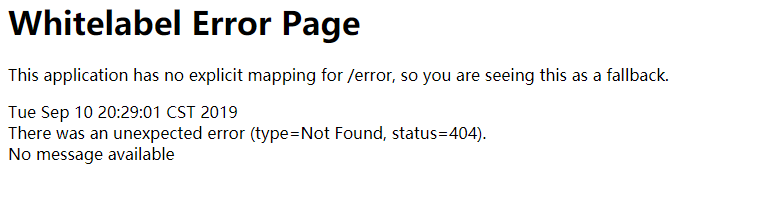
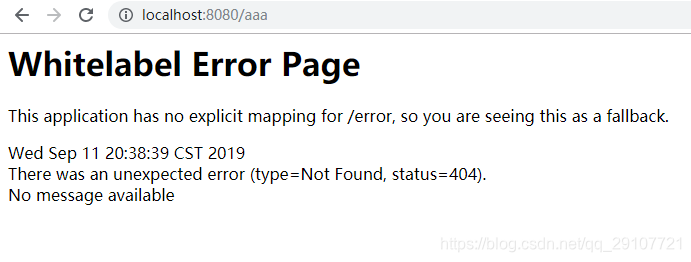
浏览器默认返回的错误页面
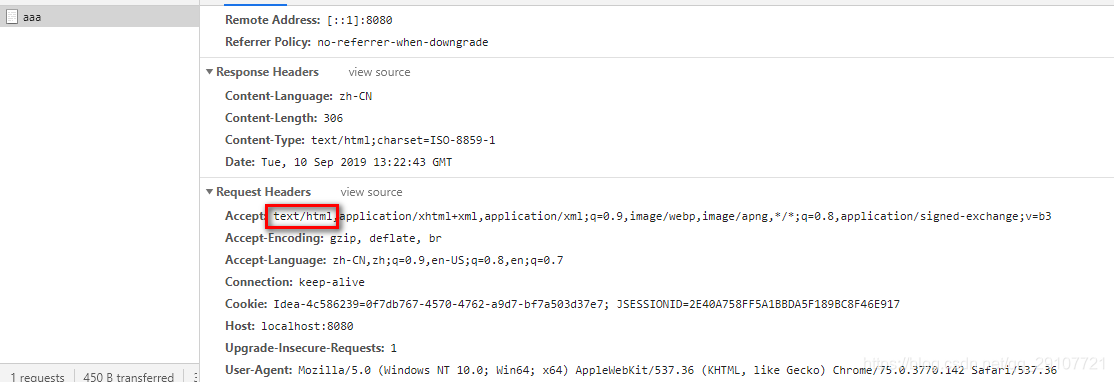
浏览器发送请求的请求头:
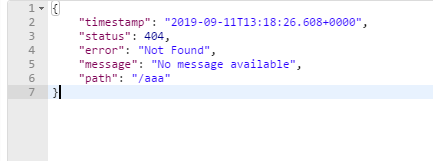
其他客户端会返回json字符串
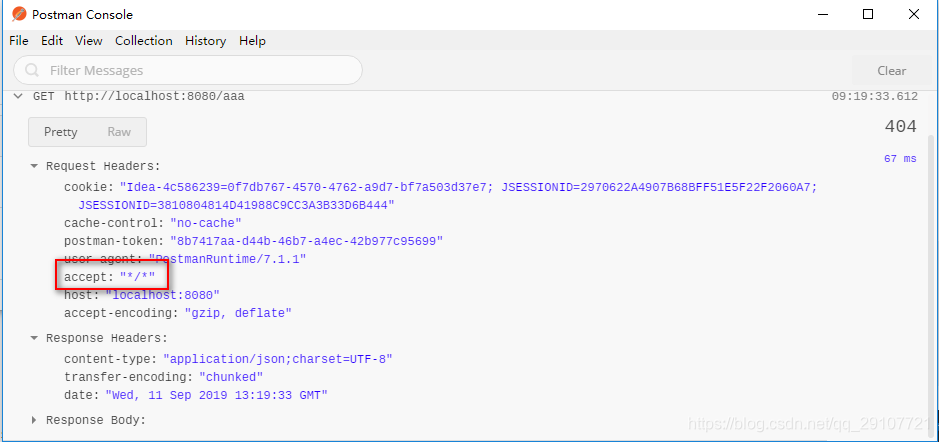
其他客户端请求的请求头中的Accept:"*/*",没有优先接收HTML数据。这就是区别
Spring Boot 默认的错误处理的自动配置在ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration类中
步骤:
- 出现了4xx或者5xx的错误,
ErrorPageCustomizer就会生效(定制错误的响应规则)- 来到/error请求,被BasicErrorController处理
- 响应页面
protected ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HttpStatus status,
Map<String, Object> model) {
for (ErrorViewResolver resolver : this.errorViewResolvers) {// ErrorViewResolver 异常视图解析求
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolver.resolveErrorView(request, status, model);
if (modelAndView != null) {
return modelAndView;
}
}
return null;
}
- 由
DefaultErrorAttributes解析
- DefaultErrorAttributes
a. 在页面共享信息
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) {
Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = new LinkedHashMap();
errorAttributes.put("timestamp", new Date());
this.addStatus(errorAttributes, webRequest);
this.addErrorDetails(errorAttributes, webRequest, includeStackTrace);
this.addPath(errorAttributes, webRequest);
return errorAttributes;
}
b.
2. BasicErrorController
处理默认的/error请求
@Controller
@RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}")
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
...
// public static final String TEXT_HTML_VALUE = "text/html"; // 产生HTML类型的数据
@RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { // 浏览器发送的请求处理方法
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request); // 获取错误的状态码
Map<String, Object> model = Collections
.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
// 获取错误页面的视图解析器;包含页面地址和页面内容
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
@RequestMapping
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) { // 产生json数据,其他客户端发送的请求处理方法
Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.ALL));
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
return new ResponseEntity<>(body, status);
}
- ErrorPageCustomizer
系统出现错误以后,来到/error请求进行处理(相当于在web.xml中配置了异常页面的映射)
@Value("${error.path:/error}")
private String path = "/error";
- DefaultErrorViewResolver
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolve(String.valueOf(status.value()), model);
if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) {
modelAndView = resolve(SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model);
}
return modelAndView;
}
private ModelAndView resolve(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
// SpringBoot 默认可以找到一个error/4xx(或5xx)页面
String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName;
// 如果模板引擎可以解析就是要引擎解析
TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this.templateAvailabilityProviders.getProvider(errorViewName,
this.applicationContext);
if (provider != null) {
// 模板引擎可用的情况下返回到errorViewName指定的视图地址error/4xx(或5xx).html
return new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model);
}
// 如果模板引擎不可用,在静态资源文件夹下找errorViewName指定的视图地址
return resolveResource(errorViewName, model);
}
定制错误响应
定制错误页面
1. 有模板引擎
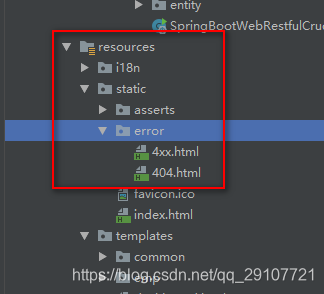
- 在error目录下创建状态码对应的页面
将错误页面命名 错误状态码.html,放在模板引擎文件夹下的error目录下,发生此状态码的错误,自动匹配当前错误页面
如:templates/error/404.html
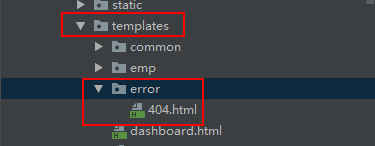

- 以4或者5开始的错误太多,每个状态码都对应一个页面,造成重复工作:可以使用4xx.html和5xx.html来匹配4xx或5xx错误。
如果有精确的状态码页面(如404.html),优先使用404.html
public class DefaultErrorViewResolver implements ErrorViewResolver, Ordered {
private static final Map<Series, String> SERIES_VIEWS;
static {
Map<Series, String> views = new EnumMap<>(Series.class);
views.put(Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "4xx");
views.put(Series.SERVER_ERROR, "5xx");
SERIES_VIEWS = Collections.unmodifiableMap(views);
}
...
}
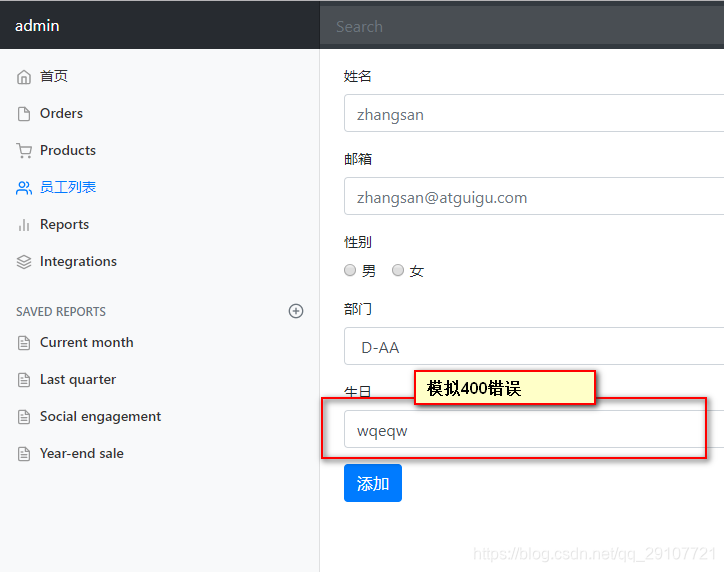
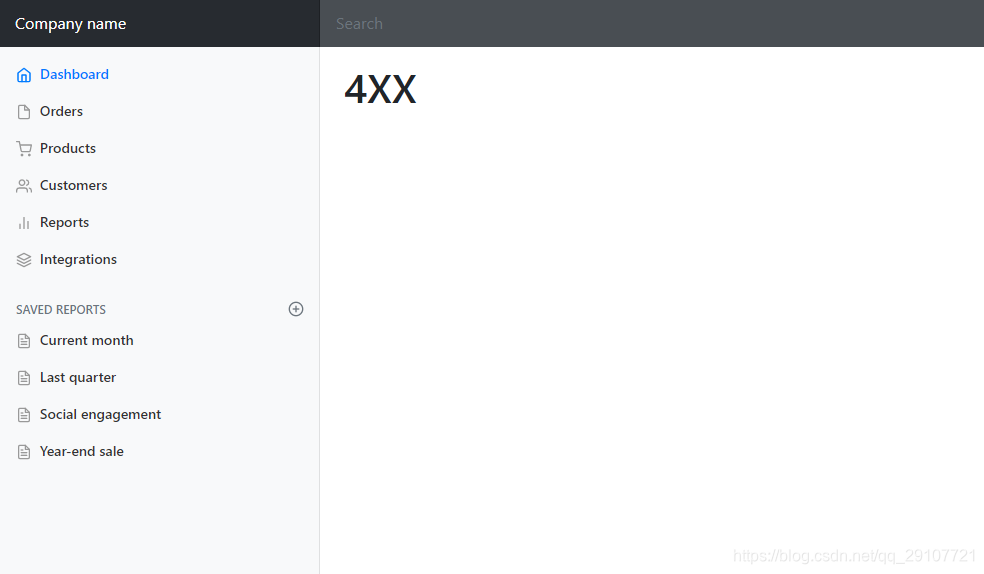
页面能获取的信息:
| key | 解释 |
|---|---|
| timestamp | 时间戳 |
| status | 状态码 |
| error | 错误提示 |
| exception | 异常对象 |
| message | 异常消息 |
| errors | JSR3030数据校验信息 |
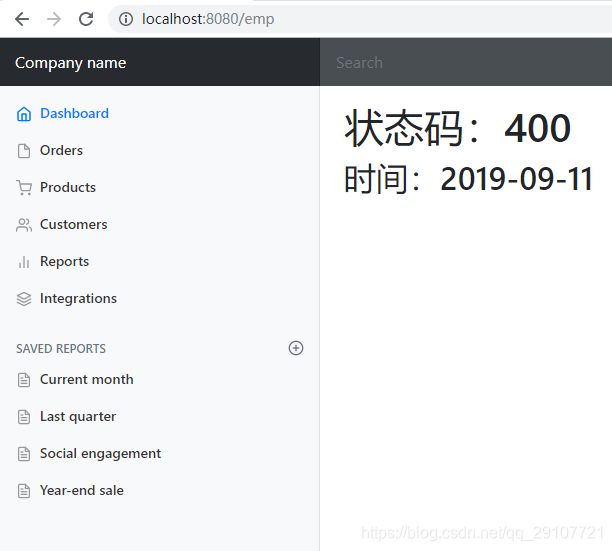
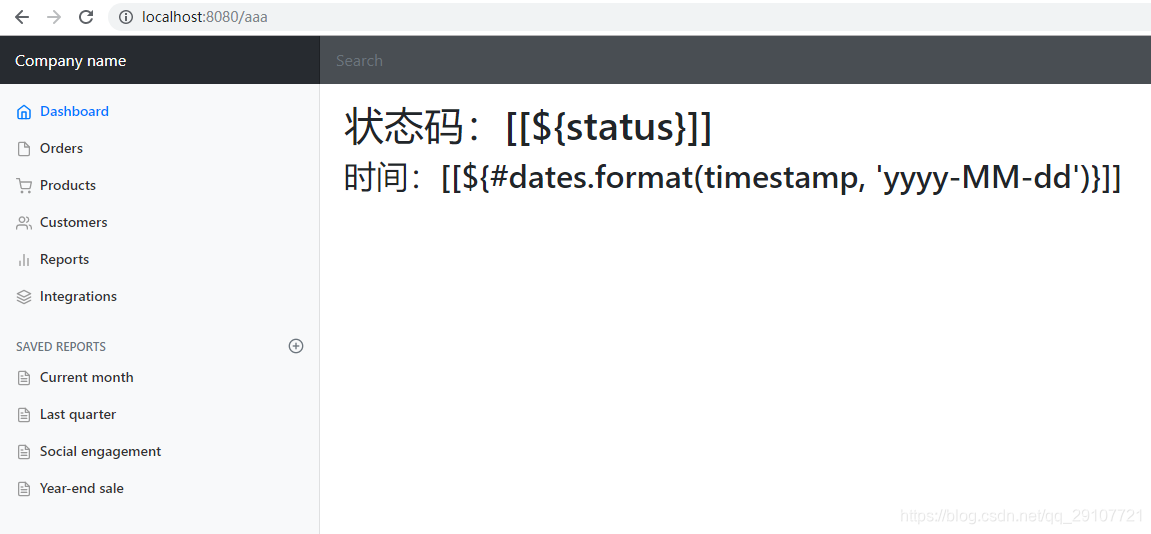
<h1>状态码:[[${status}]]</h1>
<h2>时间:[[${#dates.format(timestamp, 'yyyy-MM-dd')}]]</h2>
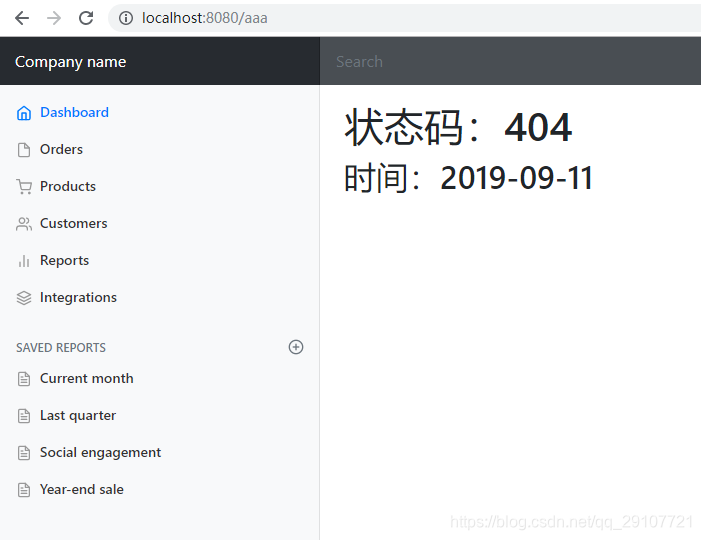
2. 没有模板引擎
模板引擎找不到当前错误页面,默认在静态资源文件夹下找,但是获取不到状态码等信息
如果模板引擎和静态资源文件夹都没有,就使用默认的页面
定制错误的json数据
- 没有自适应
自定义一个异常作测试
public class UserNotExistException extends RuntimeException{
public UserNotExistException() {
super("用户不存在!");
}
}
在访问hello请求的时候做测试
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@ResponseBody
public String hello(@RequestParam("username") String username) {
if ("aaa".equals(username)) {
throw new UserNotExistException();
}
return "hello World!!";
}
编写异常处理器
@ControllerAdvice // 异常处理器
public class MyExceptionHandler {
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class) // 要处理的异常(所有异常就是Exception.class)
public Map<String, Object> handlerException(Exception e) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("code", "user.notExist");
map.put("massage", e.getMessage());
return map;
}
}
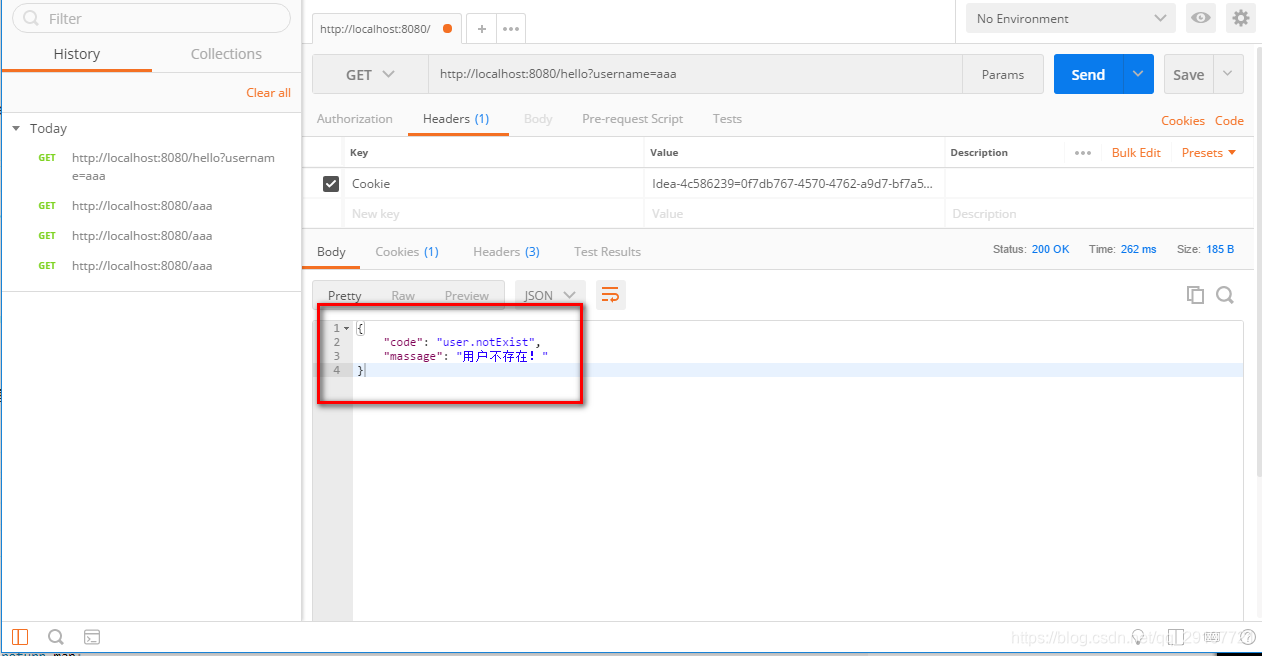
现在的Json字符串就是自己定制的。但是这样做的话页面也是出现了定制的json数据
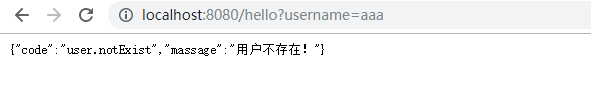
没有达到自适应的结果
- 自适应但是没有跳转到自己定制的错误页面
修改异常处理
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class) // 要处理的异常(所有异常就是Exception.class)
public String handlerException(Exception e) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("code", "user.notExist");
map.put("massage", e.getMessage());
// 转发到/error进行自适应响应效果处理
return "forward:/error";
}
浏览器
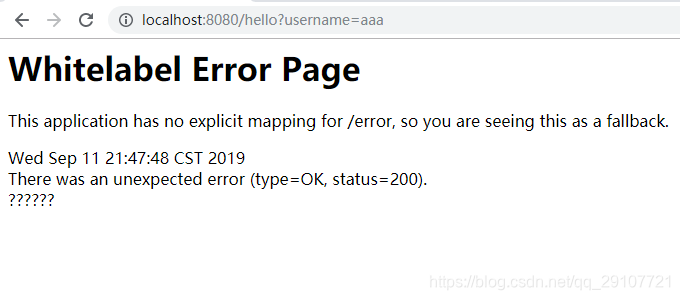
其他客户端
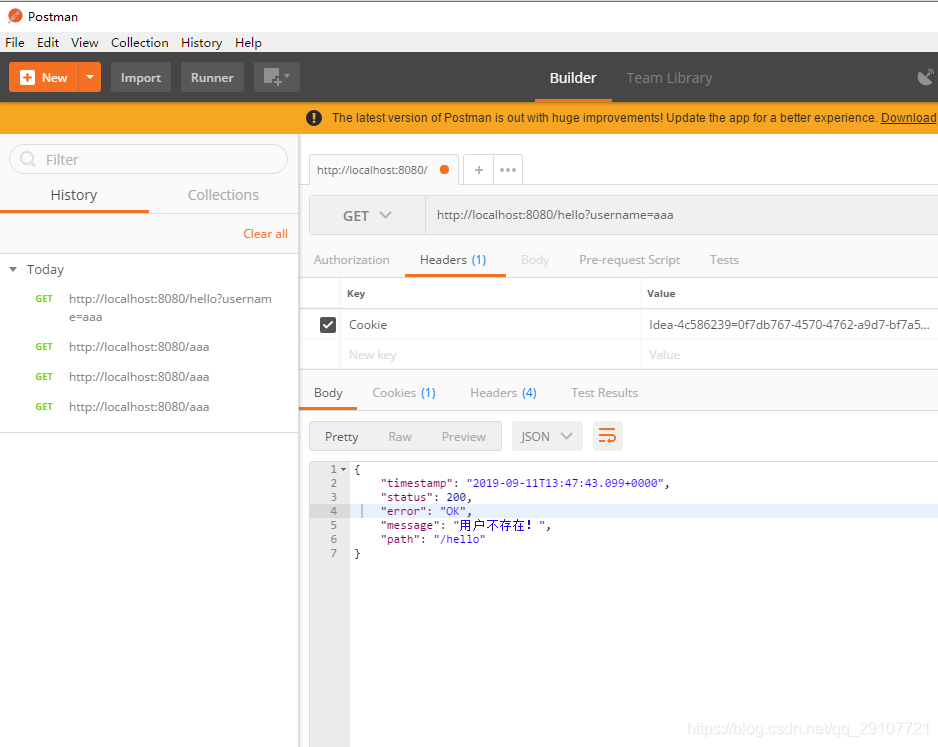
3. 自适应效果
继续修改异常处理器
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class) // 要处理的异常(所有异常就是Exception.class)
public String handlerException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// 设置错误状态码,4xx或5xx;如果不设置错误状态码,就不会跳转到自己定制的错误页面
// Integer statusCode = (Integer) request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code");
request.setAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code", 500);
map.put("code", "user.notExist");
map.put("massage", e.getMessage());
// 转发到/error进行自适应响应效果处理
return "forward:/error";
}
浏览器
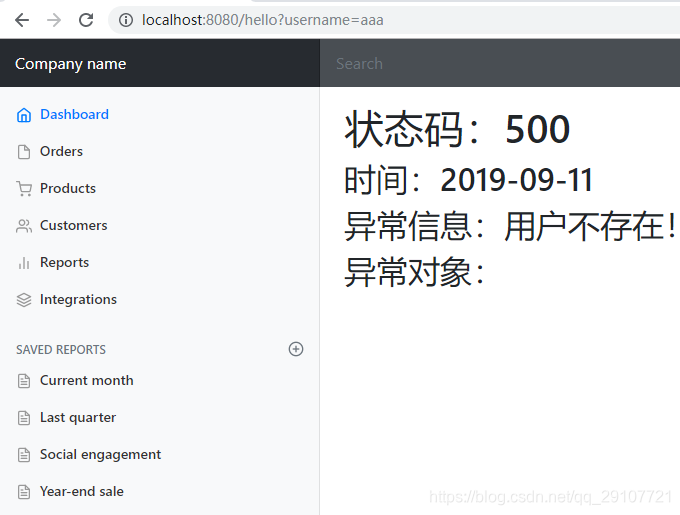
其他客户端
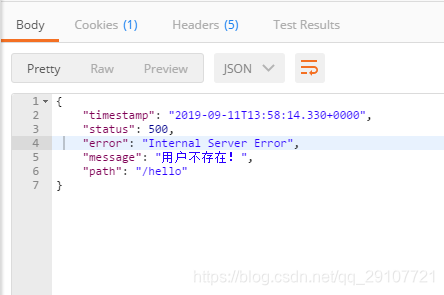
4. 将定制的json数据返回
出现错误后,会发送/error请求,被BaseErrorController处理,响应的数据是由getErrorAttributes方法得到,是AbstractErrorController规定的方法,而AbstractErrorController是一个ErrorController。当自定义得有ErrorController的时候,系统就不会使用默认的BaseErrorController。
a. 可以编写ErrorController的实现类(或者AbstractErrorController的子类),放在容器中:
b. 不管是返回的页面还是Json都是使用getErrorAttributes获取的,而getErrorAttributes是通过ErrorAttributes调用的。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorAttributes.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) // 容器中没有ErrorAttributes就添加一个默认的ErrorAttributes
public DefaultErrorAttributes errorAttributes() {
return new DefaultErrorAttributes(this.serverProperties.getError().isIncludeException());
}
定制自己的ErrorAttributes
@Component // 给容器中加入自己的错误属性
// 为了简单,继承DefaultErrorAttributes
public class MyErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes {
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) {
Map<String, Object> map = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest, includeStackTrace);
map.put("company", "caesar");
return map;
}
}
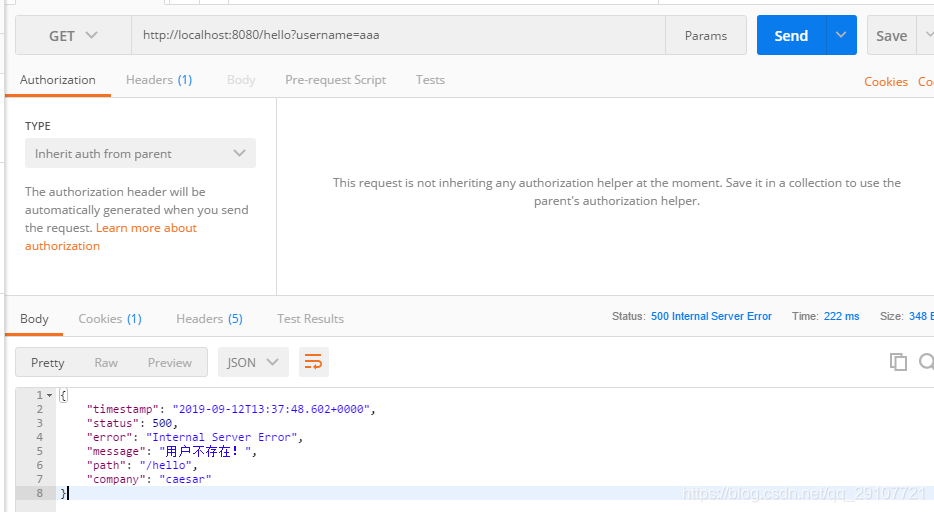
c. 添加上异常处理器中携带的数据
异常处理器
@ControllerAdvice // 异常处理器
public class MyExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class) // 要处理的异常(所有异常就是Exception.class)
public String handlerException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// 传入错误状态码,4xx或5xx
// Integer statusCode = (Integer) request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code");
request.setAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code", 500);
map.put("code", "user.notExist");
map.put("massage", "用户错误!!!!");
// 将自定的数据添加到request域中
request.setAttribute("ext", map);
// 转发到/error进行自适应响应效果处理
return "forward:/error";
}
}
自定义的错误属性
@Component // 给容器中加入自己的错误属性
// 为了简单,继承DefaultErrorAttributes
public class MyErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes {
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) {
// 最后返回给页面或Json中的值
Map<String, Object> map = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest, includeStackTrace);
map.put("company", "caesar");
// 异常处理器携带的值
Map<String, Object> ext = (Map<String, Object>) webRequest.getAttribute("ext", 0);
map.put("ext", ext);
return map;
}
}
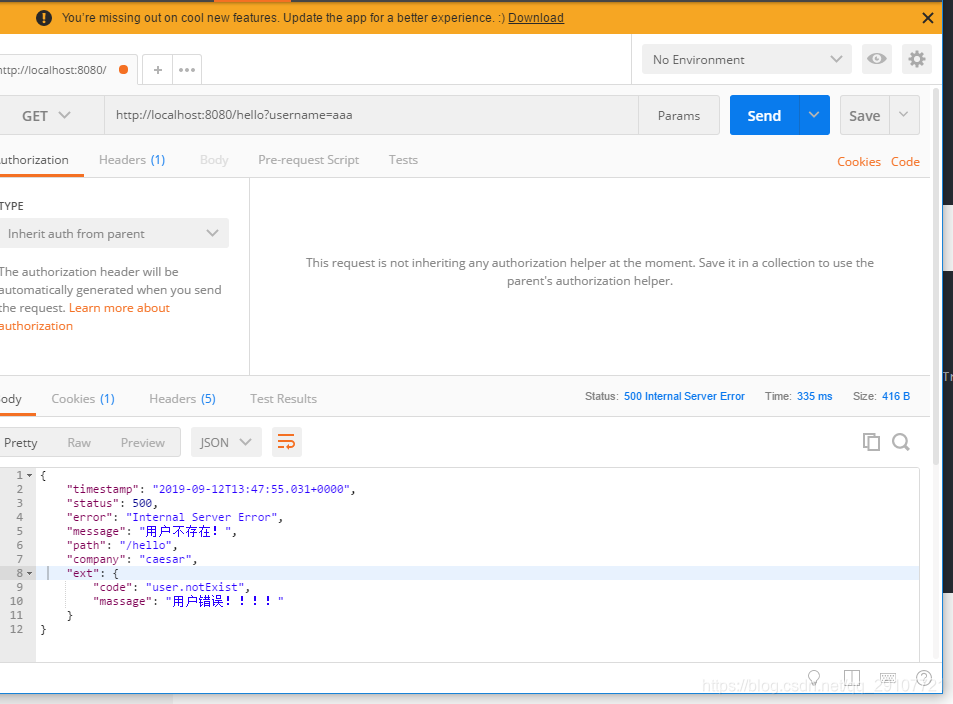
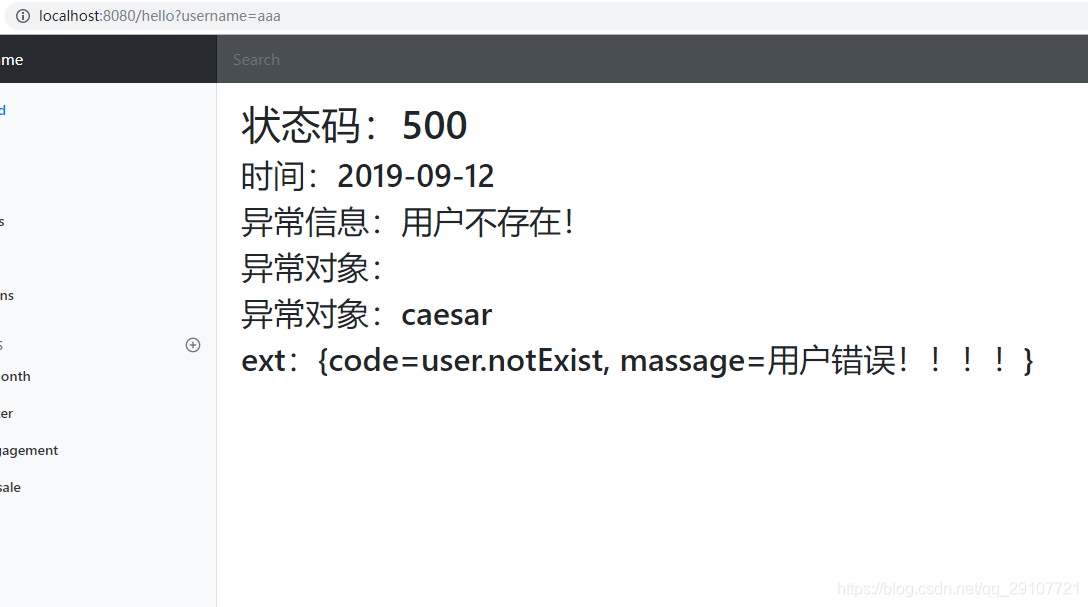
异常对象为空,是应为在生成数据的时候有一个判断,如果是默认的空参构造创建的DefaultErrorAttributes对象,includeException 是false,false返回的error
private final boolean includeException;
public DefaultErrorAttributes() {
this(false);
}
public DefaultErrorAttributes(boolean includeException) {
this.includeException = includeException;
}
...
private void addErrorDetails(Map<String, Object> errorAttributes, WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) {
Throwable error = this.getError(webRequest);
if (error != null) {
while(true) {
if (!(error instanceof ServletException) || error.getCause() == null) {
if (this.includeException) {
errorAttributes.put("exception", error.getClass().getName());
}
this.addErrorMessage(errorAttributes, error);
if (includeStackTrace) {
this.addStackTrace(errorAttributes, error);
}
break;
}
error = ((ServletException)error).getCause();
}
}
Object message = this.getAttribute(webRequest, "javax.servlet.error.message");
if ((!StringUtils.isEmpty(message) || errorAttributes.get("message") == null) && !(error instanceof BindingResult)) {
errorAttributes.put("message", StringUtils.isEmpty(message) ? "No message available" : message);
}
}
...
}
文笔简陋,理解不透彻。自己做的笔记,有不正确的地方希望指出!!





 本文详细解析了SpringBoot中错误处理的流程,包括错误页面的定制、错误JSON数据的自适应响应以及如何通过自定义ErrorController和ErrorAttributes来增强错误处理能力。
本文详细解析了SpringBoot中错误处理的流程,包括错误页面的定制、错误JSON数据的自适应响应以及如何通过自定义ErrorController和ErrorAttributes来增强错误处理能力。
















 720
720

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








