6.1 存储技术
price VS performance 所以 有了 内存的等级,越近的越快但是 贵,存储空间少, 所以只是 远处储存数据的一个 压缩映射,也就是下一级存储的cache
6.2 Locality
分为了 temporal locality(多次引用同一个资源) 和 spatial locality(引用附近的数据)
这样可以高效使用高层的cache
6.3 内存的层级
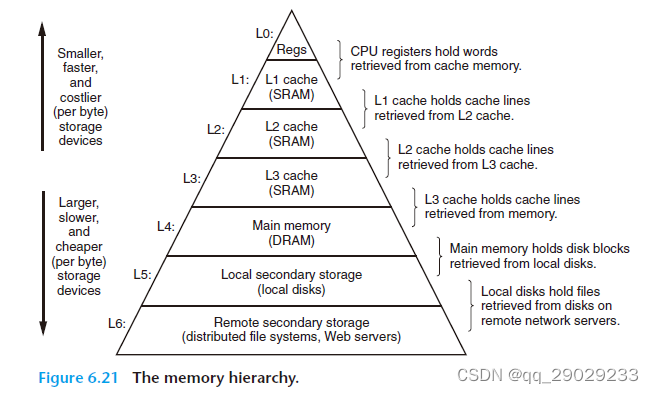
因为读取数据的周期远超cpu计算周期,所以数据如果在硬盘上,会发信号让硬盘和main memory 自己操作,搬运好了,在提示cpu进行之前的运算
6.4 cache memory
6.4.1(direct-mapped cache)

tag意味着cache压缩下一层级memory的倍数,也意味着是压缩映射;
set 类似地址的hash set
address是 t X s X b 确定的,但是cache只有 s 和 b,必须t 也满足一样,才说明cache有现在需要的数据(以及对应地址),如果 cache miss (valid = 0),就从下一级调过来数据,把line写上。如果tag不对,也是调用上来,然后覆盖原始数据。如果tag也对(cache hit),就直接使用了.

set bits 放在中间 ↑ 是因为放在首位的话,会让连着的数据(block)都放在一个set,然后会导致,如果遍历一个array ,cache里面都只会装一块array数据,cache会利用不完全

由于映射是压缩的,如果你的数据 正好都映射到一个line上,那么你就失去了 locality了。(confilct miss)
例如

这个function的X[],Y[]就会相互占用cache
解决方案,可以是在x[8] 之后加4个byte,直接定义X[12],那x【i】和y[i] 就错开了
6.4.3 set associative cache

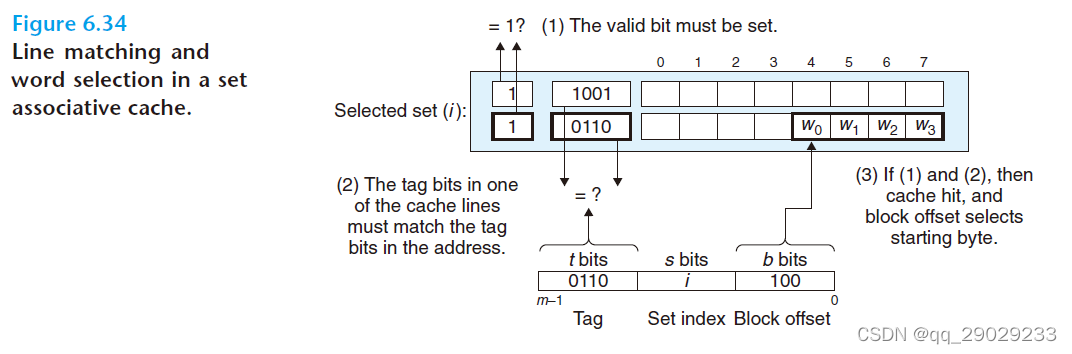 选择了多个条数,但是在C一定(cache容量)的情况下,set变少了,但是可以存放多条tag
选择了多个条数,但是在C一定(cache容量)的情况下,set变少了,但是可以存放多条tag
6.4.4 fully associative caches
E = C/ B 只有一个set,问题是要遍历来寻找是否在cache中(因为没有set bit 来缩小范围了)

6.4.5 issues with write
1. cache hit 怎么write
1)write through cache改了,下一层也改
2)write back 先改cache,如果替换cache line时发现这条改了,在把对应的下一层位置也改了
√目前用这个多 越远的用这个越多,因为改下一层太慢了,必要时才改。
2.cache miss 怎么write
1)write-allocate 先把对应的地址加载到cache 然后再write back √目前用这个多
2)no-write-allocate 直接跳过cache 改 下一层
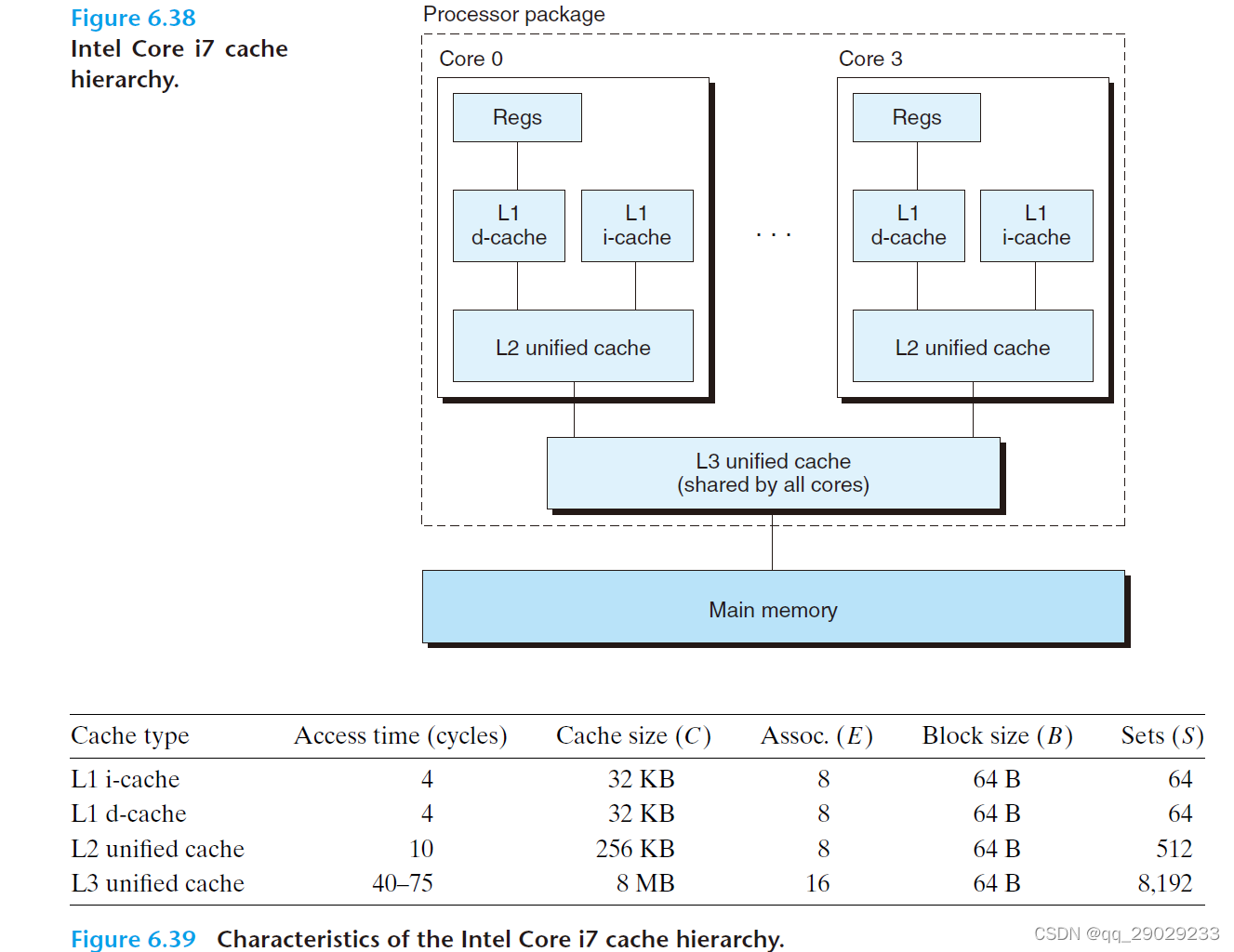
6.4.6 Anatomy of a Real Cache Hierarchy
i-cache 储存 instruction
d-cache 存储 data
unified cache 两个都存
现在的cpu 一般是i-cache(只读) 和d-cache分开,这样让cpu同时读
6.5 Writing Cache-Friendly Code
1.优化core function
2.减少 inner loop的 miss rate
- Repeated references to local variables are good because the compiler can cache them in the register file (temporal locality).
- Stride-1 reference patterns are good because caches at all levels of the memory hierarchy store data as contiguous blocks (spatial locality)
6.6.3 Exploiting Locality in Your Programs
- Focus your attention on the inner loops, where the bulk of the computations and memory accesses occur.
- Try to maximize the spatial locality in your programs by reading data objects sequentially, with stride 1, in the order they are stored in memory.
- Try to maximize the temporal locality in your programs by using a data object as often as possible once it has been read from memory.








 本文探讨了计算机存储技术的内存层次结构,包括L1、L2、L3缓存,强调了时空局部性原则对提高缓存效率的重要性。介绍了直接映射、组关联和全关联缓存的工作原理,并讨论了缓存命中与未命中时的写操作策略。此外,还提出了编写缓存友好的代码实践,以最大化程序的时空局部性,从而提升性能。
本文探讨了计算机存储技术的内存层次结构,包括L1、L2、L3缓存,强调了时空局部性原则对提高缓存效率的重要性。介绍了直接映射、组关联和全关联缓存的工作原理,并讨论了缓存命中与未命中时的写操作策略。此外,还提出了编写缓存友好的代码实践,以最大化程序的时空局部性,从而提升性能。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








