1、分布式锁实例(网上找的)
先声明自己瞎看的。有错误或者啥的欢迎指出。
先看下这个zk分布锁例子
public static void main(String[] args) {
CuratorFramework curatorFramework = CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder().connectString("127.0.0.1:2181")
.sessionTimeoutMs(30000).retryPolicy(new ExponentialBackoffRetry(4000,3))
.build();
curatorFramework.start();
//InterProcessMutex这个锁为公平锁可重入锁
final InterProcessMutex interProcessMutex = new InterProcessMutex(curatorFramework,"/locks");
ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
fixedThreadPool.submit(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
boolean flag = false;
try {
//
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
//尝试获取锁,最多等待10秒
flag = interProcessMutex.acquire(20, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if(flag){
System.out.println("线程"+currentThread.getId()+"获取锁成功");
}else{
System.out.println("线程"+currentThread.getId()+"获取锁失败");
}
//模拟业务逻辑,延时4秒
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
if(flag){
try {
//释放锁
interProcessMutex.release();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
});
}
}
2、相关类的成员变量
InterProcessMutex 成员变量
| 类型 | 名称 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| LockInternals | internals | 锁内部构件类 |
| String | basePath | 锁节点的根路径 |
| ConcurrentMap<Thread, LockData> | threadData | 锁信息映射表 |
| String | LOCK_NAME | 常量:lock- |
| LockData | lockData | 静态内部类 锁信息 |
2.1、LockData 成员变量
| 类型 | 名称 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| Thread | owningThread | 等待线程 |
| String | lockPath | 该线程对应的锁节点 |
| AtomicInteger | lockCount | 获取锁的次数 |
2.2、 LockInternals 成员变量
| 类型 | 名称 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| WatcherRemoveCuratorFramework | client | 客户端 |
| String | path | basePath+lockName |
| String | basePath | 锁节点根路径 |
| LockInternalsDriver | driver | 驱动 |
| String | lockName | 锁的名字 |
| AtomicReference < RevocationSpec> | revocable | 撤销事件 里面存了撤销时线程和线程池 |
| CuratorWatcher | revocableWatcher | 撤销监听器 |
| volatile int | maxLeases | 同时最多几个。例如读锁同时能有很多,写锁同时只能有一个 |
| Watcher | watcher | 监听。动作是notifyall() |
| static final byte[] | REVOKE_MESSAGE | 字符串为 —REVOKE— 的byte数组 |
3、 InterProcessMutex构造方法
public InterProcessMutex(CuratorFramework client, String path)
client :客户端
path :锁路径
几个构造方法最终都会走到下面这个构造方法
InterProcessMutex(CuratorFramework client, String path, String lockName, int maxLeases, LockInternalsDriver driver){
//验证锁路径是否合规
basePath = PathUtils.validatePath(path);
//这里maxLeases为1. driver为StandardLockInternalsDriver
internals = new LockInternals(client, driver, path, lockName, maxLeases);
}
4、 获取锁的流程图
图片从别人那里拐的。自己画的话,不太行
图片来自
添加链接描述
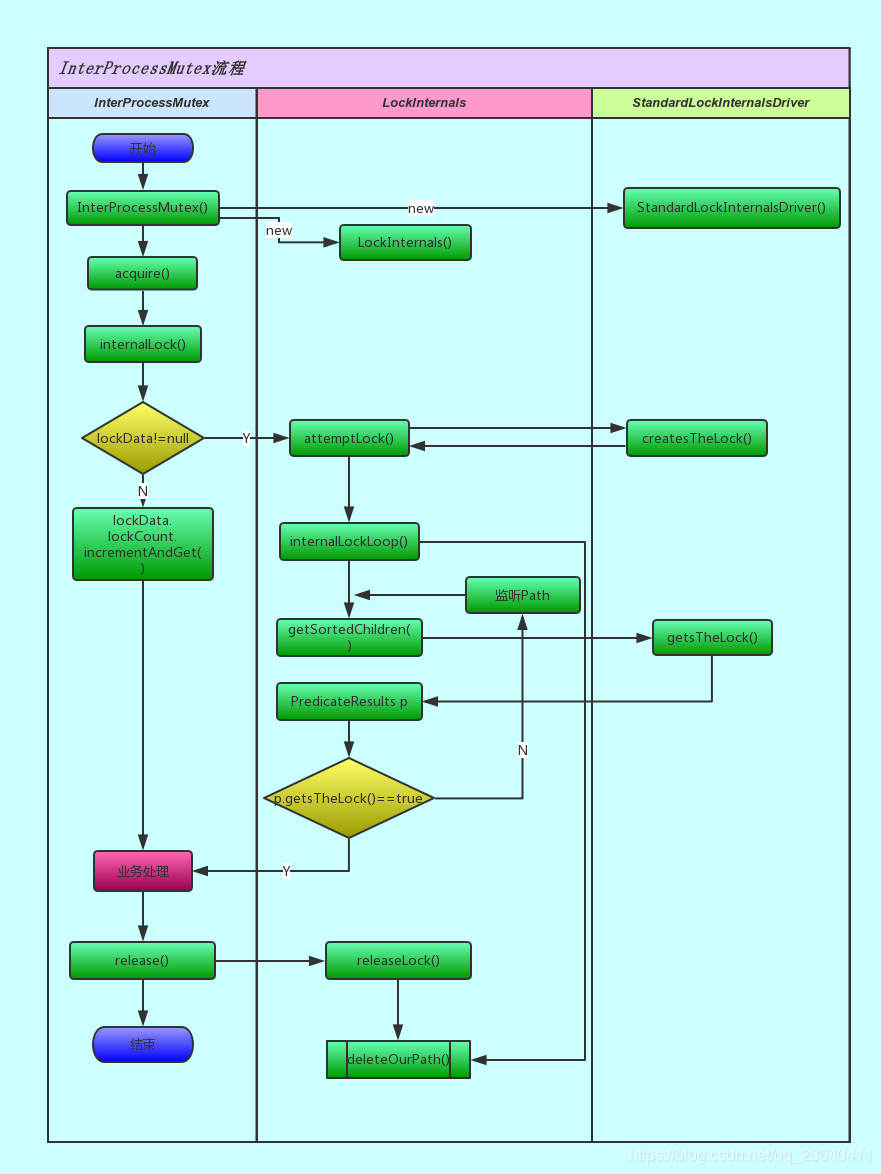
接下来主要是分析这一行代码
flag = interProcessMutex.acquire(20, TimeUnit.SECONDS); //获取锁
5、 acquire(long time, TimeUnit unit)
@Override
public boolean acquire(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception
{
return internalLock(time, unit);
}
private boolean internalLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception{
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
//当前线程作为键去获取对应的锁信息对象
LockData lockData = threadData.get(currentThread);
//获得过锁的话
if ( lockData != null ){
// 锁信息对象中锁次数加1 (可重入锁)
lockData.lockCount.incrementAndGet();
return true;
}
//尝试获取锁 getLockNodeBytes在该类中返回null,子类有其他实现。
String lockPath = internals.attemptLock(time, unit, getLockNodeBytes());
//获取到锁的话
if ( lockPath != null ){
//锁信息对象中放入 线程:锁路径
LockData newLockData = new LockData(currentThread, lockPath);
//放入 线程:锁信息对象
threadData.put(currentThread, newLockData);
return true;
}
return false;
}
5.1、 internals.attemptLock(time, unit, getLockNodeBytes());
String attemptLock(long time, TimeUnit unit, byte[] lockNodeBytes) throws Exception
{
//开始时间。用于internalLockLoop(startMillis, millisToWait, ourPath); 这里去计算时间
final long startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
//等待时间
final Long millisToWait = (unit != null) ? unit.toMillis(time) : null;
//如果撤销事件不为空,设置为new byte[0]
final byte[] localLockNodeBytes = (revocable.get() != null) ? new byte[0] : lockNodeBytes;
//重试次数
int retryCount = 0;
String ourPath = null;
boolean hasTheLock = false;
boolean isDone = false;
while ( !isDone )
{
isDone = true;
try
{
//递归创建path路径的临时有序节点,带初始内容,但此时为初始为null
ourPath = driver.createsTheLock(client, path, localLockNodeBytes);
//time时间内去获取锁
hasTheLock = internalLockLoop(startMillis, millisToWait, ourPath);
}
catch ( KeeperException.NoNodeException e )
{
//当StandardLockInternalsDriver找不到锁节点时引发
//这可能发生在会话到期等情况下。因此,如果重试允许,请再试一次
if ( client.getZookeeperClient().getRetryPolicy().allowRetry(retryCount++, System.currentTimeMillis() - startMillis, RetryLoop.getDefaultRetrySleeper()) )
{
isDone = false;
}
else
{
throw e;
}
}
}
//获取到锁返回锁的节点路径,没有返回空
if ( hasTheLock )
{
return ourPath;
}
return null;
}
5.1.1、 driver.createsTheLock(client, path, localLockNodeBytes);
@Override
public String createsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, String path, byte[] lockNodeBytes) throws Exception
{
String ourPath;
if ( lockNodeBytes != null )
{
//递归创建临时有序锁节点,并且设置值
ourPath = client.create().creatingParentContainersIfNeeded().withProtection().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL).forPath(path, lockNodeBytes);
}
else
{
//递归创建临时有序锁节点
ourPath = client.create().creatingParentContainersIfNeeded().withProtection().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL).forPath(path);
}
//返回锁节点路径
return ourPath;
}
5.1.2、 internalLockLoop(startMillis, millisToWait, ourPath);
private boolean internalLockLoop(long startMillis, Long millisToWait, String ourPath) throws Exception{
boolean haveTheLock = false;
boolean doDelete = false;
try
{
//有撤销请求
if ( revocable.get() != null )
{
// 锁节点内容监听 revocableWatcher监听。
// revocableWatcher:当变动节点的内容为 __REVOKE__ 就执行 revocable中的定义线程
client.getData().usingWatcher(revocableWatcher).forPath(ourPath);
}
//客户端为started状态,并且没有获得锁
while ( (client.getState() == CuratorFrameworkState.STARTED) && !haveTheLock )
{
//获取LockInternals类中basePath路径下的所有子节点路径,并且按照截取lock-后面的数字排序
List<String> children = getSortedChildren();
//获取创建的节点名称
String sequenceNodeName = ourPath.substring(basePath.length() + 1); // +1 to include the slash
//去获取锁
PredicateResults predicateResults = driver.getsTheLock(client, children, sequenceNodeName, maxLeases);
//获取到锁了设置为true
if ( predicateResults.getsTheLock() )
{
haveTheLock = true;
}
else
{
//上一个获取到锁的节点路径
String previousSequencePath = basePath + "/" + predicateResults.getPathToWatch();
synchronized(this)
{
try
{
// 监听上个锁节点。usingWatcher(watcher) 中是notifyall 如果上个锁有变动,并且没超时。监听器就唤醒自己开始获取锁
client.getData().usingWatcher(watcher).forPath(previousSequencePath);
//设置的等待时间为空或者等待时间还没耗尽就一直wait
if ( millisToWait != null )
{
millisToWait -= (System.currentTimeMillis() - startMillis);
startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
if ( millisToWait <= 0 )
{
doDelete = true; // timed out - delete our node
break;
}
wait(millisToWait);
}
else
{
wait();
}
}
catch ( KeeperException.NoNodeException e )
{
// it has been deleted (i.e. lock released). Try to acquire again
}
}
}
}
}
catch ( Exception e )
{
ThreadUtils.checkInterrupted(e);
doDelete = true;
throw e;
}
finally
{
//删除ourpath节点
if ( doDelete )
{
deleteOurPath(ourPath);
}
}
return haveTheLock;
}
5.1.2.1 predicateResults = driver.getsTheLock(client, children, sequenceNodeName, maxLeases);
@Override
public PredicateResults getsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, List<String> children, String sequenceNodeName, int maxLeases) throws Exception
{
//获取创建的锁节点在锁集合中的位置
int ourIndex = children.indexOf(sequenceNodeName);
//验证ourIndex是否为-1
validateOurIndex(sequenceNodeName, ourIndex);
//当前创建的锁节点位置<1 也就是第0个。则当前线程获取到锁 maxLeases这个是写死的1.
boolean getsTheLock = ourIndex < maxLeases;
//获取到锁的话。pathToWatch为空。没有则监听前一个锁节点。
String pathToWatch = getsTheLock ? null : children.get(ourIndex - maxLeases);
return new PredicateResults(pathToWatch, getsTheLock);
}
6 互斥锁撤销
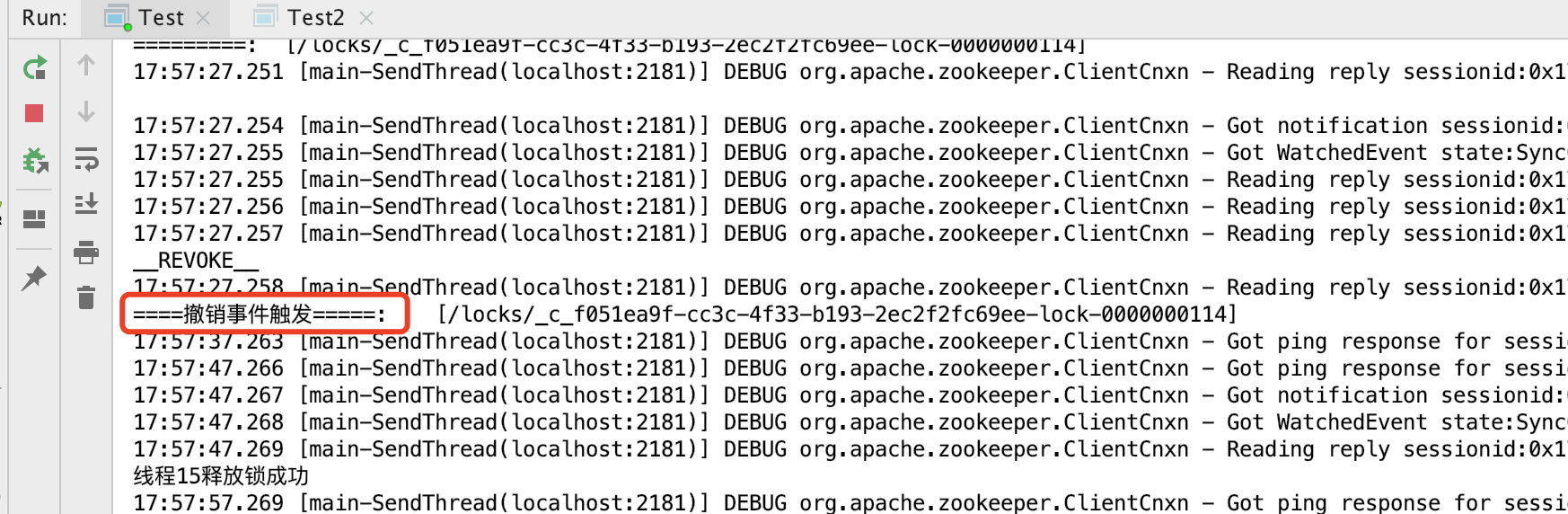
可以运行下这个例子
在有线程获取锁后,修改锁内容为LockInternals.REVOKE_MESSAGE,触发监听。
但是我自己现在还没想到哪些场景会有这个情况。
public static void main(String[] args) {
final CuratorFramework curatorFramework = CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder().connectString("127.0.0.1:2181")
.sessionTimeoutMs(30000).retryPolicy(new ExponentialBackoffRetry(4000,3))
.build();
curatorFramework.start();
//InterProcessMutex这个锁为公平锁可重入锁
final InterProcessMutex interProcessMutex = new InterProcessMutex(curatorFramework,"/locks");
interProcessMutex.makeRevocable(new RevocationListener<InterProcessMutex>() {
public void revocationRequested(InterProcessMutex forLock) {
//获取当前节点的名称
try {
Collection<String> nameList = forLock.getParticipantNodes();
System.out.println("====撤销事件触发=====:\t"+ Arrays.toString(nameList.toArray(new String[nameList.size()])));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
for (int i = 0; i < 1; i++) {
fixedThreadPool.submit(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
boolean flag = false;
try {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
//
//尝试获取锁,最多等待10秒
flag = interProcessMutex.acquire(20, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if(flag){
System.out.println("线程"+currentThread.getId()+"获取锁成功");
}else{
System.out.println("线程"+currentThread.getId()+"获取锁失败");
}
//输出锁根路径下锁有锁节点
Collection<String> nameList = interProcessMutex.getParticipantNodes();
ArrayList<String> ll = new ArrayList<String>(nameList);
System.out.println("=========:\t"+ Arrays.toString(nameList.toArray(new String[nameList.size()])));
byte[] data1 = curatorFramework.getData().forPath(ll.get(0));
System.out.println(new String(data1));
//改变第一个锁节点的值。触发撤销事件
//锁节点设值为 LockInternals.REVOKE_MESSAGE 这里不知道为啥报错所有直接写字符串了
curatorFramework.setData().forPath(ll.get(0), "__REVOKE__".getBytes("UTF-8"));
byte[] data2 = curatorFramework.getData().forPath(ll.get(0));
System.out.println(new String(data2));
//模拟业务逻辑,延时4秒
Thread.sleep(20000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
if(flag){
try {
//释放锁
interProcessMutex.release();
System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+"释放锁成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
});
}
}
执行效果结果为:





 本文详细介绍了使用Curator实现的Zookeeper分布式锁InterProcessMutex的内部工作原理,包括其成员变量、构造方法和获取锁的流程,特别是acquire(long time, TimeUnit unit)方法的详细步骤,探讨了lock的获取与撤销过程。"
1204926,129049,交易智慧:《Trading For A Living》读后感及交易策略解析,"['交易系统', '市场趋势', '技术分析', '投资策略', '风险管理']
本文详细介绍了使用Curator实现的Zookeeper分布式锁InterProcessMutex的内部工作原理,包括其成员变量、构造方法和获取锁的流程,特别是acquire(long time, TimeUnit unit)方法的详细步骤,探讨了lock的获取与撤销过程。"
1204926,129049,交易智慧:《Trading For A Living》读后感及交易策略解析,"['交易系统', '市场趋势', '技术分析', '投资策略', '风险管理']
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








