二叉树顺序储存
顺序完全二叉树
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
char * tree = new char[n + 1];
tree[0] = '0';
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> tree[i];
}
char value;
cin >> value;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (value - tree[i] == 0)
{
cout << tree[i / 2];
}
}
return 0;
}链式树
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class tNode
{
public:
T data;
tNode *pL, *pR;
};
const int MAXSIZE = 20000;
tNode<char> tree [MAXSIZE];
int N;
int main()
{
int L, R;
int id;
char a;
// 构建二叉树
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
cin >> id >> a >> L >> R;
tree[id].data = a;
if (!L)
{
tree[id].pL = NULL;
}
else
{
tree[id].pL = &tree[L];
}
if (!R)
{
tree[id].pR = NULL;
}
else
{
tree[id].pR = &tree[R];
}
}
tNode<char> *p = &tree[1]; // 搜索
while(p)
{
cout << p->data << " ";
p = p->pL;
}
return 0;
}
/*
测试
4
1 a 3 8
8 c 0 0
4 d 0 0
3 b 4 0
*/
二叉树前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class tNode
{
public:
T data;
tNode *pL, *pR;
};
// 前序遍历
template<class T>
void preOrder(tNode<T> * root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
cout << root->data << endl;
preOrder(root->pL);
preOrder(root->pR);
}
// 中序遍历
template<class T>
void midOrder(tNode<T> * root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
midOrder(root->pL);
cout << root->data << endl;
midOrder(root->pR);
}
// 后序遍历
template<class T>
void backOrder(tNode<T> * root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
backOrder(root->pL);
backOrder(root->pR);
cout << root->data << endl;
}
// 层序遍历
template<class T>
void levelOrder(tNode<T> *t)
{
queue<tNode<char> *> q;
q.push(t);
while(1)
{
if (q.empty())
break;
cout << q.front()->data << endl;
if (q.front()->pL != NULL)
q.push(q.front()->pL);
if (q.front()->pR != NULL)
q.push(q.front()->pR);
q.pop();
}
}
const int MAXSIZE = 20000;
tNode<char> tree [MAXSIZE];
int N;
int main()
{
int L, R;
int id;
char a;
// 构建二叉树
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
cin >> id >> a >> L >> R;
tree[id].data = a;
if (!L)
{
tree[id].pL = NULL;
}
else
{
tree[id].pL = &tree[L];
}
if (!R)
{
tree[id].pR = NULL;
}
else
{
tree[id].pR = &tree[R];
}
}
cout << "前序遍历" << endl;
preOrder(tree + 1);
cout << endl;
cout << "中序遍历" << endl;
midOrder(tree + 1);
cout << endl;
cout << "后序遍历" << endl;
backOrder(tree + 1);
cout << endl;
cout << "层序遍历" << endl;
levelOrder(tree + 1);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
/*
测试
6
1 A 2 3
2 B 0 5
3 C 4 0
4 D 0 0
5 E 6 0
6 F 0 0
*/
一般树的构建和前序后序及层序遍历
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int MAXSIZE = 20000;
const int dMAX = 5;
int N;
// 一般树的节点
template<class T>
class tNode
{
public:
T data;
tNode *sons[dMAX];
};
tNode<char> tree [MAXSIZE];
// 一般树的前序遍历
template<class T>
void preOrder(tNode<T> * root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
cout << root->data << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < dMAX; i++)
{
if (root->sons[i] != NULL)
{
preOrder(root->sons[i]);
}
}
}
// 一般树的后序遍历
template<class T>
void backOrder(tNode<T> * root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < dMAX; i++)
{
if (root->sons[i] != NULL)
{
backOrder(root->sons[i]);
}
}
cout << root->data << endl;
}
// 一般树的层序遍历
queue<tNode<char> *> q;
template<class T>
void levelOrder(tNode<T> * root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
q.push(root);
while(1)
{
cout << q.front()->data << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < dMAX; i++)
{
if (q.front()->sons[i] != NULL)
{
q.push(q.front()->sons[i]);
}
}
q.pop();
}
}
int main()
{
int s[dMAX];
int id;
char a;
// 构建一般树
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
cin >> id >> a;
for (int j = 0; j < dMAX; j++)
{
cin >> s[j];
}
tree[id].data = a;
for (int j = 0; j < dMAX; j++)
{
if (s[j] != 0)
{
tree[id].sons[j] = &tree[s[j]];
}
}
}
cout << "前序遍历" << endl;
preOrder(tree + 1);
cout << endl;
cout << "后序遍历" << endl;
backOrder(tree + 1);
cout << endl;
cout << "层序遍历" << endl;
levelOrder(tree + 1);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
/*
测试
6
1 A 2 3 4 0 0
2 B 0 0 0 0 0
3 C 0 0 5 0 6
4 D 0 0 0 0 0
5 E 0 0 0 0 0
6 F 0 0 0 0 0
*/
二叉排序树
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class tNode
{
public:
T data;
tNode *pL, *pR;
};
// 二叉排序树节点的递归插入
template<class T>
void insertNode(tNode<T> * &root, T x)
{
if (!root)
{
tNode<T> *r = new tNode<T>;
r->pL = r->pR = NULL;
r->data = x;
root = r;
return;
}
if (x < root->data)
{
insertNode(root->pL, x);
}
else
{
insertNode(root->pR, x);
}
}
// 二叉排序树节点的非递归插入
template<class T>
void insertNode1(tNode<T> * r, T x)
{
tNode<T> * tmp = new tNode<T>;
tmp->data = x;
tmp->pR = tmp->pL = NULL;
while(r)
{
if (x < r->data)
{
if (!r->pL)
{
r->pL = tmp;
return;
}
else
{
r = r->pL;
}
}
else
{
if (!r->pR)
{
r->pR = tmp;
return;
}
else
{
r = r->pR;
}
}
}
}
// 找到二叉排序树某一节点的前驱,用于删除有两个儿子的节点
template<class T>
tNode<T> * findpre(tNode<T> * cur, tNode<T> * &fa)
{
fa = cur;
tNode<T> * pre = cur->pL;
while(pre->pR)
{
fa = pre;
pre = pre->pR;
}
return pre;
}
// 二叉排序树节点的删除
template<class T>
void deleteNode(tNode<T> *root, T x)
{
tNode<T> * fa = NULL;
tNode<T> * cur = root;
if (root)
{
// 找到待删除节点
while(cur && cur->data != x)
{
if (x < cur->data)
{
fa = cur;
cur = cur->pL;
}
else
{
fa = cur;
cur = cur->pR;
}
}
if (cur)
{
// 若待删除节点没有左右儿子
if (!cur->pL && !cur->pR)
{
// 判断待删除节点是父节点的左儿子还是右儿子
bool flagL = 1;
if (fa->pL != cur)
{
flagL = 0;
}
if (flagL == 1)
{
delete cur;
fa->pL = NULL;
}
else
{
delete cur;
fa->pR = NULL;
}
}
// 若待删除节点有左儿子且有右儿子
else if (cur->pL && cur->pR)
{
tNode<T> * tmp = NULL;
tNode<T> * place = findpre(cur, tmp);
cur->data = place->data;
bool flagL = 1;
if (tmp->pL != place)
{
flagL = 0;
}
if (flagL == 1)
{
tmp->pL = place->pL;
delete place;
}
else
{
tmp->pR = place->pL;
delete place;
}
}
// 若待删除节点仅有左儿子或右儿子
else
{
// 判断待删除节点是父节点的左儿子还是右儿子
bool flagL = 1;
if (fa->pL != cur)
{
flagL = 0;
}
if (flagL == 1)
{
if (cur->pL)
{
fa->pL = cur->pL;
}
else
{
fa->pL = cur->pR;
}
}
else
{
if (cur->pL)
{
fa->pR = cur->pL;
}
else
{
fa->pR = cur->pR;
}
}
}
}
}
}
//二叉排序树的查找
template<class T>
tNode<T> * findNode(tNode<T> * root, T x)
{
tNode<T> * cur = root;
while(cur && cur->data != x)
{
if (x < cur->data)
{
cur = cur->pL;
}
else
{
cur = cur->pR;
}
}
return cur;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
int a[10000];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
}
tNode<int> *root = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
insertNode(root, a[i]);
}
preOrder(root); // 二叉树的前序遍历,代码在前面给出,中序遍历同
cout << endl;
midOrder(root);
cout << endl;
deleteNode(root, 8);
preOrder(root);
cout << endl;
midOrder(root);
return 0;
}
/*
测试
10
8 2 10 1 5 14 4 7 13 6
*/测试用例
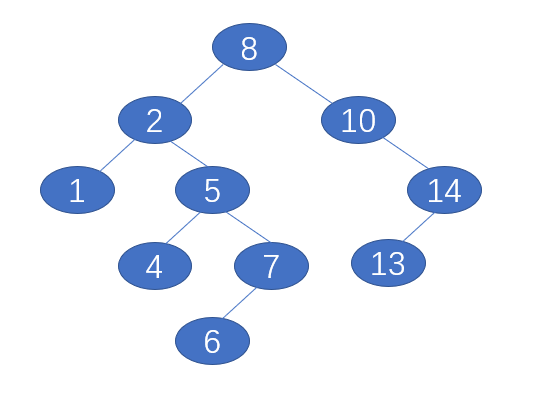
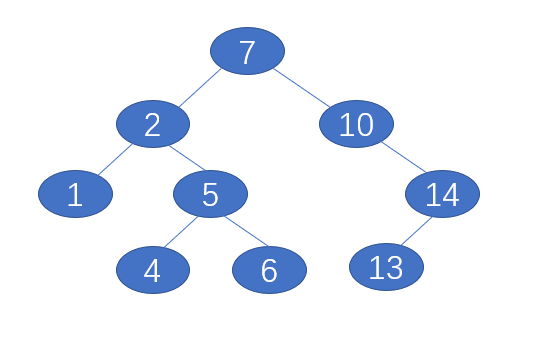
删除节点8后
树的递归释放
template<class T>
void freeTree(tNode<T> * root)
{
if (root)
{
freeTree(root->pL);
freeTree(root->pR);
delete root;
}
}哈夫曼树
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define INF_WEIGHT 1000000
struct tNode
{
int weight;
int father;
int left;
int right;
};
tNode * hfmCreate(int * w, int n)
{
tNode * ht = new tNode[2 * n];
int k, i;
ht[0].weight = n;
// n个权值节点ht[1]~ht[n]初始化为叶节点
for (k = 1; k <= n; k++)
{
ht[k].weight = w[k - 1];
ht[k].father = -1;
ht[k].left = -1;
ht[k].right = -1;
}
// 生成n -1个非叶节点ht[n + 1]~ht[2 * n - 1]
for (k = n + 1; k <= 2 * n - 1; k++)
{
// 在ht[1]~ht[k - 1]中找权值最小的两棵树first,second
ht[k].weight = INF_WEIGHT;
int first = k;
int second = k;
for (i = 1; i < k; i++)
{
if (ht[i].father < 0 && ht[i].weight < ht[first].weight)
// 找到更小的,那么第二小的改为原来最小的
{
second = first;
first = i;
}
else
{
if (ht[i].father < 0 && ht[i].weight < ht[second].weight)
{
second = i;
}
}
}
// 创建两个最小节点的父节点ht[k],修改它们的父节点指针
ht[k].weight = ht[first].weight + ht[second].weight;
ht[k].left = first;
ht[k].right = second;
ht[k].father = -1;
ht[first].father = k;
ht[second].father = k;
}
return ht;
}
int main()
{
int n;
int * w;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> w[i];
}
cout << hfmCreate(w, n)[2 * n - 1].weight << endl;
return 0;
}
/*
测试
6
3 5 8 9 10 11
*/
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








