业务简介
采购单的流程
1.根据需求部门提出采购申请表
2.采购员找供应商,询问价格,入库时间
3.根据获得的价格多少,找审核部门领导审核,审核通过,等待财务拨款,向供应商订货
4.供应商开始准备商品,产生一张发货单
5.准备采购入库单
库存模块
采购入库单(+),销售出库单(-),退货单,换货单,调货单,报损报溢,盘点单
一.框架搭建
通过使用 Spring,SpringMVC,SpringDataJPA 进行框架搭建,页面用 EasyUI 来显示。
Spring+SpringDataJPA集成和配置
<!--引入jdbc.properties文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties" />
<!--配置DataSource-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean>
<!--
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean:就是一个FactoryBean对象,返回EntityManagerFactory对象给我们
集成JPA:就是把EntityManagerFactory给它搞出来
四大金刚,方言,建表策略,显示SQL
Alt+Ins
-->
<bean id="entityManagerFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean">
<!--配置连接信息-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<!--配置包的扫描(Scan),认识JPA的注解 -->
<property name="packagesToScan" value="cn.cyj.domain" />
<!--
配置适配器 Spring+JPA(ORM规范) -> 到底用的是哪一个框架来完成的
JPA是有很多实现(Hibernate,OpenJPA,...)
-->
<property name="jpaVendorAdapter">
<bean class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaVendorAdapter">
<!--方言(确定数据库)-->
<property name="databasePlatform" value="org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect" />
<!--建表策略 true:update false:什么都不做-->
<property name="generateDdl" value="false" />
<!--支持SQL显示-->
<property name="showSql" value="true" />
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
Spring+SpringMVC集成和配置
<!-- 扫描controller部分的包 -->
<!-- @Component组件, @Repository持久层, @Service业务逻辑层, and @Controller控制器 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.cyj.controller" />
<!-- 添加mvc对@RequestMapping等注解的支持 -->
<mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:message-converters>
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter">
<property name="supportedMediaTypes">
<list>
<value>application/json; charset=UTF-8</value>
<value>application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- No serializer:配置 objectMapper 为我们自定义扩展后的 CustomMapper,解决了返回对象有关系对象的报错问题 -->
<property name="objectMapper">
<bean class="cn.cyj.common.CustomMapper"></bean>
</property>
</bean>
</mvc:message-converters>
</mvc:annotation-driven>
<!--静态资源放行-->
<mvc:default-servlet-handler />
<!-- ViewResolver 视图解析器 (struts2视图类型类似) -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<!-- 设置视图路径的前后缀,该配置可以让我们写视图路径的时候更简单。 -->
<!-- 希望跳转jsp是[/WEB-INF/views/前缀][xxx变量][.jsp后缀] -->
<!-- * @see #setPrefix -->
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/" />
<!-- * @see #setSuffix -->
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</bean>
<!-- 错误:提示告诉开发者你没有配置文件上传解析器。 -->
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
<!-- 设置上传文件的最大尺寸为1MB -->
<property name="maxUploadSize">
<value>1048576</value>
</property>
</bean>
通过不同的层级实现基本的CRUD:
1.Controller层,是对前端或者接口的响应一个逻辑处理的层,这个层级一般调用的是Service层。这个层级调用java代码实现的。
2.Service层,是对Controller的功能的响应一个逻辑处理的层,是对后台的有关联的逻辑的一个处理。这个层级一般调用的是Service层和Dao层,这个层级调用java代码实现的。
3.Repository层,封装了DAO,还有一些装配工作,把数据装配成一个完整的对象。
4.Common层,通用工具层,把项目中通用的功能放在这里。
5. Query层,把前台传过来的参数,进行封装。
在Repository层,Service层,Qurey层我们把相同的方法抽一个父类,方便再后期修改。
SpringDataJPA 功能虽然已经非常强大,但是它依然满足不了咱们的需要,在很多时候,我们需要自己去对SpringDataJpa的功能进行相应的扩展(即:自定义 Repository )。
1.直接创建BaseRepository来继承JpaRepository接口
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface BaseRepository<T,ID extends Serializable> extends JpaRepository<T,ID>,JpaSpecificationExecutor<T>{
//根据Query拿到分页对象(分页)
Page findPageByQuery(BaseQuery baseQuery);
//根据Query拿到对应的所有数据(不分页)
List<T> findByQuery(BaseQuery baseQuery);
//根据jpql与对应的参数拿到数据
List findByJpql(String jpql,Object... values);
}
- BaseRepositoryImpl功能实现
定义好自定义的方法后,我们现在通过一个基本的Repository类来实现该方法:
首先添加BaseRepositoryImpl类,继承SimpleJpaRepository类,使其拥有Jpa Repository的基本方法。
我们发现Repository有两个构造函数:
SimpleJpaRepository(JpaEntityInformation entityInformation, EntityManager entityManager)
SimpleJpaRepository(Class domainClass, EntityManager em)
这里我们实现第二个构造函数,拿到domainClass和EntityManager两个对象。
public class BaseRepositoryImpl<T,ID extends Serializable> extends SimpleJpaRepository<T,ID> implements BaseRepository<T,ID> {
private final EntityManager entityManager;
//必需要实现父类的这个构造器
public BaseRepositoryImpl(Class<T> domainClass, EntityManager em) {
super(domainClass, em);
this.entityManager = em;
}
@Override
public Page findPageByQuery(BaseQuery baseQuery) {
//第一步:拿到所有高级查询条件
Specification spec = baseQuery.createSpecification();
//第二步:拿到排序的值
Sort sort = baseQuery.createSort();
//第三步:根据条件查询分页数据并且返回
Pageable pageable = new PageRequest(baseQuery.getJpaPage(), baseQuery.getPageSize(),sort);
Page<T> page = super.findAll(spec, pageable);
return page;
}
@Override
public List<T> findByQuery(BaseQuery baseQuery) {
//第一步:拿到所有高级查询条件
Specification spec = baseQuery.createSpecification();
//第二步:拿到排序的值
Sort sort = baseQuery.createSort();
//第三步:拿到数据返回
return findAll(spec, sort);
}
@Override
public List findByJpql(String jpql, Object... values) {
//第一步:创建Query对象
Query query = entityManager.createQuery(jpql);
//第二步:把值设置到Query对象中去
if (values!=null) {
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
query.setParameter(i + 1, values[i]);
}
}
//第三步:返回数据
return query.getResultList();
}
}
- 创建自定义创建自定义RepositoryFactoryBean
接下来我们来创建一个自定义的RepositoryFactoryBean来代替默认的RepositoryFactoryBean。
RepositoryFactoryBean负责返回一个RepositoryFactory,Spring Data Jpa 将使用RepositoryFactory来创建Repository具体实现,这里我们用BaseRepositoryImpl代替SimpleJpaRepository作为Repository接口的实现。这样我们就能够达到为所有Repository添加自定义方法的目的。
我们需要覆写创建RepositoryFactory的方法:createRepositoryFactory
public class BaseRepositoryFactoryBean<T extends Repository<S, ID>, S, ID extends Serializable> extends JpaRepositoryFactoryBean<T,S,ID> {
@Override
protected RepositoryFactorySupport createRepositoryFactory(EntityManager entityManager) {
return new MyRepositoryFactory<T,ID>(entityManager); //注:这里创建是我们的自定义类
}
//继承JpaRepositoryFactory后,把返回的对象修改成我们自己的实现
private static class MyRepositoryFactory<T,ID extends Serializable> extends JpaRepositoryFactory{
private final EntityManager entityManager;
/**
* Creates a new {@link JpaRepositoryFactory}.
*
* @param entityManager must not be {@literal null}
*/
public MyRepositoryFactory(EntityManager entityManager) {
super(entityManager);
this.entityManager = entityManager;
}
//这里返回最后的功能对象
@Override
protected Object getTargetRepository(RepositoryInformation information) {
return new BaseRepositoryImpl<T,ID>((Class<T>)information.getDomainType(),entityManager);
}
//确定功能对象的类型
@Override
protected Class<?> getRepositoryBaseClass(RepositoryMetadata metadata) {
return BaseRepositoryImpl.class;
}
}
}
- applicationContext.xml 中修改配置
<!--用SpringDataJpa的方案去扫描它
只要发现接口继承了JpaRepository接口,就自动完成CRUD以及分页等功能
-->
<jpa:repositories base-package="cn.cyj.repository"
entity-manager-factory-ref="entityManagerFactory"
transaction-manager-ref="transactionManager"
factory-class="cn.cyj.repository.BaseRepositoryFactoryBean"
/>
在完成修改的时候,发现在修改完成后,密码不见了,于是我们做了以下修改:
var itsource={
//保存数据
save:function () {
var url = "/employee/save";
var id = $("#employeeId").val();
if(id){
url = "/employee/update?cmd=update";
}
employeeForm.form('submit', {
url:url,
onSubmit: function(){
//做验证
return $("#employeeForm").form("validate");
},
success:function(data){
$('#employeeGrid').datagrid('reload');
employeeDialog.dialog('close');
}
})
}
}
/**
* 特性:在执行相应方法之前都会先执行这个方法
*/
@ModelAttribute("editEmployee")
public Employee beforeEdit(Long id, String cmd){
//有id的时候-> 修改功能
if(id!=null && "update".equals(cmd)) {
Employee employee = employeeService.findOne(id);
return employee;
}
return null;
}
@RequestMapping("/save")
@ResponseBody
public Map<String,Object> save(Employee employee){
return saveOrUpdate(employee);
}
@RequestMapping("/update")
@ResponseBody
public Map<String,Object> update(@ModelAttribute("editEmployee")Employee employee){
return saveOrUpdate(employee);
}
部门修改的n-to-n
@ModelAttribute("editEmployee")
public Employee beforeEdit(Long id, String cmd){
//有id的时候-> 修改功能
if(id!=null && "update".equals(cmd)) {
Employee employee = employeeService.findOne(id);
//把这个要修改的关联对象设置为null,可以解决n-to-n的问题
employee.setDepartment(null);
return employee;
}
return null;
}
因为表单多,为避免过多的重复代码,我们基本功能CRUD,通过代码生成器生成–>EasyCode
目前市面上主流模板技术 velocity 和 freemarker
二.权限模块
权限
Apache Shiro是一个强大且易用的Java安全框架,有身份验证、授权、密码学和会话管理。使用Shiro的易于理解的API,您可以快速、轻松地获得任何应用程序,从最小的移动应用程序到最大的网络和企业应用程序。
Spring security 重量级安全框架
Apache Shiro轻量级安全框架
导入Jar
<!-- shiro的支持包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-all</artifactId>
<version>1.4.0</version>
<type>pom</type>
</dependency>
<!-- shiro与Spring的集成包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.4.0</version>
</dependency>
自定义Realm一般直接继承AuthorizingRealm接口即可(里面包含身份认证与授权两个方法)
/**
* 自定义一个Realm
*/
public class MyRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
//获取到这个Realm的名称(随便取)
@Override
public String getName() {
return "MyRealm";
}
//进行授权判断(权限)
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
return null;
}
//进行身份认证(登录)
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
return null;
}
}
在web.xml中配置
<!-- Spring与shiro集成:需要定义一个shiro过滤器(这是一个代理过滤器,它会到spring的配置中找一个名称相同的真实过滤器) -->
<filter>
<filter-name>shiroFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>targetFilterLifecycle</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>shiroFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
Spring+Shiro配置
<!-- securityManager:Spring创建核心对象 -->
<bean id="securityManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager">
</bean>
<!-- 建议大家把它留着,它可以支持我们做注解权限判断 -->
<bean id="lifecycleBeanPostProcessor" class="org.apache.shiro.spring.LifecycleBeanPostProcessor"/>
<bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator"
depends-on="lifecycleBeanPostProcessor"/>
<bean class="org.apache.shiro.spring.security.interceptor.AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor">
<property name="securityManager" ref="securityManager"/>
</bean>
<bean id="shiroFilter" class="org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean">
<property name="securityManager" ref="securityManager"/>
<!--如果你没有登录,就会进入这个页面-->
<property name="loginUrl" value="/login"/>
<!--如果登录成功,就会进入这个页面-->
<property name="successUrl" value="/s/main.jsp"/>
<!--如果没有权限,就会进入这个页面-->
<property name="unauthorizedUrl" value="/s/unauthorized.jsp"/>
<property name="filterChainDefinitions">
<value>
/s/login.jsp = anon
/** = authc
</value>
</property>
</bean>
加密认证
<bean id="aiSellRealm" class="cn.cyj.shiro.AiSellRealm">
<property name="credentialsMatcher">
<bean class="org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.HashedCredentialsMatcher">
<property name="hashAlgorithmName" value="MD5"/>
<property name="hashIterations" value="10" />
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
菜单
用户拥有对应的权限就拥有对应的菜单(二级菜单),如果此菜单有父菜单(一级菜单)也同时拥有
@Override
public List<Menu> findByLoginUser(Long userId) {
//准备父菜单容器
List<Menu> parentMenus = new ArrayList<>();
//从数据库中拿到子菜单
List<Menu> childrenMenus = menuRepository.findByLoginUser(userId);
//遍历子菜单(如果有父菜单放进入,没有单独创建)
for (Menu childrenMenu : childrenMenus) {
//拿到子菜单对应的父菜单
Menu parent = childrenMenu.getParent();
//判断如果父菜单中是否有这个菜单
if(parentMenus.contains(parent)){
//有的话,咱们就把子菜单放到父菜单中去
int i = parentMenus.indexOf(parent);
Menu parentMenu = parentMenus.get(i);
parentMenu.getChildren().add(childrenMenu);
}else{
//如果没有,再单独把父菜单放进去
parentMenus.add(parent);
parent.getChildren().add(childrenMenu);
}
}
return parentMenus;
}
业务模块
导入导出
jxl:只能对Excel进行操作,属于比较老的框架。
POI:是apache的项目,可对ms的word,Excel,PPT进行操作,包括office2003和2007。
在这我们使用EasyPOI。
采购订单
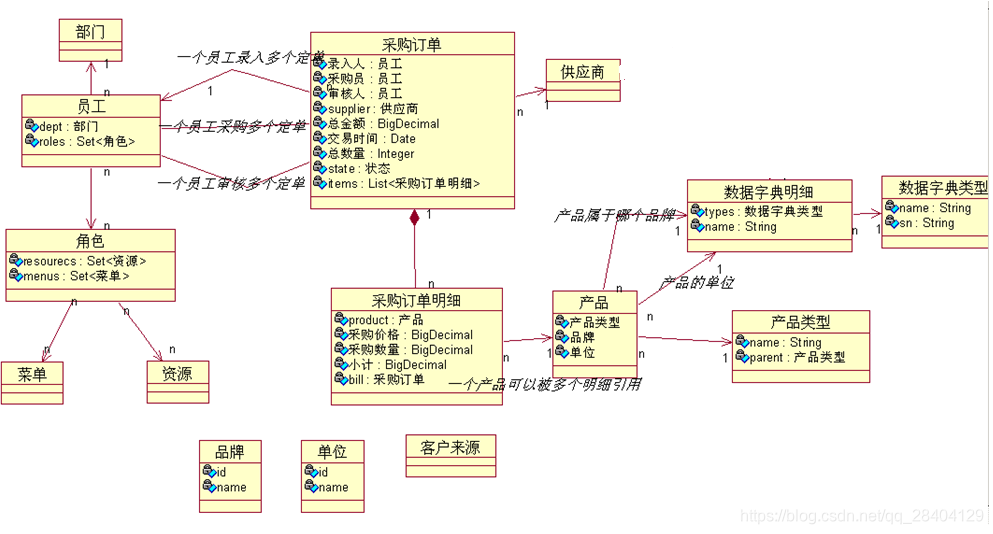
组合关系映射配置要求
- 整体和部分,整体和部分不能分割,本质还是双向一对多
- 一方(主表):
@OneToMany(cascade = CascadeType.ALL, mappedBy = "bill", fetch = FetchType.LAZY, orphanRemoval = true)
private List<purchasebillitem> items = new ArrayList<purchasebillitem>();
cascade = CascadeType.ALL级联操作最全
mappedBy = "bill"一方放弃管理多方,多方的外键字段bill_id,一方不管
orphanRemoval = true如果在一方解除了和多方的关系,一方是可以删除掉多方
- 多方(从表)billitem:bill_id配置为非空
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY, optional = false)
@JoinColumn(name = "bill_id")
private Purchasebill bill;// 组合关系,非空
- 页面管理:一方和多方同时管理
报表
在domain层下面新建vo层:
public class PurchasebillitemVO {
//编号
private Long id;
//供应商名称
private String supplierName;
//采购员名称
private String buyerNmae;
//产品名称
private String productNmae;
//产品图片
private String productImages;
//产品分类
private String productType;
//交易时间
private Date vdate;
//采购数量
private BigDecimal num;
//价格
private BigDecimal price;
//小计
private BigDecimal amount;
//状态
private Integer status = 0;
...
}
解决分组的问题,根据前台的传参使用不同的分组方案
public PurchasebillitemVO(Purchasebillitem item, PurchasebillitemQuery query) {
this.id = item.getId();
this.supplierName = item.getBill().getSupplier().getName();
this.buyerNmae = item.getBill().getBuyer().getUsername();
this.productNmae = item.getProduct().getName();
this.productImages = item.getProduct().getPic();
this.productType = item.getProduct().getProducttype().getName();
this.vdate = item.getBill().getVdate();
this.num = item.getNum();
this.price = item.getPrice();
this.amount = item.getAmount();
this.status = item.getBill().getStatus();
switch (query.getGroupField()){
case 1:
this.groupField = this.supplierName;
break;
case 2:
this.groupField = this.productNmae;
break;
case 3:
this.groupField = this.buyerNmae;
break;
case 4:
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.setTime(vdate);
this.groupField = (calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1) + "月";
break;
default:
this.groupField = this.supplierName;
break;
}
}
图形报表
效果更佳直接
使用HighChart 完成




 本文介绍了一个采购系统的搭建过程,包括使用Spring、SpringMVC、SpringDataJPA进行框架搭建,EasyUI进行页面展示,并实现了基本的CRUD操作。此外,还介绍了权限模块的实现方式,采用Apache Shiro进行权限管理和认证。
本文介绍了一个采购系统的搭建过程,包括使用Spring、SpringMVC、SpringDataJPA进行框架搭建,EasyUI进行页面展示,并实现了基本的CRUD操作。此外,还介绍了权限模块的实现方式,采用Apache Shiro进行权限管理和认证。
















 1433
1433

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








