题目描述
A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked ‘Start’ in the diagram below).
The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked ‘Finish’ in the diagram below).
How many possible unique paths are there?
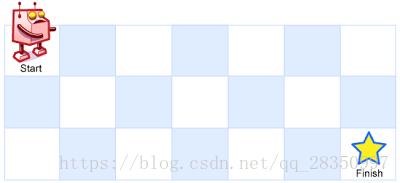
Above is a 7 x 3 grid. How many possible unique paths are there?
Note: m and n will be at most 100.
Example 1:
Input: m = 3, n = 2
Output: 3
Explanation:
From the top-left corner, there are a total of 3 ways to reach the bottom-right corner:
1. Right -> Right -> Down
2. Right -> Down -> Right
3. Down -> Right -> Right
Example 2:
Input: m = 7, n = 3
Output: 28
思路
类似于爬梯子的问题。
递归
可以使用递归方法,其中会超时,大量重复计算的,递归的截止条件是只有一行,或者一列,只有一种,此时只有一种路径, return 1,
= 1, if(m==1 || n==1) f(m,n) = f(m-1,n)+f(m,n-1) if(m>0 && n>0) = 1, if(m==1 || n==1)
视频讲解
递归代码
Java
public int solution_1(int m, int n){
return unqiue_path_1(n,m);
//n 代表row, m代表 columns
}
//递归方法,总的方法等于右下两种方法叠加起来的总体情况,超时
private int unqiue_path_1(int row,int column){
//当只有一行或者一列的时候只有一种情况,一条路径,
if(row==1 || column==1) return 1;
//m代表向右走的情况(总的路径数), n代表向做,
return unqiue_path_1(row,column-1)+unqiue_path_1(row-1,column) ; //在这里不用加上2
}改进一:记录型递归
增加一个二维数组dp[row][column]
如果dp[i][j]>0, 证明已经是算过的,避免重复计算,直接返回即可
代码
public int solution_2(int m,int n){
int [][] dp = new int[n][m];
return unqiue_path_2(0,0,n,m,dp);
}
private int unqiue_path_2(int i,int j, int row, int column,int [][]dp){
if(i==row-1 || start_j==column-1) return 1;
if(i>=row || j>=column) return 0;
if(dp[i][j]>0) return dp[i][j];
dp[i][j] = unqiue_path_2(i+1,j,row,column,dp)+unqiue_path_2(i,j+1,row,column,dp);
return dp[i][j];
}原始动态
dp[i][j]表示从起点位置走到(i,j)处的大小,
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]+dp[i][j];
在dp[0][j]=1,dp[i][0]=1,只有一种路径,可以走,也是初始化的条件
//倒过来求解的
public int solution_3(int m, int n){
int [][] dp=new int [n][m];
//只能往右走只有一种路径
for(int i=0;i<m;++i){
dp[0][i] =1;
}
//只能向下走只有一条路径
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
dp[j][0]=1;
}
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<m;j++){
dp[i][j] =dp[i-1][j]+dp[i][j-1];
}
}
return dp[n-1][m-1];
性能
时间复杂度为0(n^2), 空间复杂度为0(n*m)
改进版动态规划
思路
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j-1]+dp[i-1][j],可以采用逐步叠加的方法,先处理每一行的情况,从左到右,从上到下,可以用滚动数组实现
从第一行开始,也可以从第一列开始
代码
public int solution_3_1(int m, int n){
if(m<1||n<1) return 0;
int [] dp = new int[m];
//第一行路径只能为1,
Arrays.fill(dp,1);
//从第二行开始,因为第一行智能有一种路径
for(int i=1;i<n;++i){
//从第二列开始,因为第一列只能有只用路径
for(int j=1;j<m;++j){
//每一行处理dp[j],相单于dp[i-1][j], dp[j-1]相单于dp[i][j-1]
dp[j] = dp[j-1]+dp[j];
}
}
return dp[m-1];
}复杂度分析
时间复杂度为0(n*m), 空间复杂度为0(min(m,n)
讲解视频(VPN)







 本文探讨了如何通过递归和动态规划解决迷宫问题,详细介绍了递归方法及其性能问题,并通过改进引入动态规划方法,优化了解决方案。文章提供了不同方法的时间复杂度和空间复杂度分析,帮助读者理解不同算法的特点。
本文探讨了如何通过递归和动态规划解决迷宫问题,详细介绍了递归方法及其性能问题,并通过改进引入动态规划方法,优化了解决方案。文章提供了不同方法的时间复杂度和空间复杂度分析,帮助读者理解不同算法的特点。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








