1.题目:
Two Sum
Given an array of integers, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to a specific target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
Example:
Given nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9,
Because nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9,
return [0, 1].
descript:给定一个整数数组,返回两个数字的索引,使它们加起来成为一个特定的目标。可以假定每个输入只有一个解决方案,并且不能使用同一个元素两次。
(所以不需要考虑有多种求解方式)
2.碰到的问题
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int> &numbers, int target) {
int n = numbers.size();
vector<int> result;
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
for(int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if(numbers[i] + numbers[j] == target)
{
result.push_back(i);
resul.push_back(j);
return result;
}
}
}
}
};
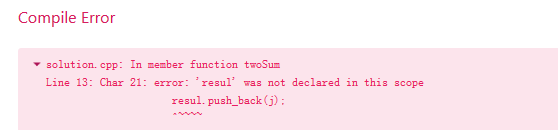
正确的程序:(修改return的位置)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int> &numbers, int target) {
int n = numbers.size();
vector<int> result;
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
for(int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if(numbers[i] + numbers[j] == target)
{
result.push_back(i);
result.push_back(j);
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
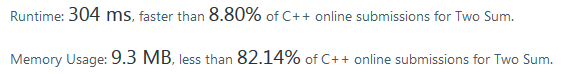
用了暴力搜索的方法,遍历了所有的两个数字的组合,然后算其和,这样虽然节省了空间,但是时间复杂度高,时间复杂度是O(n^2)。
3.求解方法
一般来说,我们为了提高时间的复杂度,需要用空间来换,这算是一个trade off吧,我们只想用线性的时间复杂度来解决问题,那么就是说只能遍历一个数字,那么另一个数字呢,我们可以事先将其存储起来,使用一个HashMap,来建立数字和其坐标位置之间的映射,我们都知道HashMap是常数级的查找效率,这样,我们在遍历数组的时候,用target减去遍历到的数字,就是另一个需要的数字了,直接在HashMap中查找其是否存在即可,注意要判断查找到的数字不是第一个数字,比如target是4,遍历到了一个2,那么另外一个2不能是之前那个2,整个实现步骤为:先遍历一遍数组,建立HashMap映射,然后再遍历一遍,开始查找,找到则记录index。代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
unordered_map<int, int> m;
vector<int> res;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
m[nums[i]] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
int t = target - nums[i];
if (m.count(t) && m[t] != i) {
res.push_back(i);
res.push_back(m[t]);
break;
}
}
return res;
}
};

运行时间很快,但是内存占用率高
为了代码更加简洁一些,把两个for循环合并成一个:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
unordered_map<int, int> m;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
if (m.count(target - nums[i])) {
return {i, m[target - nums[i]]};
}
m[nums[i]] = i;
}
return {};
}
};









 本文探讨了TwoSum问题的两种解决策略:暴力搜索与哈希表映射。暴力搜索虽简单但时间复杂度高,而哈希表映射通过牺牲空间换取时间效率,实现了线性时间复杂度。文章提供了详细的代码示例与优化建议。
本文探讨了TwoSum问题的两种解决策略:暴力搜索与哈希表映射。暴力搜索虽简单但时间复杂度高,而哈希表映射通过牺牲空间换取时间效率,实现了线性时间复杂度。文章提供了详细的代码示例与优化建议。
















 292
292

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








