文章目录
1、求两数之和
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素不能使用两遍。你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
class Solution(object):
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
hashmap={}
for index,num in enumerate(nums):
if hashmap.get(target-num) is not None:
#hashmap.get(target-num) 等价于hashmap[target-num]
return [index, hashmap.get(target-num)]
hashmap[num]=index
class Solution(object):
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
list1=[]
for index, num in enumerate(nums):
if target-num in list1:
return [index, list1.index(target-num)]
list1.append(num)
执行结果
执行结果:
通过
显示详情
执行用时:
20 ms
, 在所有 Python 提交中击败了
68.71%
的用户
内存消耗:
13.2 MB
, 在所有 Python 提交中击败了
19.06%
的用户
2、最接近的三数之和
给你一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?请你找出所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
- 解题思路

class Solution:
def threeSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
n=len(nums)
res=[]
if(not nums or n<3 or nums[0] > 0):
return res
nums.sort()
for i in range(n):
if(nums[i]>0):
return res
if(i>0 and nums[i]==nums[i-1]):
"""跳过当前循环的剩余语句,然后继续进行下一轮循环,避免重复"""
continue
L=i+1
R=n-1
while(L<R):
if(nums[i]+nums[L]+nums[R]==0):
res.append([nums[i],nums[L],nums[R]])
"""下面的两个while为了避免重复的三元组出现"""
while(L<R and nums[L]==nums[L+1]):
L=L+1
while(L<R and nums[R]==nums[R-1]):
R=R-1
L=L+1
R=R-1
elif(nums[i]+nums[L]+nums[R]>0):
""""如果相加大于零,说明最大的数太大,需要左移"""
R=R-1
else:
""""如果相加小于零,说明最小的数太小,需要右移"""
L=L+1
return res
- 执行结果

3、求众数
给定一个大小为 n 的整数数组,找出其中所有出现超过 ⌊ n/3 ⌋ 次的元素。
进阶:尝试设计时间复杂度为 O(n)、空间复杂度为 O(1)的算法解决此问题。
class Solution:
def majorityElement(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
nums_dict = {}
for num in nums:
"""将num出现的次数以字典的value的形式存储起来"""
nums_dict[num] = nums_dict.get(num,0) + 1
"""使用列表中的元组将次数大于要求的第一个元素打印出来"""
return [i[0] for i in nums_dict.items() if i[1]>len(nums)//3]
- 运行结果
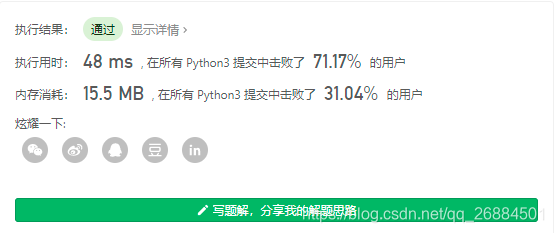
拓展
dict.get(key, default=None)
#key -- 字典中要查找的键。
#default -- 如果没有传入key值时,则使用默认key=default=None。
dict.items()
#Python 字典(Dictionary) items() 函数以列表返回可遍历的(键, 值) 元组数组。
- 执行过程
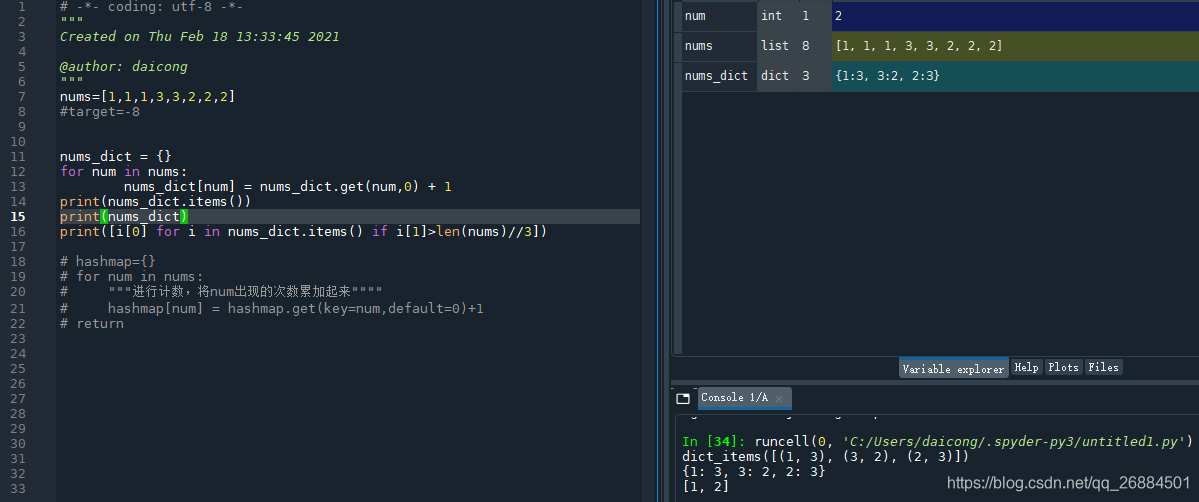
总结:灵活的使用dic.get()和dic.item()真是事半功倍!!!
"""
因为有
for key, value in nums_dict.items():
print([key,value])
所以为了便于理解,也可以写成下面这样,并且运行速度貌似更快了
"""
class Solution:
def majorityElement(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
nums_dict = {}
for num in nums:
"""将num出现的次数以字典的value的形式存储起来"""
nums_dict[num] = nums_dict.get(num,0) + 1
"""将字典中value次数大于要求的key打印出来"""
return [key for key, value in nums_dict.items() if value > len(nums)//3]
4、判断快乐数字
编写一个算法来判断一个数 n 是不是快乐数。
「快乐数」定义为:
对于一个正整数,每一次将该数替换为它每个位置上的数字的平方和。
然后重复这个过程直到这个数变为 1,也可能是 无限循环 但始终变不到 1。
如果 可以变为 1,那么这个数就是快乐数。
如果 n 是快乐数就返回 true ;不是,则返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入:19
输出:true
解释:
12 + 92 = 82
82 + 22 = 68
62 + 82 = 100
12 + 02 + 02 = 1
class Solution:
def isHappy(self, n: int) -> bool:
def get_next(n):
total_sum = 0
while n > 0 :
"""不断的对10进行整除进行取余操作,一旦n=0时,说明是个位数,跳出循环"""
n, num2 = divmod(n,10)
"""将取余后的数进行累加,即将每一位的数字进行平方后累加"""
total_sum += num2**2
return total_sum
seen = set()
"""设置seen集合,避免有重复的输出导致死循环"""
while ( n != 1 and n not in seen):
seen.add(n)
"""不断的往下迭代,直到满足n=1或者陷入死循环,再跳出循环"""
n = get_next(n)
"""跳出循环的条件有两个,这里判断时候是因为n=1才跳出的循环"""
return n == 1
5、求中位数
给定两个大小为 m 和 n 的有序数组 nums1 和 nums2。
请你找出这两个有序数组的中位数,并且要求算法的时间复杂度为 O(log(m + n))。
你可以假设 nums1 和 nums2 不会同时为空
nums=[7,8,9,11,12]
nums2=[7,8,9,11]
nums+=nums2
nums.sort()
if len(nums)%2 ==0:
print((nums[len(nums)//2]+nums[len(nums)//2-1])/2)
else:
print(nums[len(nums)//2])
##print(11/2,11//2,11%2) 分别是5.5 ,5 ,1
6、最大连续1的个数 III(1004)
给定一个由若干 0 和 1 组成的数组 A,我们最多可以将 K 个值从 0 变成 1 。
返回仅包含 1 的最长(连续)子数组的长度。
示例
输入:A = [0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1], K = 3
输出:10
解释:
[0,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1]
粗体数字从 0 翻转到 1,最长的子数组长度为 10。

参考动画
class Solution:
def longestOnes(self, A: List[int], K: int) -> int:
left,right,res,zeroCount = 0,0,0,0
"""设置两个指针,都是从index=0开始,进行右移"""
while right < len(A):
if (A[right] == 0):
"""一旦有0就统计下来"""
zeroCount +=1
"""如果0的个数不满足要求,那么就左移指针,直到满足要求为止"""
while (zeroCount > K ):
if A[left] == 0:
zeroCount -=1
left +=1
"""统计在满足要求的情况下,最大的长度,因为从index=0开始的,所以长度需要+1"""
res = max(res,right -left +1)
"""不断的右移直至最后一个元素满足条件"""
right +=1
return res
滑动窗口模板
《挑战程序设计竞赛》这本书中把滑动窗口叫做「虫取法」,我觉得非常生动形象。因为滑动窗口的两个指针移动的过程和虫子爬动的过程非常像:前脚不动,把后脚移动过来;后脚不动,把前脚向前移动。
我分享一个滑动窗口的模板,能解决大多数的滑动窗口问题:
def findSubArray(nums):
N = len(nums) # 数组/字符串长度
left, right = 0, 0 # 双指针,表示当前遍历的区间[left, right],闭区间
sums = 0 # 用于统计 子数组/子区间 是否有效,根据题目可能会改成求和/计数
res = 0 # 保存最大的满足题目要求的 子数组/子串 长度
while right < N: # 当右边的指针没有搜索到 数组/字符串 的结尾
sums += nums[right] # 增加当前右边指针的数字/字符的求和/计数
while 区间[left, right]不符合题意:# 此时需要一直移动左指针,直至找到一个符合题意的区间
sums -= nums[left] # 移动左指针前需要从counter中减少left位置字符的求和/计数
left += 1 # 真正的移动左指针,注意不能跟上面一行代码写反
# 到 while 结束时,我们找到了一个符合题意要求的 子数组/子串
res = max(res, right - left + 1) # 需要更新结果
right += 1 # 移动右指针,去探索新的区间
return res
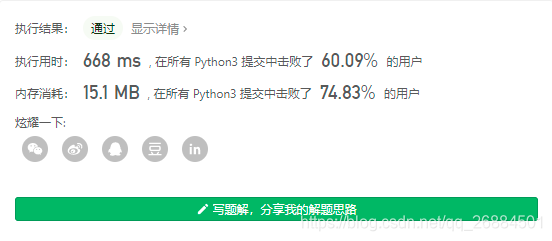
7、盛最多水的容器(11)
给你 n 个非负整数 a1,a2,…,an,每个数代表坐标中的一个点 (i, ai) 。在坐标内画 n 条垂直线,垂直线 i 的两个端点分别为 (i, ai) 和 (i, 0) 。找出其中的两条线,使得它们与 x 轴共同构成的容器可以容纳最多的水。
我自己做的代码,使用的是暴力破解,一听到暴力就知道,虽然能过了测试用例,但是一定会超时的
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
if (not nums or len(nums) < 2 ):
return []
res = -1
for i in range(len(nums)):
R = len(nums) -1
while (i < R ):
if ((R - i) * min(nums[i],nums[R]) > res):
res = (R - i) * min(nums[i],nums[R])
else:
R -= 1
return res
"""
上面的if判断代码也可以优化,一行搞定
while (i < R ):
res = max((R - i) * min(nums[i],nums[R]),res)
R -= 1
"""
代码的改进版本,主要是计算方法上的优化:

参考动画
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
res,left,right = 0,0,len(nums)-1
while left < right:
"""使用高度来进行对比,如果高度高的话,则高的不动,使用低的计算面积,如果左边低,则左移"""
if nums[left] < nums[right]:
"""更新最大面积"""
res = max(res,nums[left]*(right - left))
left += 1
else:
"""右边低则右移"""
res = max(res,nums[right]*(right - left))
right -= 1
return res
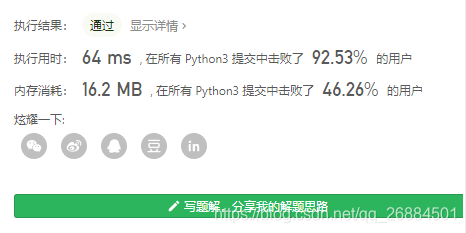
8、删除排序数组中的重复项
给定一个排序数组,你需要在 原地 删除重复出现的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次,返回移除后数组的新长度。
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在 原地 修改输入数组 并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。
- 这个题首先删除重复的元素指的是相邻的元素不能重复,其次输出结果应该是列表而非长度。虽然返回值是长度,在测试时,结果输出的是列表,因为根据你的函数返回的长度, 它会打印出数组中该长度范围内的所有元素
- 使用双指针,行云流水,万能解法
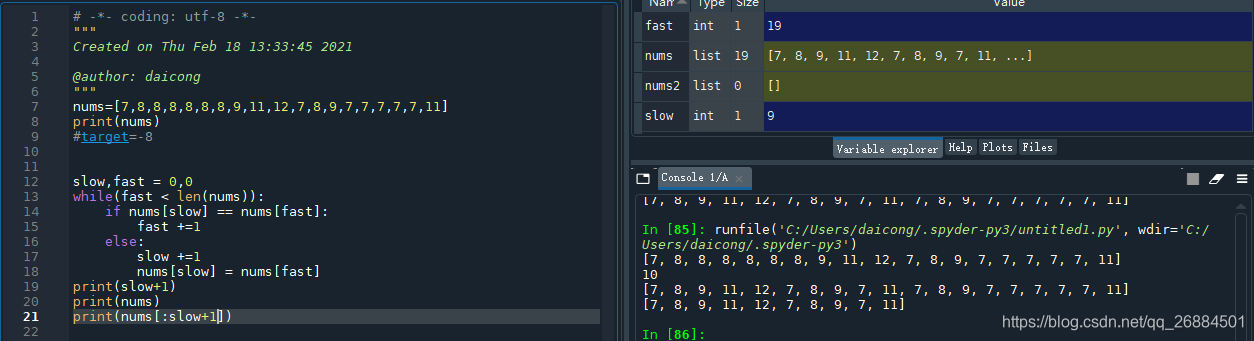
class Solution:
def removeDuplicates(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
slow,fast = 0,0
while(fast < len(nums)):
if nums[slow] == nums[fast]:
fast +=1
else:
slow +=1
nums[slow] = nums[fast]
return slow+1
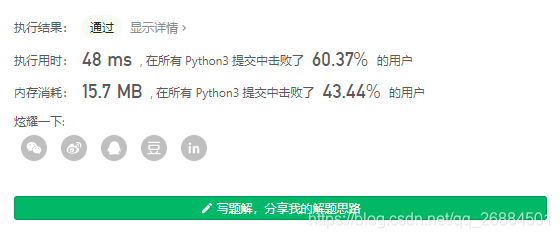
9、搜索旋转排序数组
升序排列的整数数组 nums 在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转(例如,[0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 经旋转后可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] )。
请你在数组中搜索 target ,如果数组中存在这个目标值,则返回它的索引,否则返回 -1 。
- 解题思路
数组从任意位置劈开后,至少有一半是有序的。
基于这个事实。我们可以先找到哪一段是有序的 (只要判断端点即可),然后看 target 在不在这一段里,如果在,那么就把另一半丢弃。如果不在,那么就把这一段丢弃。
class Solution:
def search(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
if not nums:
return -1
left = 0
right = len(nums) - 1
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if nums[mid] == target:
return mid
# 左半段有序
if nums[mid] >= nums[left]:
if nums[left] <= target <= nums[mid]:
right = mid - 1
else:
left = mid + 1
# 右半段有序
else:
if nums[mid] <= target <= nums[right]:
left = mid + 1
else:
right = mid - 1
return -1
貌似被算法得的复杂度限制了,使用下面的代码也能够通过测试
class Solution:
def search(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
for index, num in enumerate(nums):
if target == num:
return index
return -1

10、螺旋矩阵(54)

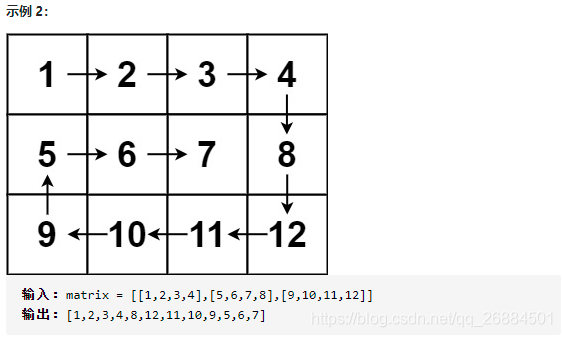
class Solution(object):
def spiralOrder(self, matrix):
"""
:type matrix: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[int]
row start row end
column start column end
"""
rs, cs = 0, 0 # 设置行的起始位置rs=0和列的起始位置cs=0
re, ce = len(matrix), len(matrix[0]) # 设置行的结束位置re=n和列的结束位置ce=n
res = [] # 存放结果的数组
while rs < re and cs < ce:
"""如果非最后一行并且非最后一列,则则执行循环"""
for i in range(cs,ce): # 遍历首行
res.append(matrix[rs][i])
rs += 1
if rs>=re:
"""如果是最后一行,那么跳出循环"""
break
for j in range(rs,re): # 遍历尾列
res.append(matrix[j][ce-1])
ce -= 1
if cs>=ce:
"""如果是最后一列,那么跳出循环"""
break
for i in range(ce-1,cs-1,-1): # 遍历尾行
"""因为不包括最后一行,所有ce-1,因为想取到第一行,所以cs-1"""
res.append(matrix[re-1][i])
re -= 1
if rs>=re:
"""如果是最后一行,那么跳出循环"""
break
for j in range(re-1,rs-1,-1): # 遍历首列
res.append(matrix[j][cs])
cs += 1
if cs>=ce:
"""如果是最后一列,那么跳出循环"""
break
return res

11、螺旋矩阵II
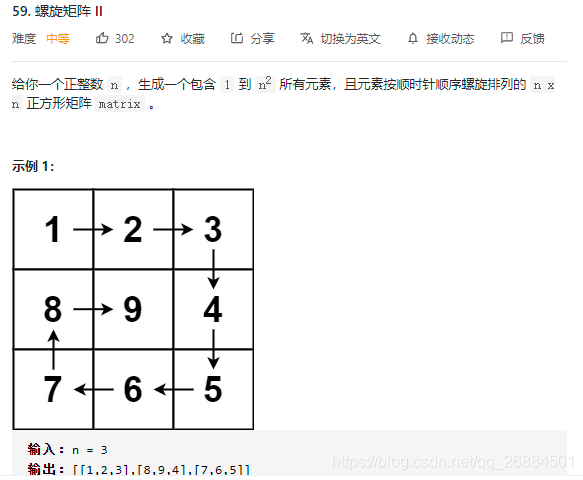

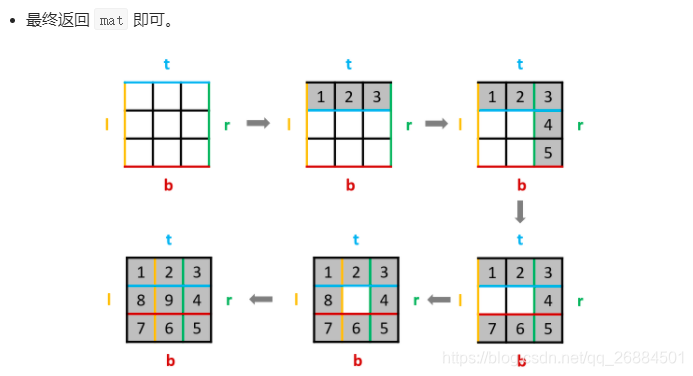
- 本想着这个题和上面的题一样,只不过输入是我们自己自定义,仔细研究才发现还是不一样的,这一题是按照顺时针的顺序,将数一个一个的放进去,去生成这个矩阵。实际上还是可以用到上面的遍历方式,将数字一个一个的放进去
for j in range(n):
matrix = [[i+n*j for i in range(1,n+1)] for j in range(n)]
#n=3
#输出[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
- 解法
class Solution:
def generateMatrix(self, n: int) -> List[List[int]]:
matrix = [[0 for i in range(n)] for _ in range(n)]
rs, cs = 0, 0
re, ce = n, n
num = 1
end = n * n
while num <= end:
"""首行"""
for i in range(cs,ce):
matrix[rs][i] = num
num += 1
rs += 1
"""尾列"""
for i in range(rs,re):
matrix[i][ce-1] = num
num += 1
ce -= 1
"""尾行"""
for i in range(ce-1,cs-1,-1):
matrix[re-1][i] = num
num += 1
re -= 1
"""首列"""
for i in range(re-1,rs-1,-1):
matrix[i][cs] = num
num += 1
cs += 1
return matrix
12、螺旋矩阵III
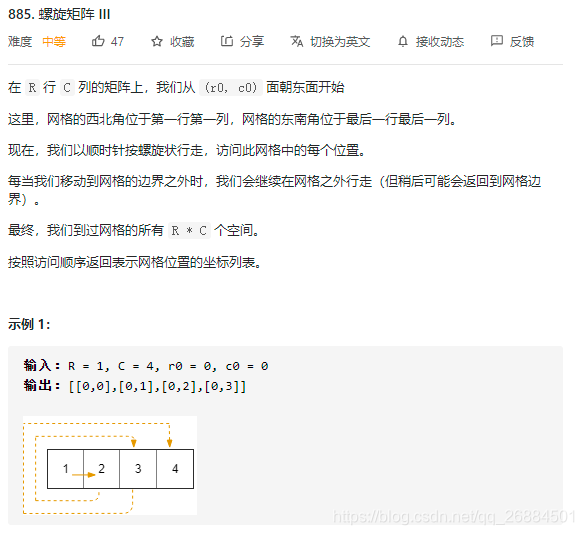
class Solution:
def spiralMatrixIII(self, R: int, C: int, r0: int, c0: int) -> List[List[int]]:
ans = []
di, dj, step = 0, 1, 0
# 从内往外走,初始值走一步就要转
while len(ans) < R*C:
for s in range(step//2+1):
if 0<=r0<R and 0<=c0<C:
ans.append((r0, c0))
r0, c0 = r0+di, c0+dj
di, dj, step = dj, -di, step+1
return ans

13、环形链表
判断链表中是否存在环
使用的是快慢指针的思想,解释的极其详尽
参考1为什么使用快慢指针
参考2为什么步长为二
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
"""如果链表为空挥或者只有一个元素,就无法形成环"""
if not head or not head.next: return False
slow = head
fast = head.next
while slow != fast:
"""如果慢指针和快指针始终不相等,那么说明是没有环的"""
if not fast or not fast.next:
"""如果遍历到底了,那么就没有环"""
return False
"""慢指针每次走一步,快指针每次走两步"""
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
"""跳出while循环说明是有环的"""
return True

13、环形数组循环
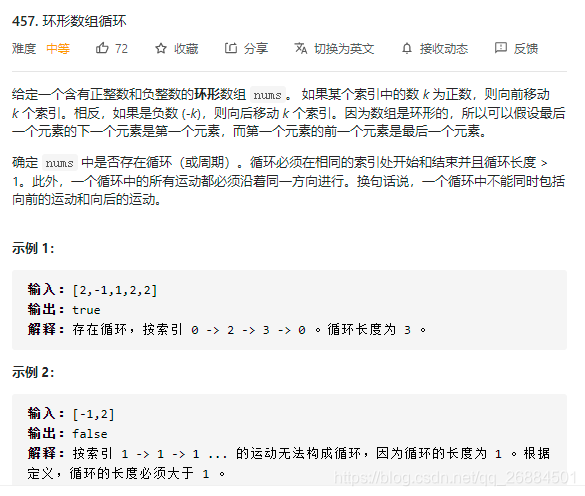
思路:快慢指针
通过快慢指针找到是否存在环
时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度为O(1)
思路是:
对于查找数组或链表中有没有环的问题,多可以朝快慢指针的方向去想,本题也不例外。基本思想是快慢指针。还有一些小细节和技巧的东西需要考虑在内。
1)数组长度为0时,认为无环。
2)快慢指针的思想是慢指针走一步,快指针走两步,若他俩相遇肯定是在环中的某一个节点上相遇,则证明存在环。
3)假设位置i的元素是环中的一点,通过快慢指针的思想,假定慢指针为j快指针为k,那么一定会有j==k的时候。问题是位置i可能不是环中的一个节点。鉴于此肯定是要遍历全部的节点的。for(i = 0; i < nums.length;++i>)对于这样的i都要试一试是否是环中的一个节点,若是则return true,否则则return false;如果这样的话,肯定做不到时间复杂度是O(n)的程度,要稍微“剪下枝”。
4)根据提示,nums中所有元素都不可能是0。这是剪枝可以进行的关键。另一个原则是如果存在环,那么环中的所有数字的符号都必须是一致,否则不满足题意。这时我们认为本链条不处于环上。然后将节点i到当前位置的所有元素置0,以标记这些节点都不在环上。
5)另一点是:当某节点j指向已经确定不在环中的节点时,就不必继续走下去了,节点j肯定也不在环上。
6)当循环长度为1是,也是不存在环的,比如[8,2]这个数组,从任意位置开始都指向它自己。我们认为他是无环的。
基本思路说完了,不知道读者懂没懂_。
重述下无环的判定依据:
1)当快慢指针指向的新节点发现和上一个节点符号不一致。
2)当快慢指针指向的位置不变时。
3)快慢指针指向了不可能是环中节点的节点(该节点位置已经置0的节点)时。
class Solution:
def circularArrayLoop(self, nums: List[int]) -> bool:
n = len(nums)
# x的下一个位置
nxt = lambda x: (x + nums[x]) % n
for i in range(n):
if nums[i] == 0: continue
slow = i
fast = nxt(i)
# 快慢指针
"""符号相同保证是同一个方向移动"""
while nums[slow] * nums[fast] > 0 and nums[fast] * nums[nxt(fast)] > 0:
"""快指针每次走两步,如果快慢指针相等,说明有环"""
if slow == fast:
"""如果是自身环,那么退出循环"""
if slow == nxt(slow):
break
else:
return True
"""更新状态,快指针每次走两步"""
slow = nxt(slow)
fast = nxt(nxt(fast))
# 访问过的置0
"""如果上面那轮没有return,说明上面遍历过的元素都不可能成环,为避免再次遍历陷入无效查找,故将查找过的元素置零,再次遍历时直接跳过"""
while nums[i] > 0:
"""先找到下一个元素的index"""
tmp = nxt(i)
"""将当前的元素置零"""
nums[i] = 0
"""向下走一步"""
i = tmp
return False
"""
使用的快慢指针,初始列表中的元素不可能有0
1、首先判断方向一致
2、有环的情况下,判断是否是自身环
3、没环的情况下,将遍历过的元素置零避免重复遍历
"""
14、接雨水(42)
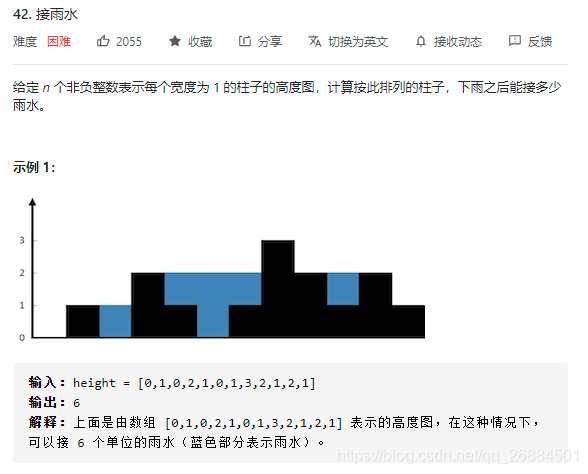

- 暴力法:
时间复杂度:O(N^2)。
空间复杂度:O(1)。
class Solution:
def trap(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
if len(height) <= 2:
return 0
res = 0
for i in range(1, len(height)-1):
left_max = max(height[:i+1])
right_max = max(height[i:])
res += (min(left_max, right_max) - height[i])
return res

- 双指针法:
时间复杂度:O(N)。
空间复杂度:O(1)。
class Solution:
def trap(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
if len(height) <= 2:
return 0
res = 0
left, right = 0, len(height) - 1
left_max, right_max = height[0], height[-1]
while left <= right:
left_max = max(left_max, height[left])
right_max = max(right_max, height[right])
if left_max < right_max:
res += left_max - height[left]
left += 1
else:
res += right_max - height[right]
right -= 1
return res

15、接雨水II(407)


使用小顶堆的方式
- 这个视频很清晰:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cJayBq38VYw
from heapq import *
class Solution:
def trapRainWater(self, heightMap: List[List[int]]) -> int:
"""
水从高出往低处流,某个位置储水量取决于四周最低高度,从最外层向里层包抄,用小顶堆动态找到未访问位置最小的高度
"""
if not heightMap:return 0
imax = float('-inf')
ans = 0
heap = []
visited = set()
row = len(heightMap)
col = len(heightMap[0])
# 将最外层放入小顶堆
# 第一行和最后一行
for j in range(col):
# 将该位置的高度、横纵坐标插入堆
heappush(heap, [heightMap[0][j], 0, j])
heappush(heap, [heightMap[row - 1][j], row - 1, j])
visited.add((0, j))
visited.add((row - 1, j))
# 第一列和最后一列
for i in range(row):
heappush(heap, [heightMap[i][0], i, 0])
heappush(heap, [heightMap[i][col - 1], i, col - 1])
visited.add((i, 0))
visited.add((i, col - 1))
while heap:
h, i, j = heappop(heap)
# 之前最低高度的四周已经探索过了,所以要更新为次低高度开始探索
imax = max(imax, h)
# 从堆顶元素出发,探索四周储水位置
for x, y in [[0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0]]:
tmp_x = x + i
tmp_y = y + j
# 是否到达边界
if tmp_x < 0 or tmp_y < 0 or tmp_x >= row or tmp_y >= col or (tmp_x, tmp_y) in visited:
continue
visited.add((tmp_x, tmp_y))
if heightMap[tmp_x][tmp_y] < imax:
ans += imax - heightMap[tmp_x][tmp_y]
heappush(heap, [heightMap[tmp_x][tmp_y], tmp_x, tmp_y])
return ans

16、最长回文子串
class Solution:
def longestPalindrome(self, s: str) -> str:
n = len(s)
dp = [[False] * n for _ in range(n)]
ans = ""
# 枚举子串的长度 l+1
for l in range(n):
# 枚举子串的起始位置 i,这样可以通过 j=i+l 得到子串的结束位置
for i in range(n):
j = i + l
if j >= len(s):
break
if l == 0:
dp[i][j] = True
elif l == 1:
dp[i][j] = (s[i] == s[j])
else:
dp[i][j] = (dp[i + 1][j - 1] and s[i] == s[j])
if dp[i][j] and l + 1 > len(ans):
ans = s[i:j+1]
return ans
上面的代码没问题太,就是运行超时,需要进行优化
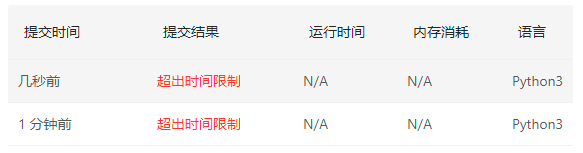
- 优化版本1
class Solution:
def expandAroundCenter(self, s, left, right):
while left >= 0 and right < len(s) and s[left] == s[right]:
left -= 1
right += 1
return left + 1, right - 1
def longestPalindrome(self, s: str) -> str:
start, end = 0, 0
for i in range(len(s)):
left1, right1 = self.expandAroundCenter(s, i, i)
left2, right2 = self.expandAroundCenter(s, i, i + 1)
if right1 - left1 > end - start:
start, end = left1, right1
if right2 - left2 > end - start:
start, end = left2, right2
return s[start: end + 1]
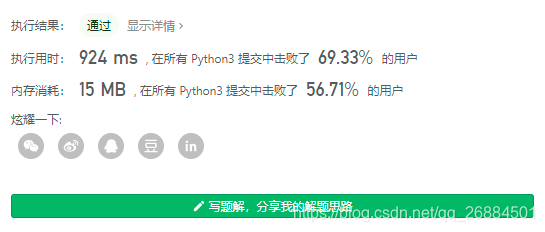
- 优化版本2
class Solution:
def expand(self, s, left, right):
while left >= 0 and right < len(s) and s[left] == s[right]:
left -= 1
right += 1
return (right - left - 2) // 2
def longestPalindrome(self, s: str) -> str:
end, start = -1, 0
s = '#' + '#'.join(list(s)) + '#'
arm_len = []
right = -1
j = -1
for i in range(len(s)):
if right >= i:
i_sym = 2 * j - i
min_arm_len = min(arm_len[i_sym], right - i)
cur_arm_len = self.expand(s, i - min_arm_len, i + min_arm_len)
else:
cur_arm_len = self.expand(s, i, i)
arm_len.append(cur_arm_len)
if i + cur_arm_len > right:
j = i
right = i + cur_arm_len
if 2 * cur_arm_len + 1 > end - start:
start = i - cur_arm_len
end = i + cur_arm_len
return s[start+1:end+1:2]
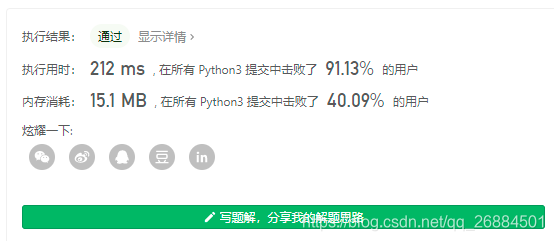
17、买卖股票的最佳时机
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
"""定义最小的价格为无穷大"""
minprice = float("inf")
res = 0
for price in prices:
"""找出最小的价格"""
minprice = min(minprice, price)
"""保存最大的利润差"""
res = max(res,price-minprice)
return res
- 使用动态规划,参考

class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
n = len(prices)
if n == 0: return 0 # 边界条件
dp = [0] * n
minprice = prices[0]
for i in range(1, n):
minprice = min(minprice, prices[i])
"""将临时最优解决存储在dp中,最后返回最优解"""
dp[i] = max(dp[i - 1], prices[i] - minprice)
return dp[-1]

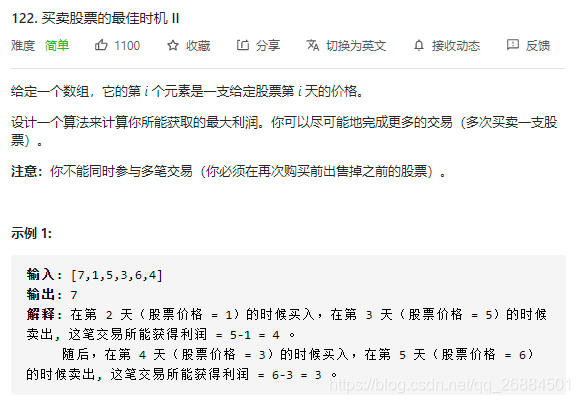
18、买卖股票的最佳时机 II
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
"""贪心算法"""
res = 0
for i in range(1,len(prices)):
"""只要今天比昨天高,就立即卖出获得收益"""
if prices[i] > prices[i-1]:
res += prices[i] - prices[i-1]
return res
使用动态规划
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
"""动态规划算法,i表示天,0表示手里没股票持有收益,1表示有股票,当天卖出的话得到截至当天的总收益"""
n = len(prices)
dp = [[0 for _ in range(2)] for _ in range(n)]
"""
第0天之前收益肯定是0,所以第0天:
如果手里面没有股票,那么收益为0;
如果有股票,说明是当天买的,当天卖出的话获得截至当天的总收益-prices[0]
"""
dp[0][0] = 0
dp[0][1] = -prices[0]
for i in range(1,n):
"""
今天手中没有股票:
1、前一天手中也没有股票;
2、前一天手中有股票,今天卖掉了,所以利润加上销售所得prices[i]
"""
dp[i][0] = max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] + prices[i])
"""
今天手中有股票:
1、前一天手中也股票;
2、前一天手中没有股票,今天买了,所以利润减去开销prices[i]
"""
dp[i][1] = max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] - prices[i])
"""返回最后一天手里没有股票的最大收益。截至前一天的利润一定是最大化的,如果考虑今天手中股票说明今天买的,还要减去卖股的钱,利润就会变少"""
return dp[n - 1][0]
19、约瑟夫环
class Solution:
def lastRemaining(self, n: int, m: int) -> int:
if n == 1:
return 0
last = 0
for i in range(2, n + 1):
last = (last + m) % i
return last
n = 5
m = 3
s = Solution()
print(s.lastRemaining(n, m))
20、二叉树最大深度
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root: return 0
return max(self.maxDepth(root.left), self.maxDepth(root.right)) + 1
21、二叉树非递归中序遍历
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
TreeNode *predecessor = nullptr;
while (root != nullptr) {
if (root->left != nullptr) {
// predecessor 节点就是当前 root 节点向左走一步,然后一直向右走至无法走为止
predecessor = root->left;
while (predecessor->right != nullptr && predecessor->right != root) {
predecessor = predecessor->right;
}
// 让 predecessor 的右指针指向 root,继续遍历左子树
if (predecessor->right == nullptr) {
predecessor->right = root;
root = root->left;
}
// 说明左子树已经访问完了,我们需要断开链接
else {
res.push_back(root->val);
predecessor->right = nullptr;
root = root->right;
}
}
// 如果没有左孩子,则直接访问右孩子
else {
res.push_back(root->val);
root = root->right;
}
}
return res;
}
};
22、二叉树最大通路
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
递归求解
class Solution {
public int maxHeight(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
return maxChildHeight(root.left) + maxChildHeight(root.right);
}
public int maxChildHeight(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = maxChildHeight(root.left);
int rightHeight = maxChildHeight(root.right);
return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
}
}
迭代求解
public class Solution {
public int maxHeight(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
return maxChildHeight(root.left) + maxChildHeight(root.right);
}
public int maxChildHeight(TreeNode root) {
int height = 0;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
height++;
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
}
return height;
}
}
23、牛顿法求解方程

通过上面的解释就可以对方程进行求解了,比如下面这道题

相当于是求解f(x) = x**2 -m使得f(x) =0的解,当然这里的f(x)只能无限的趋近于零,因为要保留小数点的后4位,我们可以令f(x)=1e-5
f’(x) = 2x,带入上面的泰勒展开式的求解方程中,可以得到x=x0/2-(x0**2-m)/2*x0

def newton(m):
x0 = m/2 #初始点,也可以是别的值
x1 = x0/2 + m/(x0*2)
while abs(x1-x0)>1e-5:
x0 = x1
x1 = x0/2 + m/(x0*2)
return x1
#输出精确到小数点后四位
print('%.4f'%newton(2))
"""
1.4142
"""
同理我们可以得到算术立方根的求解方法
f(x) = x**3 -m
f’(x) = 3x**2
带入公式可得x1 = 2*x0/3 + m/(3*x0**2)
代码实现:
def three_sqr(m):
x0 = m/2
x1 = 2*x0/3 + m/(3*x0**2)
while abs(x1-x0) > 1e-5:
x0 = x1
x1 = 2*x0/3 + m/(3*x0**2)
return x1
print( '%.4f'%three_sqr(5))
print(1.71**3)
"""
1.7100
5.000210999999999
"""
同理可得算术q阶根
def q_sqr(m,q):
x0 = m/2
x1 = x0 - (x0**q-m)/(q*x0**(q-1))
while abs(x1-x0) > 1e-5:
x0 = x1
x1 = x0 - (x0**q-m)/(q*x0**(q-1))
return x1
print( '%.4f'%q_sqr(8,4))
print(1.6818**4)
"""
1.6818
8.000136417057536
"""
利用魔法数字求解

float Q_rsqrt( float number )
{
long i;
float x2, y;
const float threehalfs = 1.5F;
x2 = number * 0.5F;
y = number;
i = * ( long * ) &y; // evil floating point bit level hacking
i = 0x5f3759df - ( i >> 1 ); // what the fuck?
y = * ( float * ) &i;
y = y * ( threehalfs - ( x2 * y * y ) ); // 1st iteration
// y = y * ( threehalfs - ( x2 * y * y ) ); // 2nd iteration, this can be removed
#ifndef Q3_VM
#ifdef __linux__
assert( !isnan(y) ); // bk010122 - FPE?
#endif
#endif
return y;
}
加速版本
float InvSqrt(float x)
{
float xhalf = 0.5f * x;
int i = *(int *)&x;
i = 0x5f3759df - (i>>1);
x = *(float *)&i;
x = x * (1.5f - xhalf * x * x);
return x;
}
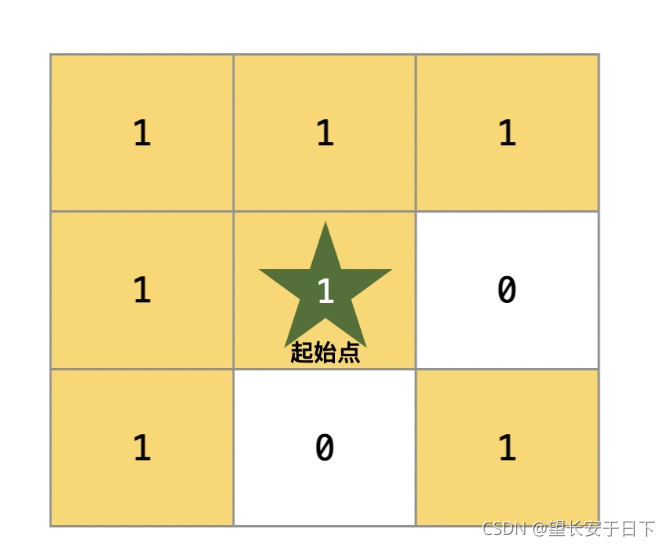
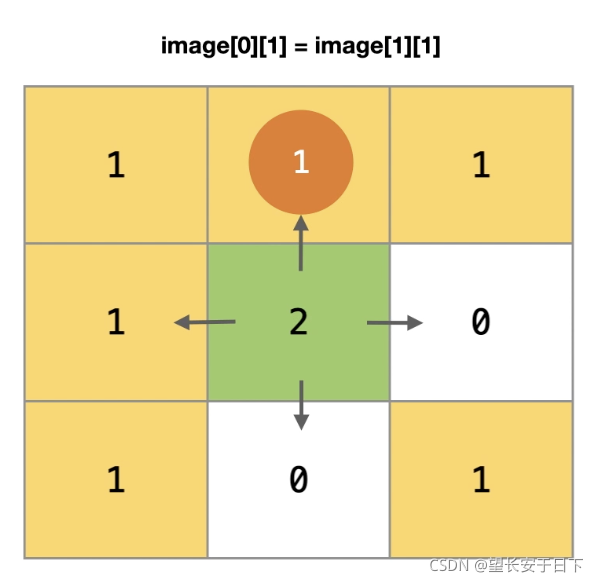
24. 图像渲染
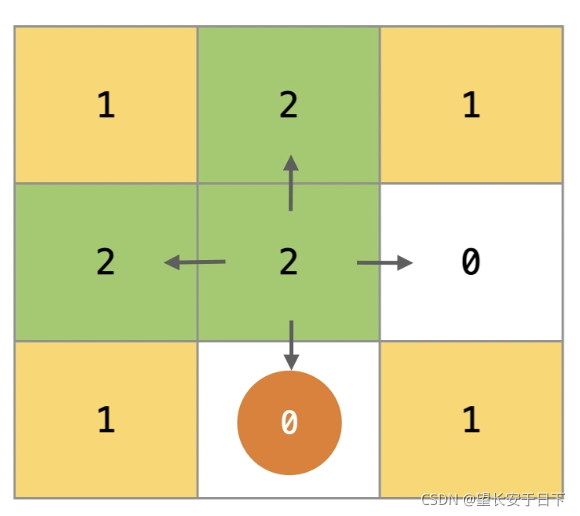
class Solution:#使用递归
def floodFill(self, image: List[List[int]], sr: int, sc: int, newColor: int) -> List[List[int]]:
if image[sr][sc] != newColor:
old,image[sr][sc] = image[sr][sc], newColor
for i,j in zip((sr,sr+1,sr,sr-1),(sc+1,sc,sc-1,sc)):
if 0 <= i < len(image) and 0 <= j < len(image[0]) and image[i][j] == old:#边界条件,不能超出长和宽,并且还要颜色不一样
self.floodFill(image,i,j,newColor)
return image
26. 最大岛屿
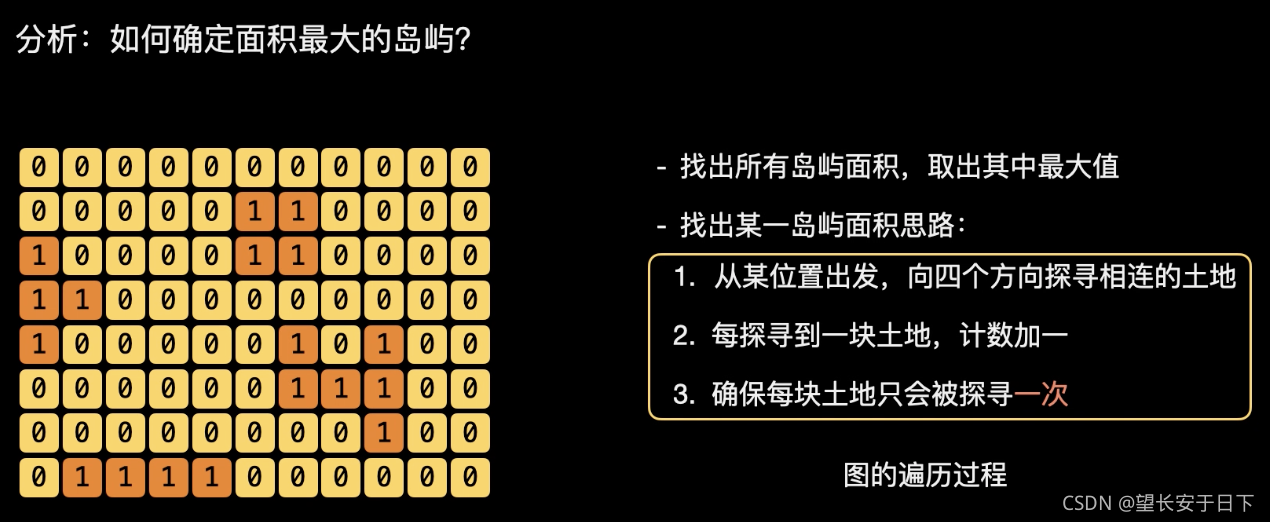

"""深度优先+栈"""
"""
方法一通过函数的调用来表示接下来想要遍历哪些土地,让下一层函数来访问这些土地。而方法二把接下来想要遍历的土地放在栈里,然后在取出这些土地的时候访问它们。
访问每一片土地时,我们将对围绕它四个方向进行探索,找到还未访问的土地,加入到栈 stack 中;
另外,只要栈 stack 不为空,就说明我们还有土地待访问,那么就从栈中取出一个元素并访问。
"""
class Solution:
def maxAreaOfIsland(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
ans = 0
for i, l in enumerate(grid):
for j, n in enumerate(l):
cur = 0
stack = [(i, j)]
while stack:
cur_i, cur_j = stack.pop()
if cur_i < 0 or cur_j < 0 or cur_i == len(grid) or cur_j == len(grid[0]) or grid[cur_i][cur_j] != 1:
continue
cur += 1
grid[cur_i][cur_j] = 0
for di, dj in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
next_i, next_j = cur_i + di, cur_j + dj
stack.append((next_i, next_j))
ans = max(ans, cur)
return ans
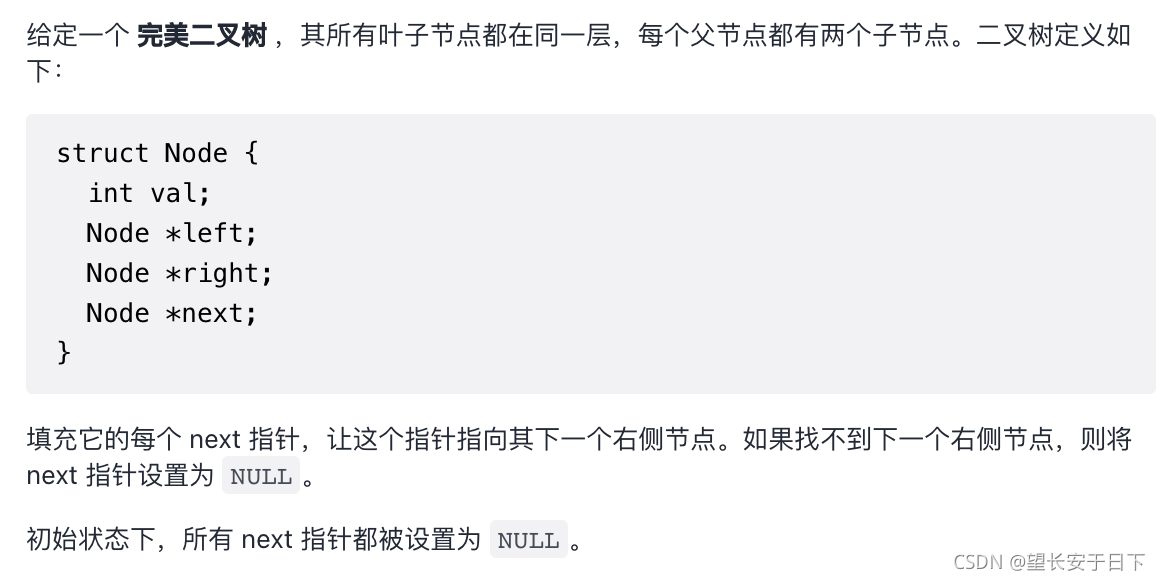
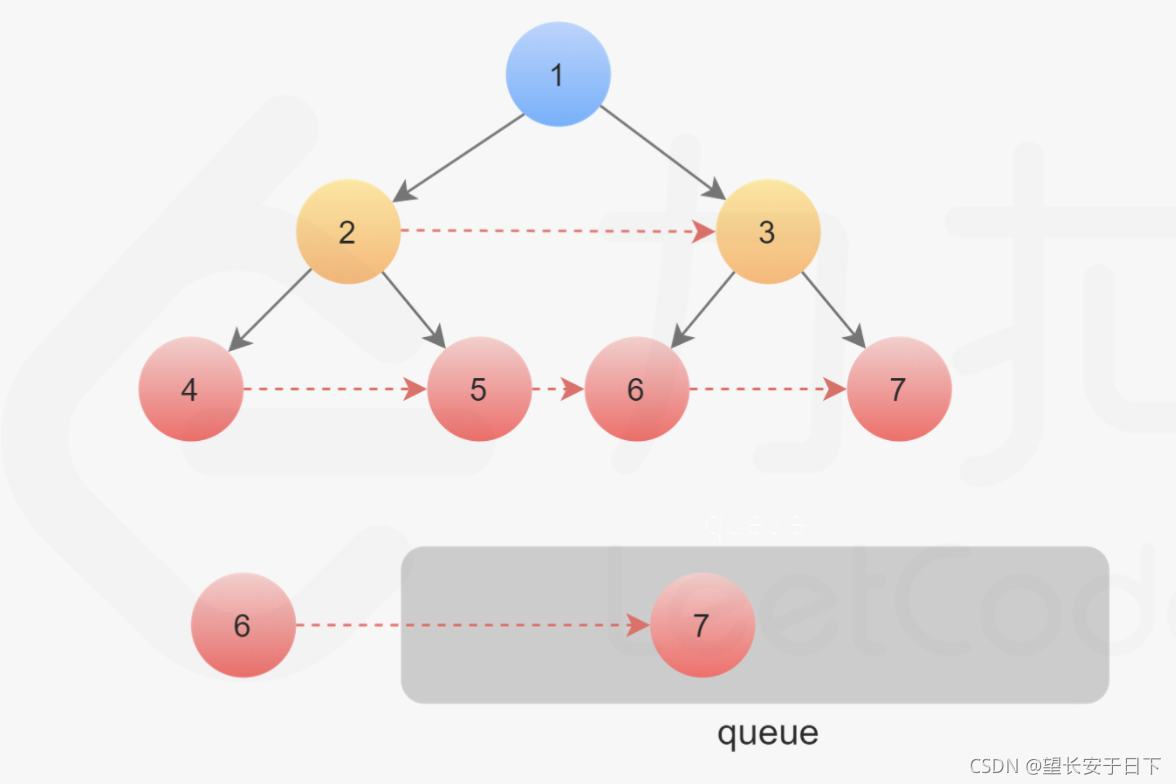
27.完美二叉树
28. 矩阵






















 430
430

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








