Java实现二叉排序树
1.二叉树的概念和特点
1.1二叉树
- 特点
- 每个节点最多有两颗子树
- 左子树和右子树是有顺序的,次序不能颠倒。
- 即使某个节点只有一个子树,也要区分左右子树
- 图示
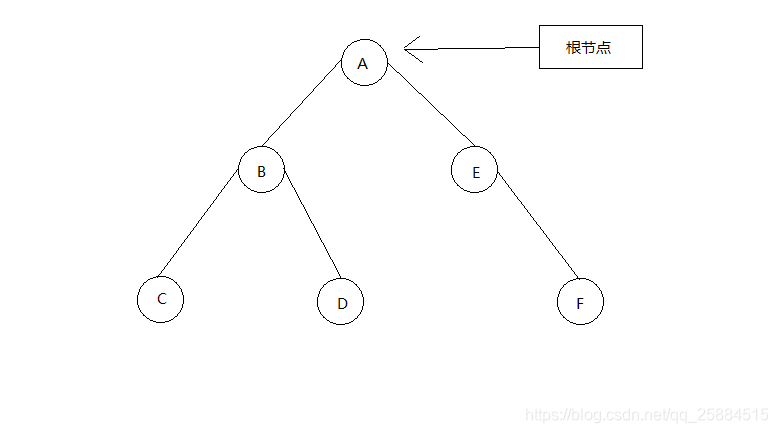
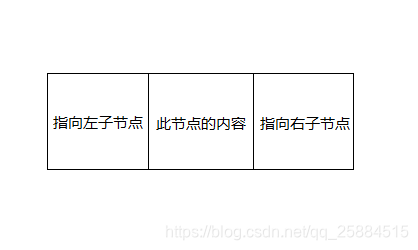
1.2节点
1.3二叉排序树
- 二叉排序树的特点
- 每个根节点中的左子节点的值都小于根节点中的值
- 每个根节点中的右子节点的值都大于根节点中的值
- 树中没有重复的值
2.实现二叉排序树
2.1实现节点
public class Node {
private int value;
private Node leftNode;
private Node rightNode;
public Node(){
}
public Node(int value){
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"value=" + value +
'}';
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Node getLeftNode() {
return leftNode;
}
public void setLeftNode(Node leftNode) {
this.leftNode = leftNode;
}
public Node getRightNode() {
return rightNode;
}
public void setRightNode(Node rightNode) {
this.rightNode = rightNode;
}
}
2.2实现二叉树
public class BinaryTree {
private Node root;
public BinaryTree(){
}
public BinaryTree(Node root){
this.root = root;
}
public Node getRoot() {
return root;
}
}
2.3添加节点方法
public boolean add(int value){
if (this.root == null){
this.root = new Node(value);
return true;
}else{
Node current = root;
while (true){
if (value < current.getValue()){
if (current.getLeftNode() == null){
current.setLeftNode(new Node(value));
return true;
}else{
current = current.getLeftNode();
}
}else if (value > current.getValue()){
if (current.getRightNode() == null){
current.setRightNode(new Node(value));
return true;
}else{
current = current.getRightNode();
}
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
}
2.4获取指定节点
public Node get(int value){
Node current = root;
while(true){
if (value == current.getValue()){
return current;
}else if (value < current.getValue()){
current = current.getLeftNode();
}else if (value > current.getValue()){
current = current.getRightNode();
}
if (current == null){
return null;
}
}
}
2.5遍历二叉树
public void order(Node node){
if (node == null) return;
order(node.getLeftNode());
System.out.println(node);
order(node.getRightNode());
}
2.6toString()方法遍历
private String restr;
public void order2(Node node){
if (node == null) return;
order2(node.getLeftNode());
restr = restr + " " + node.getValue();
order2(node.getRightNode());
}
- 在
BinaryTree中重写toString()方法
@Override
public String toString() {
restr = "[";
order2(root);
return restr+" ]";
}
2.7测试
int[] a = {3, 1, 0, 2, 7, 5, 8, 9};
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
for (int i : a) {
binaryTree.add(i);
}
System.out.println(binaryTree.get(5));
binaryTree.order(binaryTree.getRoot());
System.out.println(binaryTree);
Node{value=5}
Node{value=0}
Node{value=1}
Node{value=2}
Node{value=3}
Node{value=5}
Node{value=7}
Node{value=8}
Node{value=9}
[ 0 1 2 3 5 7 8 9 ]










 本文详细介绍了二叉树的概念和特点,包括其每个节点最多有两个子树、左子树值小于根节点值、右子树值大于根节点值等特性。接着,通过Java代码实现了二叉排序树的节点、二叉树结构,并提供了添加节点、获取指定节点及遍历二叉树的方法。最后,进行了测试并展示了输出结果。
本文详细介绍了二叉树的概念和特点,包括其每个节点最多有两个子树、左子树值小于根节点值、右子树值大于根节点值等特性。接着,通过Java代码实现了二叉排序树的节点、二叉树结构,并提供了添加节点、获取指定节点及遍历二叉树的方法。最后,进行了测试并展示了输出结果。

















 156
156

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










