(尊重劳动成果,转载请注明出处:http://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_25827845/article/details/72026734冷血之心的博客)
总结下面试题中常见的单链表反转:
- 常规的反转单链表
- 以K个为一组反转单链表,最后不足K个节点的部分也反转
- 以K个为一组反转单链表,最后不足K个节点的部分不反转
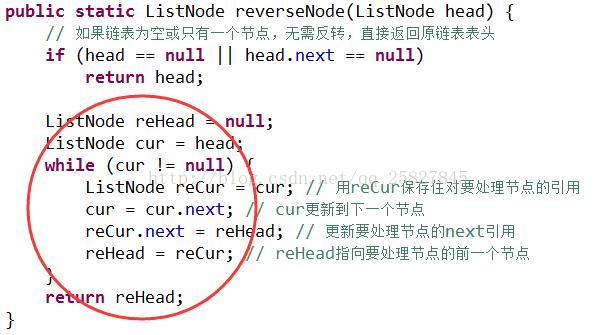
1、反转单链表:
代码如下:
/*
* 翻转链表(遍历)
* 从头到尾遍历原链表,每遍历一个结点,
* 将其摘下放在新链表的最前端。
* 注意链表为空和只有一个结点的情况。时间复杂度为O(n)
*/
public static ListNode reverseNode(ListNode head){
// 如果链表为空或只有一个节点,无需反转,直接返回原链表表头
if(head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode reHead = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode reCur = cur; // 用reCur保存住对要处理节点的引用
cur = cur.next; // cur更新到下一个节点
reCur.next = reHead; // 更新要处理节点的next引用
reHead = reCur; // reHead指向要处理节点的前一个节点
}
return reHead;
}2、以K个为一组反转单链表,最后不足K个节点的部分也反转
/**
* 分组反转单链表,最后不足K个节点的部分也反转
* @param head
* @param k
* @return
*/
public static ListNode reverseKgroup(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null)
return head;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode reHead = null;
int count = 0;
/* Reverse first k nodes of linked list */
while (count < k && cur != null) {
ListNode reCur = cur;
cur = cur.next;
reCur.next = reHead;
reHead = reCur;
count++;
}
/*
* cur is now a pointer to (k+1)th node Recursively call for the
* list starting from current. And make rest of the list as next of
* first node
*/
if (cur != null)
head.next = reverseKgroup(cur, k);
return reHead;
}举例解释:
输入的原始单链表为3-5-6-9-7-2-1-12,其中K为3;
经过第一次while循环,单链表变为6-5-3-9-7-2-1-12。此时跳出while循环是因为count<k不成立了,cur节点指向了9,head节点指向了3。所以接着判断cur是否为null,若不是,则刚好递归求出head.next。
经过第二次while循环,单链表为6-5-3-2-7-9-1-12。此时跳出while循环是因为count<k不成立了,cur节点指向了1,head节点指向了9。接着判断cur,并且递归求head.next节点。
第三次循环,跳出while是因为cur==null了,直接返回reHead,此时reHead指向了12。
可以看出,K个为一组反转单链表,核心代码还是常规的如何反转单链表。
3、以K个为一组反转单链表,最后不足K个节点的部分不反转
这是一道LeetCode原题:https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/#/description
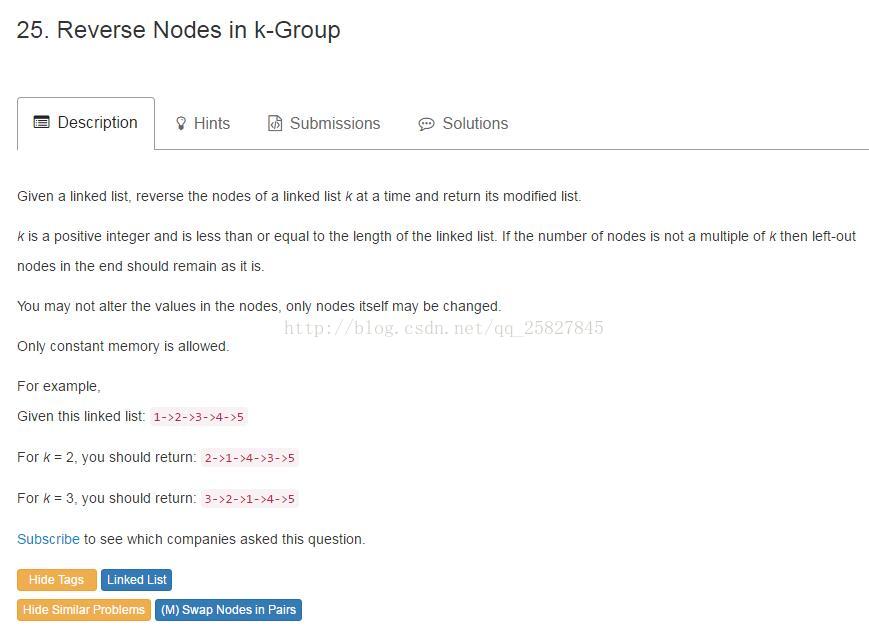
思路:核心代码还是反转常规的单链表,不过此题需要加上节点数量的判断,当节点数目不足K个时,不进行反转操作,直接返回。
/**
* 分组反转单链表,最后不足K个节点的部分不反转
* @param head
* @param k
* @return
*/
public static ListNode reverseKgroups(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null)
return head;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode reHead = null;
int count = 0;
if (getSize(cur) >= k) {
/* Reverse first k nodes of linked list */
while (count < k && cur != null) {
ListNode reCur = cur;
cur = cur.next;
reCur.next = reHead;
reHead = reCur;
count++;
}
/*
* cur is now a pointer to (k+1)th node Recursively call for the
* list starting from current. And make rest of the list as next of
* first node
*/
if (cur != null)
head.next = reverseKgroups(cur, k);
return reHead;
}
return cur;
}统计节点数目函数如下:
/**
* 统计该节点之后的节点数量
* @param head
* @return
*/
public static int getSize(ListNode head) {
int count = 0;
ListNode curNode = head;
while (curNode != null) {
count++;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
return count;
}AC结果如下:
总结:
各个形式的反转单链表,最重要的理清楚head、reHead和cur三个节点的关系,通过核心代码和方法的递归来实现分组反转。
附上完整代码:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(3);
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(5);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(6);
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(9);
ListNode node4 = new ListNode(7);
ListNode node5 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode node6 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode node7 = new ListNode(12);
head.next = node1;
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
node4.next = node5;
node5.next = node6;
node6.next = node7;
printList(head);
// printList(reverseNode(head));
// printList(reverseKgroups(head, 3));
printList(reverseKgroup(head, 3));
}
// 打印链表的方法,方便test函数
public static void printList(ListNode head) {
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.val + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 分组反转单链表,最后不足K个节点的部分不反转
* @param head
* @param k
* @return
*/
public static ListNode reverseKgroups(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null)
return head;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode reHead = null;
int count = 0;
if (getSize(cur) >= k) {
/* Reverse first k nodes of linked list */
while (count < k && cur != null) {
ListNode reCur = cur;
cur = cur.next;
reCur.next = reHead;
reHead = reCur;
count++;
}
/*
* cur is now a pointer to (k+1)th node Recursively call for the
* list starting from current. And make rest of the list as next of
* first node
*/
if (cur != null)
head.next = reverseKgroups(cur, k);
return reHead;
}
return cur;
}
/**
* 分组反转单链表,最后不足K个节点的部分也反转
* @param head
* @param k
* @return
*/
public static ListNode reverseKgroup(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null)
return head;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode reHead = null;
int count = 0;
/* Reverse first k nodes of linked list */
while (count < k && cur != null) {
ListNode reCur = cur;
cur = cur.next;
reCur.next = reHead;
reHead = reCur;
count++;
}
/*
* cur is now a pointer to (k+1)th node Recursively call for the
* list starting from current. And make rest of the list as next of
* first node
*/
if (cur != null)
head.next = reverseKgroup(cur, k);
return reHead;
}
/**
* 统计该节点之后的节点数量
* @param head
* @return
*/
public static int getSize(ListNode head) {
int count = 0;
ListNode curNode = head;
while (curNode != null) {
count++;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
return count;
}
/*
* 翻转链表(遍历) 从头到尾遍历原链表,每遍历一个结点, 将其摘下放在新链表的最前端。 注意链表为空和只有一个结点的情况。时间复杂度为O(n)
*/
public static ListNode reverseNode(ListNode head) {
// 如果链表为空或只有一个节点,无需反转,直接返回原链表表头
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode reHead = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode reCur = cur; // 用reCur保存住对要处理节点的引用
cur = cur.next; // cur更新到下一个节点
reCur.next = reHead; // 更新要处理节点的next引用
reHead = reCur; // reHead指向要处理节点的前一个节点
}
return reHead;
}
}
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
如果对你有帮助,记得点赞哦~欢迎大家关注我的博客,可以进群366533258一起交流学习哦~











 本文总结了三种常见的单链表反转面试题:常规反转、以K个为一组反转(包括不足K个节点反转和不反转的情况)。通过分析代码和关键节点关系,详细解析了反转过程,并提供了完整解决方案。
本文总结了三种常见的单链表反转面试题:常规反转、以K个为一组反转(包括不足K个节点反转和不反转的情况)。通过分析代码和关键节点关系,详细解析了反转过程,并提供了完整解决方案。



















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










