函数基本知识
函数原型
按值传递函数参数
设计处理数组的函数
使用const指针参数
设计处理文本字符串的函数
设计处理结构的函数
设计处理string对象的函数
调用自身的函数(递归)
指向函数的指针
目录
7.1 复习函数的基本知识
C++自带包含函数的大型库
提供函数定义
提供函数原型
调用函数// calling.cpp -- defining, prototyping, and calling a function
#include <iostream>
void simple(); // function prototype
int main()
{
using namespace std;
cout << "main() will call the simple() function:\n";
simple(); // function call
cout << "main() is finished with the simple() function.\n";
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
// function definition
void simple()
{
using namespace std;
cout << "I'm but a simple function.\n";
}
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ g++ calling.cpp
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ ./a.out
main() will call the simple() function:
I'm but a simple function.
main() is finished with the simple() function.7.1.1 定义函数
对于有返回值的函数,结果的类型被转化为typeName的类型,
对于返回值的类型,不能是数组,但可以是其他类型
7.1.2 函数原型和函数调用
// calling.cpp -- defining, prototyping, and calling a function
#include <iostream>
void simple(); // function prototype
int main()
{
using namespace std;
cout << "main() will call the simple() function:\n";
simple(); // function call
cout << "main() is finished with the simple() function.\n";
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
// function definition
void simple()
{
using namespace std;
cout << "I'm but a simple function.\n";
}
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ g++ protos.cpp
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ ./a.out
Cheers! Cheers! Cheers! Cheers! Cheers!
Give me a number: 5
A 5-foot cube has a volume of 125 cubic feet.
Cheers! Cheers! Cheers! Cheers! Cheers! Cheers! Cheers! Cheers! 

原型的功能:
(1)编译器正确处理函数返回值
(2)编译器检查使用的参数数目是否正确
(3)编译器检查使用的参数类型是否正确,如果不正确,则转换为正确的类型(如果可能)7.2 定义函数
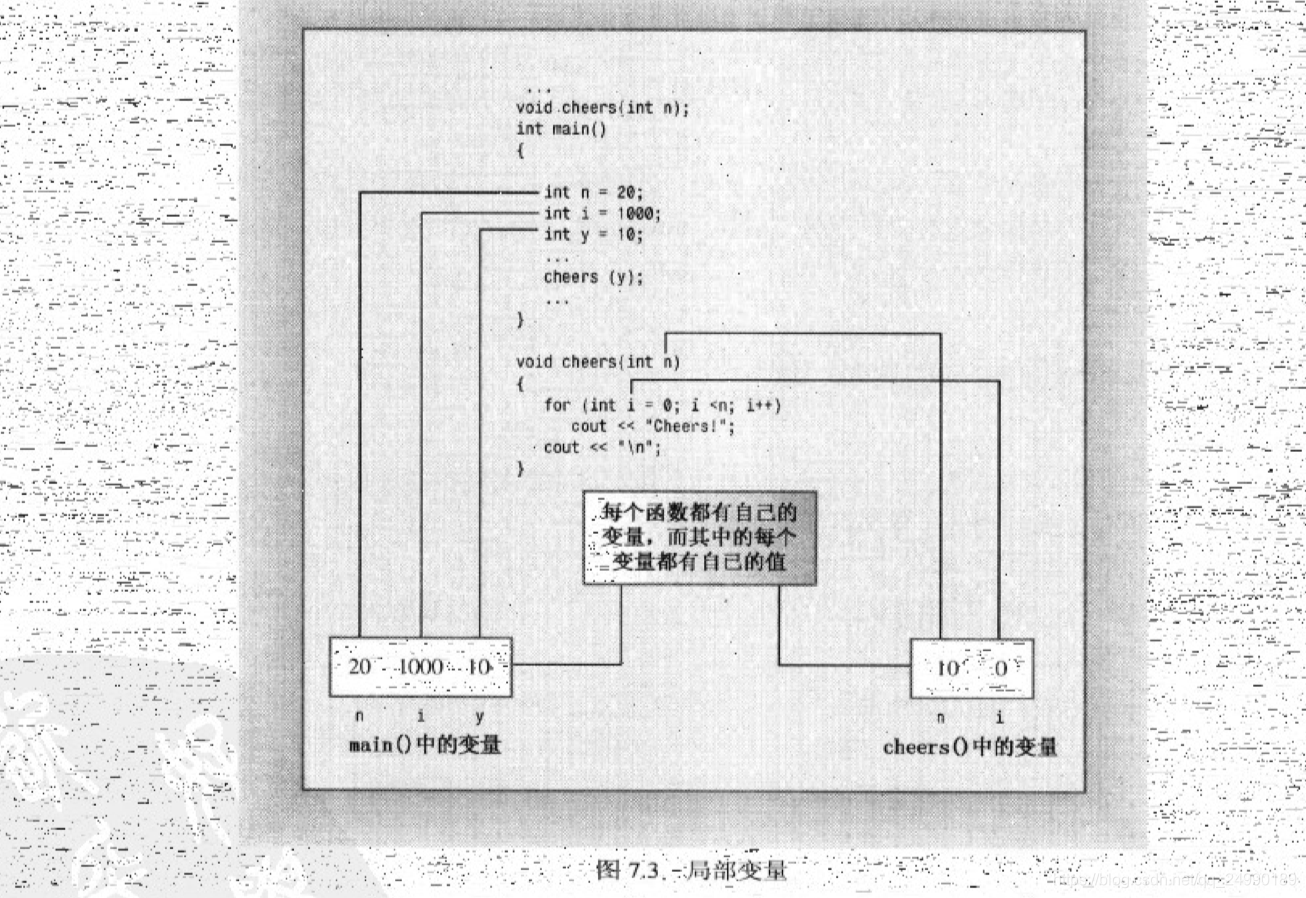
C++标准使用argument表示实参,使用parameter表示行参
在函数中声明的变量(包括参数)是该函数私有的。在函数被调用时,计算机将为这些变量分配内存;在函数结束时,计算机将释放这些变量使用的内存(C++将分配和释放内存称为创建和毁坏变量),保证了数据的完整性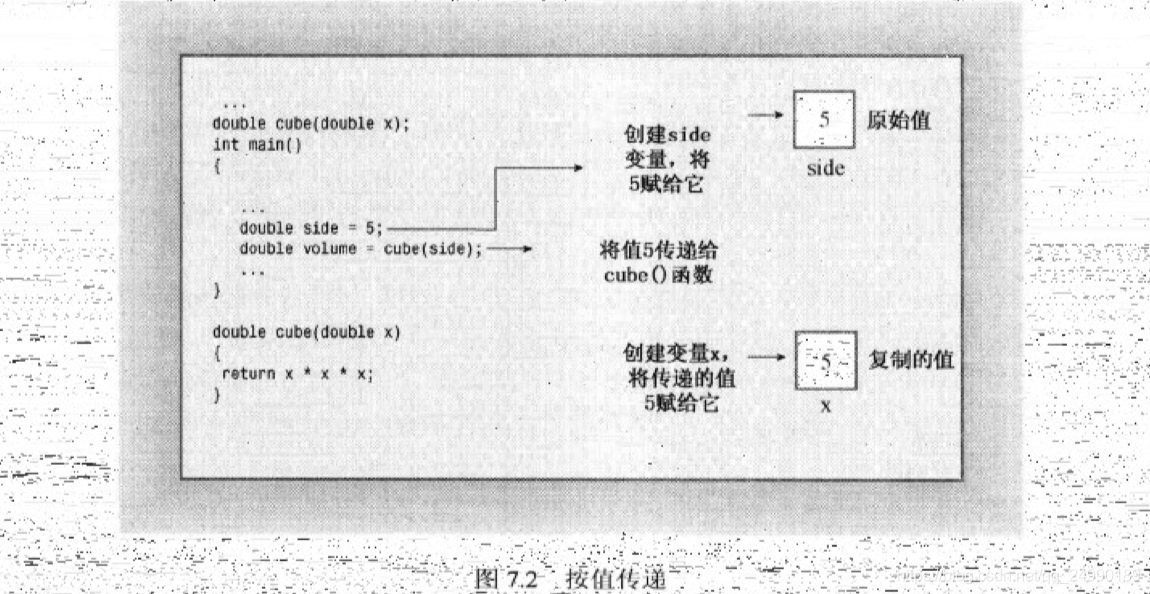
7.2.1 多个参数
// twoarg.cpp -- a function with 2 arguments
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void n_chars(char, int);
int main()
{
int times;
char ch;
cout << "Enter a character: ";
cin >> ch;
while (ch != 'q') // q to quit
{
cout << "Enter an integer: ";
cin >> times;
n_chars(ch, times); // function with two arguments
cout << "\nEnter another character or press the"
" q-key to quit: ";
cin >> ch;
}
cout << "The value of times is " << times << ".\n";
cout << "Bye\n";
// cin.get();
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
void n_chars(char c, int n) // displays c n times
{
while (n-- > 0) // continue until n reaches 0
cout << c;
}
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ g++ twoarg.cpp
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ ./a.out
Enter a character: W
Enter an integer: 79
WWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWW
Enter another character or press the q-key to quit: q
The value of times is 79.
Bye使用cin>>ch的原因是
两个cin.get()函数读取所有的输入字符,包括空格和换行符。而cin>>跳过空格和换行符
当用户对程序提示作出响应时,必须在每行的最后按Enter键,生成换行符,而cin>>ch可以跳过这些换行符,7.2.2 另外一个接受两个参数的函数
// lotto.cpp -- probability of winning
#include <iostream>
// Note: some implementations require double instead of long double
long double probability(unsigned numbers, unsigned picks);
int main()
{
using namespace std;
double total, choices;
cout << "Enter the total number of choices on the game card and\n"
"the number of picks allowed:\n";
while ((cin >> total >> choices) && choices <= total)
{
cout << "You have one chance in ";
cout << probability(total, choices); // compute the odds
cout << " of winning.\n";
cout << "Next two numbers (q to quit): ";
}
cout << "bye\n";
// cin.get();
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
// the following function calculates the probability of picking picks
// numbers correctly from numbers choices
long double probability(unsigned numbers, unsigned picks)
{
long double result = 1.0; // here come some local variables
long double n;
unsigned p;
for (n = numbers, p = picks; p > 0; n--, p--)
result = result * n / p ;
return result;
}
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ g++ lotto.cpp
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ ./a.out
Enter the total number of choices on the game card and
the number of picks allowed:
49 6
You have one chance in 1.39838e+07 of winning.
Next two numbers (q to quit): 51 6
You have one chance in 1.80095e+07 of winning.
Next two numbers (q to quit): q
bye7.3 函数和数组
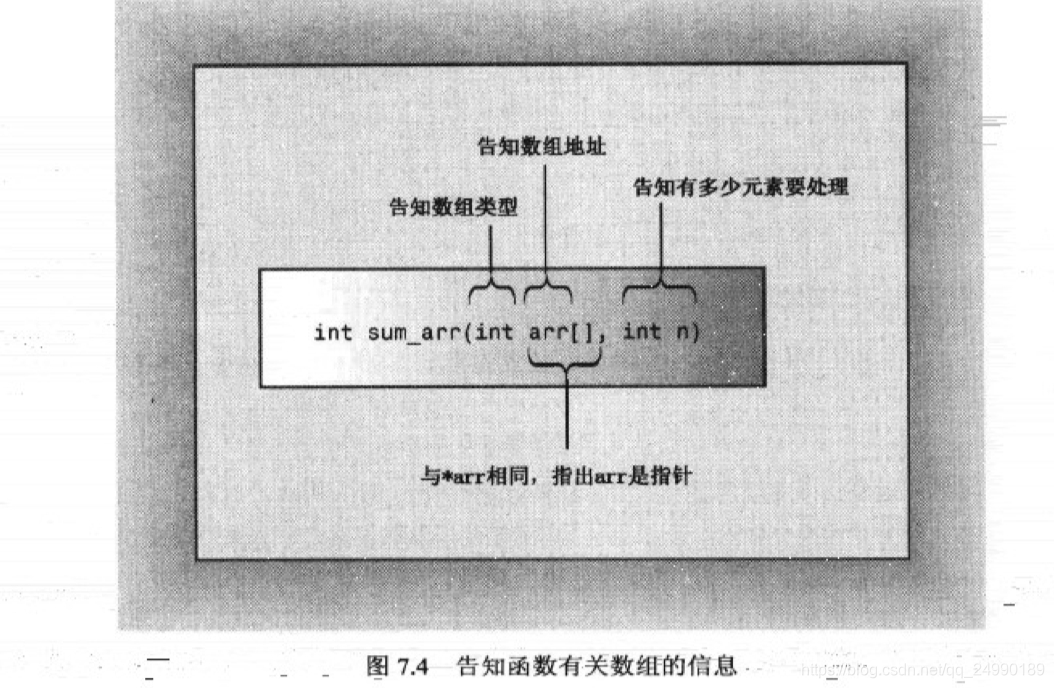
int sum_arr(int arr[], int n);
arr是指针,看作可以将如何长度的数组传递给该函数// arrfun1.cpp -- functions with an array argument
#include <iostream>
const int ArSize = 8;
int sum_arr(int arr[], int n); // prototype
int main()
{
using namespace std;
int cookies[ArSize] = {1,2,4,8,16,32,64,128};
// some systems require preceding int with static to
// enable array initialization
int sum = sum_arr(cookies, ArSize);
cout << "Total cookies eaten: " << sum << "\n";
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
// return the sum of an integer array
int sum_arr(int arr[], int n)
{
int total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
total = total + arr[i];
return total;
}
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ g++ arrfun1.cpp
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ ./a.out
Total cookies eaten: 2557.3.1 函数如何使用指针来处理数组
cookies == &cokkies[0] //array name is address of first element

7.3.2 将数组作为参数意味着什么

// arrfun2.cpp -- functions with an array argument
#include <iostream>
const int ArSize = 8;
int sum_arr(int arr[], int n);
// use std:: instead of using directive
int main()
{
int cookies[ArSize] = {1,2,4,8,16,32,64,128};
// some systems require preceding int with static to
// enable array initialization
std::cout << cookies << " = array address, ";
// some systems require a type cast: unsigned (cookies)
std::cout << sizeof cookies << " = sizeof cookies\n";
int sum = sum_arr(cookies, ArSize);
std::cout << "Total cookies eaten: " << sum << std::endl;
sum = sum_arr(cookies, 3); // a lie
std::cout << "First three eaters ate " << sum << " cookies.\n";
sum = sum_arr(cookies + 4, 4); // another lie
std::cout << "Last four eaters ate " << sum << " cookies.\n";
// std::cin.get();
return 0;
}
// return the sum of an integer array
int sum_arr(int arr[], int n)
{
int total = 0;
std::cout << arr << " = arr, ";
// some systems require a type cast: unsigned (arr)
std::cout << sizeof arr << " = sizeof arr\n";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
total = total + arr[i];
return total;
}
0x7ffeefbff500 = array address, 32 = sizeof cookies
0x7ffeefbff500 = arr, 8 = sizeof arr
Total cookies eaten: 255
0x7ffeefbff500 = arr, 8 = sizeof arr
First three eaters ate 7 cookies.
0x7ffeefbff510 = arr, 8 = sizeof arr
Last four eaters ate 240 cookies.
Program ended with exit code: 0sizeof cookies是整个数组的长度,而sizeof arr是指针变量的长度
注意:
void filArray(int arr[], in size)//
void filArray(int arr[size])7.3.3 更多数组函数示例
// arrfun3.cpp -- array functions and const
#include <iostream>
const int Max = 5;
// function prototypes
int fill_array(double ar[], int limit);
void show_array(const double ar[], int n); // don't change data
void revalue(double r, double ar[], int n);
int main()
{
using namespace std;
double properties[Max];
int size = fill_array(properties, Max);
show_array(properties, size);
if (size > 0)
{
cout << "Enter revaluation factor: ";
double factor;
while (!(cin >> factor)) // bad input
{
cin.clear();
while (cin.get() != '\n')
continue;
cout << "Bad input; Please enter a number: ";
}
revalue(factor, properties, size);
show_array(properties, size);
}
cout << "Done.\n";
// cin.get();
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
int fill_array(double ar[], int limit)
{
using namespace std;
double temp;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < limit; i++)
{
cout << "Enter value #" << (i + 1) << ": ";
cin >> temp;
if (!cin) // bad input
{
cin.clear();
while (cin.get() != '\n')
continue;
cout << "Bad input; input process terminated.\n";
break;
}
else if (temp < 0) // signal to terminate
break;
ar[i] = temp;
}
return i;
}
// the following function can use, but not alter,
// the array whose address is ar
void show_array(const double ar[], int n)
{
using namespace std;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cout << "Property #" << (i + 1) << ": $";
cout << ar[i] << endl;
}
}
// multiplies each element of ar[] by r
void revalue(double r, double ar[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
ar[i] *= r;
}
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ g++ arrfun3.cpp
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ ./a.out
Enter value #1: 100000
Enter value #2: 8000
Enter value #3: 222000
Enter value #4: 240000
Enter value #5: 118000
Property #1: $100000
Property #2: $8000
Property #3: $222000
Property #4: $240000
Property #5: $118000
Enter revaluation factor: 0.8
Property #1: $80000
Property #2: $6400
Property #3: $177600
Property #4: $192000
Property #5: $94400
Done.C++将声明const double ar [] 解释为 const double *ar;7.3.4 使用数组区间的函数
// arrfun4.cpp -- functions with an array range
#include <iostream>
const int ArSize = 8;
int sum_arr(const int * begin, const int * end);
int main()
{
using namespace std;
int cookies[ArSize] = {1,2,4,8,16,32,64,128};
// some systems require preceding int with static to
// enable array initialization
int sum = sum_arr(cookies, cookies + ArSize);
cout << "Total cookies eaten: " << sum << endl;
sum = sum_arr(cookies, cookies + 3); // first 3 elements
cout << "First three eaters ate " << sum << " cookies.\n";
sum = sum_arr(cookies + 4, cookies + 8); // last 4 elements
cout << "Last four eaters ate " << sum << " cookies.\n";
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
// return the sum of an integer array
int sum_arr(const int * begin, const int * end)
{
const int * pt;
int total = 0;
for (pt = begin; pt != end; pt++)
total = total + *pt;
return total;
}[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ g++ arrfun4.cpp
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ ./a.out
Total cookies eaten: 255
First three eaters ate 7 cookies.
Last four eaters ate 240 cookies.7.3.5 指针和const
C++禁止将const的地址赋给非const指针
const float g_earth = 9.80;
(const) float* pe = &g_earth;
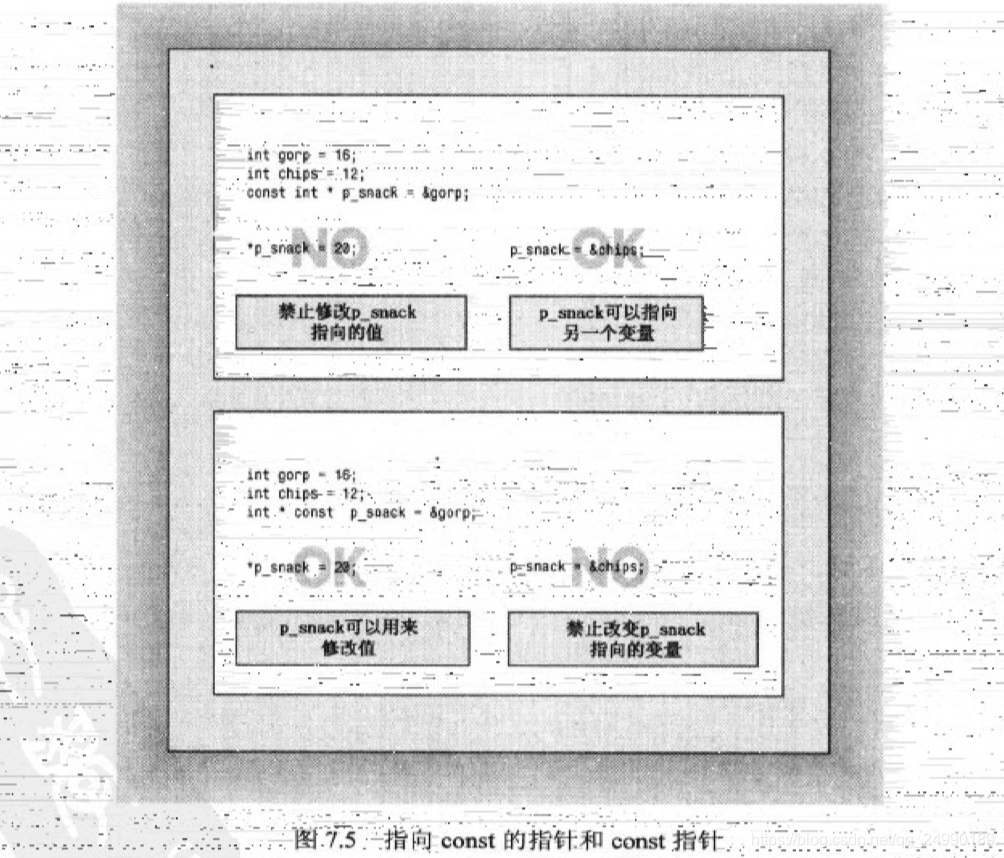
double trouble = 2..0E30;
const double* const stick = &trouble;
stick只能指向trouble, 而stick不能用来修改trouble的值。7.4 函数和二维数组


7.5 函数和C-风格字符串
7.5.1 将C-风格字符串作为参数的函数

// strgfun.cpp -- functions with a string argument
#include <iostream>
unsigned int c_in_str(const char * str, char ch);
int main()
{
using namespace std;
char mmm[15] = "minimum"; // string in an array
// some systems require preceding char with static to
// enable array initialization
char *wail = "ululate"; // wail points to string
unsigned int ms = c_in_str(mmm, 'm');
unsigned int us = c_in_str(wail, 'u');
cout << ms << " m characters in " << mmm << endl;
cout << us << " u characters in " << wail << endl;
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
// this function counts the number of ch characters
// in the string str
unsigned int c_in_str(const char * str, char ch)
{
unsigned int count = 0;
while (*str) // quit when *str is '\0'
{
if (*str == ch)
count++;
str++; // move pointer to next char
}
return count;
}
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ g++ strgfun.cpp
strgfun.cpp:11:18: warning: conversion from string literal to 'char *' is deprecated [-Wc++11-compat-deprecated-writable-strings]
char *wail = "ululate"; // wail points to string
^
1 warning generated.7.5.2 返回C-风格字符串的函数
// strgback.cpp -- a function that returns a pointer to char
#include <iostream>
char * buildstr(char c, int n); // prototype
int main()
{
using namespace std;
int times;
char ch;
cout << "Enter a character: ";
cin >> ch;
cout << "Enter an integer: ";
cin >> times;
char *ps = buildstr(ch, times);
cout << ps << endl;
delete [] ps; // free memory
ps = buildstr('+', 20); // reuse pointer
cout << ps << "-DONE-" << ps << endl;
delete [] ps; // free memory
// cin.get();
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
// builds string made of n c characters
char * buildstr(char c, int n)
{
char * pstr = new char[n + 1];
pstr[n] = '\0'; // terminate string
while (n-- > 0)
pstr[n] = c; // fill rest of string
return pstr;
}
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ g++ strgback.cpp
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ ./a.out
Enter a character: V
Enter an integer: 46
VVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVV
++++++++++++++++++++-DONE-++++++++++++++++++++7.6 函数和结构
7.6.1 传递和返回结构
// travel.cpp -- using structures with functions
#include <iostream>
struct travel_time
{
int hours;
int mins;
};
const int Mins_per_hr = 60;
travel_time sum(travel_time t1, travel_time t2);
void show_time(travel_time t);
int main()
{
using namespace std;
travel_time day1 = {5, 45}; // 5 hrs, 45 min
travel_time day2 = {4, 55}; // 4 hrs, 55 min
travel_time trip = sum(day1, day2);
cout << "Two-day total: ";
show_time(trip);
travel_time day3= {4, 32};
cout << "Three-day total: ";
show_time(sum(trip, day3));
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
travel_time sum(travel_time t1, travel_time t2)
{
travel_time total;
total.mins = (t1.mins + t2.mins) % Mins_per_hr;
total.hours = t1.hours + t2.hours +
(t1.mins + t2.mins) / Mins_per_hr;
return total;
}
void show_time(travel_time t)
{
using namespace std;
cout << t.hours << " hours, "
<< t.mins << " minutes\n";
}
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ g++ travel.cpp
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ ./a.out
Two-day total: 10 hours, 40 minutes
Three-day total: 15 hours, 12 minutes7.6.2 另一个处理结构的函数示例
7.6.3 传递结构的地址
// strctptr.cpp -- functions with pointer to structure arguments
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
// structure templates
struct polar
{
double distance; // distance from origin
double angle; // direction from origin
};
struct rect
{
double x; // horizontal distance from origin
double y; // vertical distance from origin
};
// prototypes
void rect_to_polar(const rect * pxy, polar * pda);
void show_polar (const polar * pda);
int main()
{
using namespace std;
rect rplace;
polar pplace;
cout << "Enter the x and y values: ";
while (cin >> rplace.x >> rplace.y)
{
rect_to_polar(&rplace, &pplace); // pass addresses
show_polar(&pplace); // pass address
cout << "Next two numbers (q to quit): ";
}
cout << "Done.\n";
return 0;
}
// show polar coordinates, converting angle to degrees
void show_polar (const polar * pda)
{
using namespace std;
const double Rad_to_deg = 57.29577951;
cout << "distance = " << pda->distance;
cout << ", angle = " << pda->angle * Rad_to_deg;
cout << " degrees\n";
}
// convert rectangular to polar coordinates
void rect_to_polar(const rect * pxy, polar * pda)
{
using namespace std;
pda->distance =
sqrt(pxy->x * pxy->x + pxy->y * pxy->y);
pda->angle = atan2(pxy->y, pxy->x);
}
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ g++ travel.cpp
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ ./a.out
Two-day total: 10 hours, 40 minutes
Three-day total: 15 hours, 12 minutes
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ g++ strctptr.cpp
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ ./a.out
Enter the x and y values: 30 40
distance = 50, angle = 53.1301 degrees
Next two numbers (q to quit): 100 -100
distance = 141.421, angle = -45 degrees
Next two numbers (q to quit): q
Done.7.7 函数和string对象
// strctptr.cpp -- functions with pointer to structure arguments
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
// structure templates
struct polar
{
double distance; // distance from origin
double angle; // direction from origin
};
struct rect
{
double x; // horizontal distance from origin
double y; // vertical distance from origin
};
// prototypes
void rect_to_polar(const rect * pxy, polar * pda);
void show_polar (const polar * pda);
int main()
{
using namespace std;
rect rplace;
polar pplace;
cout << "Enter the x and y values: ";
while (cin >> rplace.x >> rplace.y)
{
rect_to_polar(&rplace, &pplace); // pass addresses
show_polar(&pplace); // pass address
cout << "Next two numbers (q to quit): ";
}
cout << "Done.\n";
return 0;
}
// show polar coordinates, converting angle to degrees
void show_polar (const polar * pda)
{
using namespace std;
const double Rad_to_deg = 57.29577951;
cout << "distance = " << pda->distance;
cout << ", angle = " << pda->angle * Rad_to_deg;
cout << " degrees\n";
}
// convert rectangular to polar coordinates
void rect_to_polar(const rect * pxy, polar * pda)
{
using namespace std;
pda->distance =
sqrt(pxy->x * pxy->x + pxy->y * pxy->y);
pda->angle = atan2(pxy->y, pxy->x);
}
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ g++ topfive.cpp
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ ./a.out
Enter your 5 favorite astronomical sights:
1: Orion Nebula
2: M13
3: Saturn
4: Jupiter
5: Moon
Your list:
1: Orion Nebula
2: M13
3: Saturn
4: upiter
5: Moon7.8 函数与array对象
//arrobj.cpp -- functions with array objects
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
#include <string>
const int Seasons = 4;
const std::array<std::string, Seasons> Snames =
{"Spring", "Summer", "Fall", "Winter"};
void fill(std::array<double, Seasons> * pa);
void show(std::array<double, Seasons> da);
int main()
{
std::array<double, 4> expenses;
fill(&expenses);
show(expenses);
// std::cin.get();
// std::cin.get();
return 0;
}
void fill(std::array<double, Seasons> * pa)
{
for (int i = 0; i < Seasons; i++)
{
std::cout << "Enter " << Snames[i] << " expenses: ";
std::cin >> (*pa)[i];
}
}
void show(std::array<double, Seasons> da)
{
double total = 0.0;
std::cout << "\nEXPENSES\n";
for (int i = 0; i < Seasons; i++)
{
std::cout << Snames[i] << ": $" << da[i] << '\n';
total += da[i];
}
std::cout << "Total: $" << total << '\n';
}
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ g++ arrobj.cpp
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ ./a.out
Enter Spring expenses: 212
Enter Summer expenses: 256
Enter Fall expenses: 208
Enter Winter expenses: 244
EXPENSES
Spring: $212
Summer: $256
Fall: $208
Winter: $244
Total: $9207.9 递归
7.9.1 包含一个递归调用的递归
// recur.cpp -- using recursion
#include <iostream>
void countdown(int n);
int main()
{
countdown(4); // call the recursive function
// std::cin.get();
return 0;
}
void countdown(int n)
{
using namespace std;
cout << "Counting down ... " << n << endl;
if (n > 0)
countdown(n-1); // function calls itself
cout << n << ": Kaboom!\n";
}
// recur.cpp -- using recursion
#include <iostream>
void countdown(int n);
int main()
{
countdown(4); // call the recursive function
// std::cin.get();
return 0;
}
void countdown(int n)
{
using namespace std;
cout << "Counting down ... " << n << endl;
if (n > 0)
countdown(n-1); // function calls itself
cout << n << ": Kaboom!\n";
}
7.9.2 包含多个递归调用的递归
// ruler.cpp -- using recursion to subdivide a ruler
#include <iostream>
const int Len = 66;
const int Divs = 6;
void subdivide(char ar[], int low, int high, int level);
int main()
{
char ruler[Len];
int i;
for (i = 1; i < Len - 2; i++)
ruler[i] = ' ';
ruler[Len - 1] = '\0';
int max = Len - 2;
int min = 0;
ruler[min] = ruler[max] = '|';
std::cout << ruler << std::endl;
for (i = 1; i <= Divs; i++)
{
subdivide(ruler,min,max, i);
std::cout << ruler << std::endl;
for (int j = 1; j < Len - 2; j++)
ruler[j] = ' '; // reset to blank ruler
}
// std::cin.get();
return 0;
}
void subdivide(char ar[], int low, int high, int level)
{
if (level == 0)
return;
int mid = (high + low) / 2;
ar[mid] = '|';
subdivide(ar, low, mid, level - 1);
subdivide(ar, mid, high, level - 1);
}
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ g++ ruler.cpp
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ ./a.out
| |
| | |
| | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||7.10 函数指针
与数据项相似,函数也有地址,函数的地址是存储其及其语言代码的内存的开始地址。7.10.1 函数指针的基础知识



7.10.2 函数指针示例
// fun_ptr.cpp -- pointers to functions
#include <iostream>
double betsy(int);
double pam(int);
// second argument is pointer to a type double function that
// takes a type int argument
void estimate(int lines, double (*pf)(int));
int main()
{
using namespace std;
int code;
cout << "How many lines of code do you need? ";
cin >> code;
cout << "Here's Betsy's estimate:\n";
estimate(code, betsy);
cout << "Here's Pam's estimate:\n";
estimate(code, pam);
// cin.get();
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
double betsy(int lns)
{
return 0.05 * lns;
}
double pam(int lns)
{
return 0.03 * lns + 0.0004 * lns * lns;
}
void estimate(int lines, double (*pf)(int))
{
using namespace std;
cout << lines << " lines will take ";
cout << (*pf)(lines) << " hour(s)\n";
}
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ g++ fun_ptr.cpp
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ ./a.out
How many lines of code do you need? 30
Here's Betsy's estimate:
30 lines will take 1.5 hour(s)
Here's Pam's estimate:
30 lines will take 1.26 hour(s)7.10.3 深入探讨函数指针
// arfupt.cpp -- an array of function pointers
#include <iostream>
// various notations, same signatures
const double * f1(const double ar[], int n);
const double * f2(const double [], int);
const double * f3(const double *, int);
int main()
{
using namespace std;
double av[3] = {1112.3, 1542.6, 2227.9};
// pointer to a function
const double *(*p1)(const double *, int) = f1;
auto p2 = f2; // C++0x automatic type deduction
// pre-C++0x can use the following code instead
// const double *(*p2)(const double *, int) = f2;
cout << "Using pointers to functions:\n";
cout << " Address Value\n";
cout << (*p1)(av,3) << ": " << *(*p1)(av,3) << endl;
cout << p2(av,3) << ": " << *p2(av,3) << endl;
// pa an array of pointers
// auto doesn't work with list initialization
const double *(*pa[3])(const double *, int) = {f1,f2,f3};
// but it does work for initializing to a single value
// pb a pointer to first element of pa
auto pb = pa;
// pre-C++0x can use the following code instead
// const double *(**pb)(const double *, int) = pa;
cout << "\nUsing an array of pointers to functions:\n";
cout << " Address Value\n";
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
cout << pa[i](av,3) << ": " << *pa[i](av,3) << endl;
cout << "\nUsing a pointer to a pointer to a function:\n";
cout << " Address Value\n";
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
cout << pb[i](av,3) << ": " << *pb[i](av,3) << endl;
// what about a pointer to an array of function pointers
cout << "\nUsing pointers to an array of pointers:\n";
cout << " Address Value\n";
// easy way to declare pc
auto pc = &pa;
// pre-C++0x can use the following code instead
// const double *(*(*pc)[3])(const double *, int) = &pa;
cout << (*pc)[0](av,3) << ": " << *(*pc)[0](av,3) << endl;
// hard way to declare pd
const double *(*(*pd)[3])(const double *, int) = &pa;
// store return value in pdb
const double * pdb = (*pd)[1](av,3);
cout << pdb << ": " << *pdb << endl;
// alternative notation
cout << (*(*pd)[2])(av,3) << ": " << *(*(*pd)[2])(av,3) << endl;
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
// some rather dull functions
const double * f1(const double * ar, int n)
{
return ar;
}
const double * f2(const double ar[], int n)
{
return ar+1;
}
const double * f3(const double ar[], int n)
{
return ar+2;
}
[wlsh@wlsh-MacbookPro] chapter_7$ g++ arfupt.cpp
arfupt.cpp:15:5: warning: 'auto' type specifier is a C++11 extension [-Wc++11-extensions]
auto p2 = f2; // C++0x automatic type deduction
^
arfupt.cpp:28:5: warning: 'auto' type specifier is a C++11 extension [-Wc++11-extensions]
auto pb = pa;
^
arfupt.cpp:44:5: warning: 'auto' type specifier is a C++11 extension [-Wc++11-extensions]
auto pc = &pa;
^
3 warnings generated.7.10.4 使用typedef进行简化
7.11 总结


























 1190
1190

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








