一、窗口操作
1、Keyed Windows
stream
.keyBy(...) <- keyed versus non-keyed windows
.window(...) <- required: "assigner"
[.trigger(...)] <- optional: "trigger" (else default trigger)
[.evictor(...)] <- optional: "evictor" (else no evictor)
[.allowedLateness(...)] <- optional: "lateness" (else zero)
[.sideOutputLateData(...)] <- optional: "output tag" (else no side output for late data)
.reduce/aggregate/fold/apply() <- required: "function"
[.getSideOutput(...)] <- optional: "output tag"
2、Non-Keyed Windows
stream
.windowAll(...) <- required: "assigner"
[.trigger(...)] <- optional: "trigger" (else default trigger)
[.evictor(...)] <- optional: "evictor" (else no evictor)
[.allowedLateness(...)] <- optional: "lateness" (else zero)
[.sideOutputLateData(...)] <- optional: "output tag" (else no side output for late data)
.reduce/aggregate/fold/apply() <- required: "function"
[.getSideOutput(...)] <- optional: "output tag"
测试源数据处理:
//点击日志
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple3<String, String, String>> clickStream = FlinkUtil.getKafkaStream(Common.KAFKA_BROKER, Common.APP_NEWSAPP_TOPIC, Common.KAFKA_CONSUMER_GROUP_ID)
.map(new MapFunction<String, Tuple3<String, String, String>>() {
@Override
public Tuple3<String, String, String> map(String input) throws Exception {
String[] split = input.split("\t");
String userKey = split[5];//用户key
String ct = split[10];//用户行为操作时间
String opa = split[11];//用户行为类型
return new Tuple3<>(userKey, ct, opa);
}
});
二、window
按照窗口的Assigner来分,窗口可以分为Tumbling window, sliding window,session window,global window;每种窗口又可分别基于processing time和event time,这样的话,窗口的类型严格来说就有很多;还有一种window叫做count window,依据元素到达的数量进行分配。
1、Tumbling window
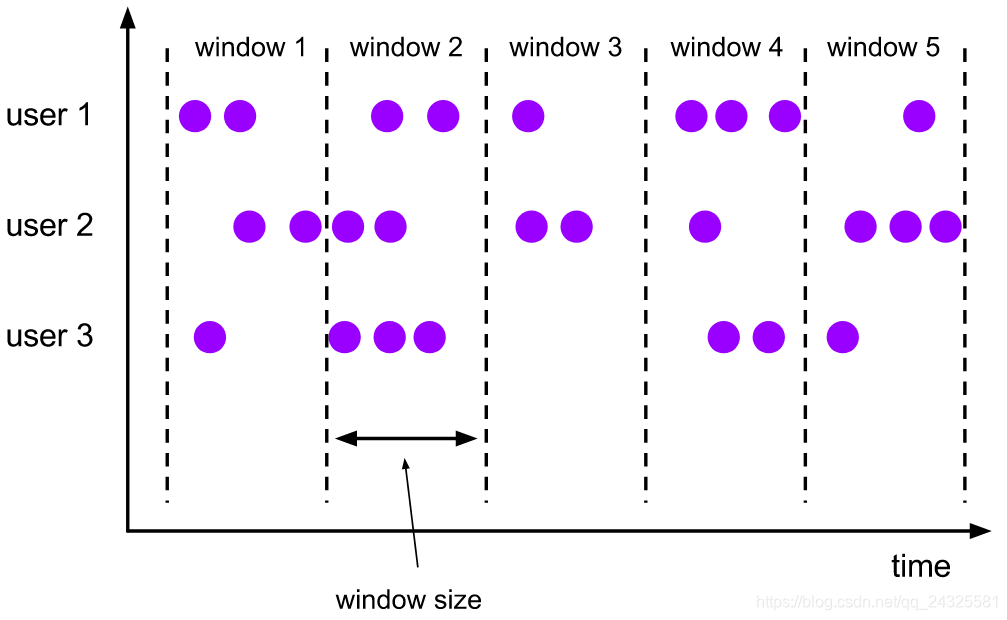
//处理时间
clickStream
.keyBy(tuple->tuple.f0)
.window(TumblingProcessingTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(60)))
//事件时间
clickStream
.keyBy(tuple->tuple.f0)
.window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(60)))
2、sliding window
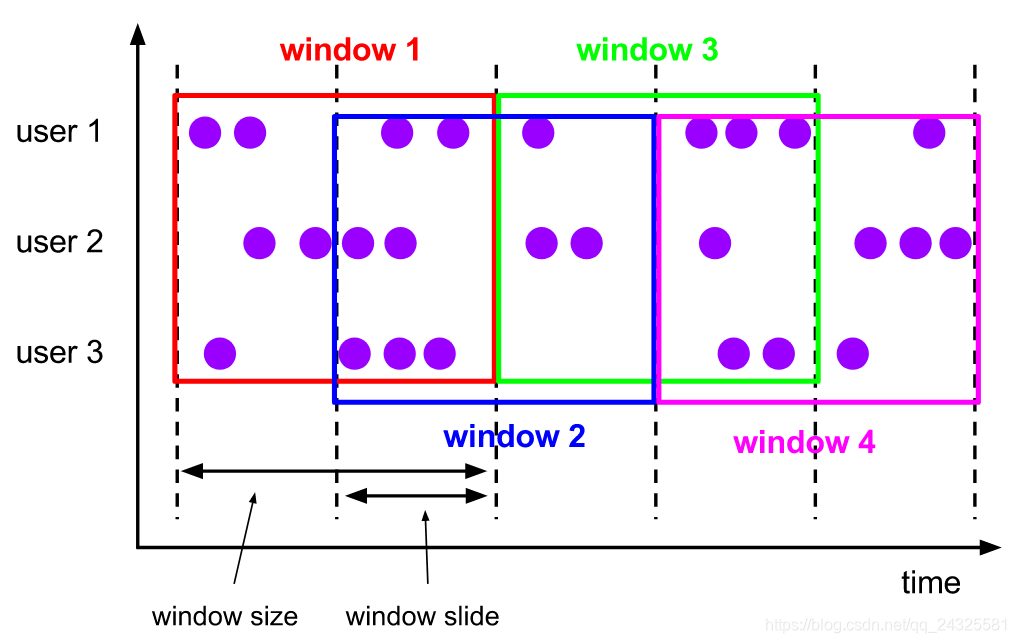
//事件时间
clickStream
.keyBy(tuple->tuple.f0)
.window(SlidingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(10),Time.seconds(5))) //10秒为窗口大小,5秒为滑动大小
clickStream
.keyBy(tuple -> tuple.f0)
.window(SlidingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(10), Time.seconds(5), Time.seconds(-3))) //Time.seconds(-3):窗口当前时间向左偏移3秒作为窗口的起始时间(窗口开始的时候使用该偏移量)
//处理时间操作如上
3、session window
这种窗口主要是根据活动的事件进行窗口化,他们通常不重叠,也没有一个固定的开始和结束时间。一个session window关闭通常是由于一段时间没有收到元素。在这种用户交互事件流中,我们首先想到的是将事件聚合到会话窗口中(一段用户持续活跃的周期),由非活跃的间隙分隔开。
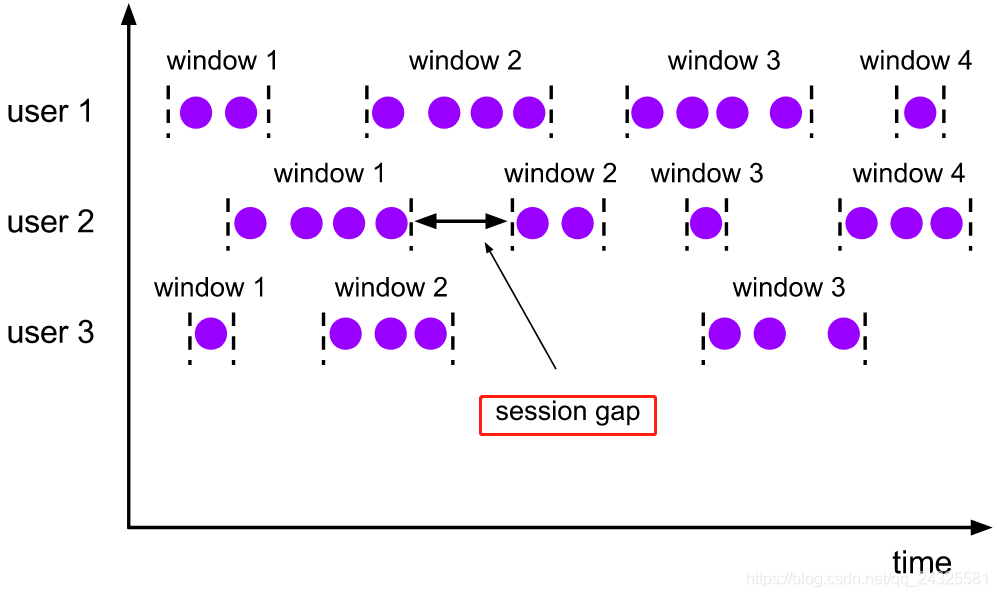
//处理时间
//静态间隔时间
clickStream
.keyBy(tuple -> tuple.f0)
.window(EventTimeSessionWindows.withGap(Time.seconds(10))) //10秒无数据窗口即关闭
//动态间隔时间
clickStream
.keyBy(tuple -> tuple.f0)
.window(EventTimeSessionWindows.withDynamicGap((element)->{
// determine and return session gap
}))
//事件时间操作如上
4、global window
全局窗口赋值器将具有相同键的所有元素分配给同一个全局窗口。此窗口方案仅在指定自定义触发器时有用。否则,不会执行任何计算,因为全局窗口没有可以处理聚合元素的自然结束。
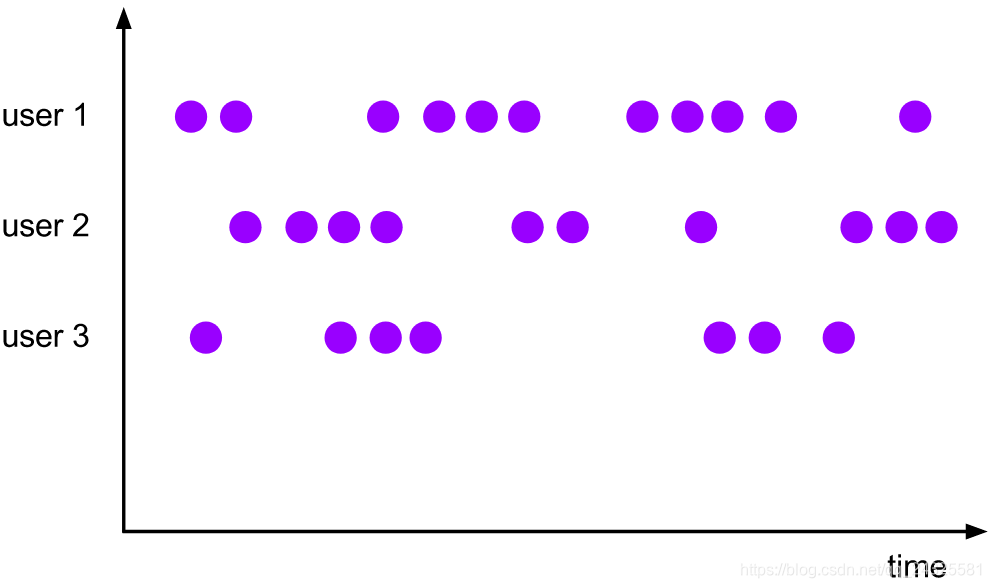
clickStream
.keyBy(tuple -> tuple.f0)
.window(GlobalWindows.create())
5、count window
Count Window 是根据元素个数对数据流进行分组的。
//翻滚计数窗口
clickStream
.keyBy(tuple -> tuple.f0)
.countWindow(100) //窗口大小为100个元素
//滑动计数窗口
clickStream
.keyBy(tuple -> tuple.f0)
.countWindow(100,10) //窗口大小为100,滑动间隔为10
三、窗口函数
1、ReduceFunction
ReduceFunction指定如何将输入中的两个元素组合在一起以产生相同类型的输出元素。 Flink使用ReduceFunction来逐步聚合窗口的元素。
ReduceFunction源码如下:
@Public
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ReduceFunction<T> extends Function, Serializable {
/**
* The core method of ReduceFunction, combining two values into one value of the same type.
* The reduce function is consecutively applied to all values of a group until only a single value remains.
*
* @param value1 The first value to combine.
* @param value2 The second value to combine.
* @return The combined value of both input values.
*
* @throws Exception This method may throw exceptions. Throwing an exception will cause the operation
* to fail and may trigger recovery.
*/
T reduce(T value1, T value2) throws Exception; //注意:返回值与输入数据类型一致
}
测试案例:
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple3<String, String, String>> reduceFunctionStream = clickStream
.keyBy(tuple -> tuple.f0)
.window(TumblingProcessingTimeWindows.of(Time.minutes(1)))
.reduce(new ReduceFunction<Tuple3<String, String, String>>() {
@Override
public Tuple3<String, String, String> reduce(Tuple3<String, String, String> input1, Tuple3<String, String, String> input2) throws Exception {
return new Tuple3<>(input1.f0, input1.f1, input2.f1); //结果为:userkey,开始时间,最终时间
}
});
2、AggregateFunction
AggregateFunction是ReduceFunction的通用版本,具有三种类型:输入类型(IN),累加器类型(ACC)和输出类型(OUT)。 输入类型是输入流中元素的类型,AggregateFunction具有一种将一个输入元素添加到累加器的方法。 该接口还具有创建初始累加器,将两个累加器合并为一个累加器以及从累加器提取输出(OUT类型)的方法。 我们将在下面的示例中看到它的工作原理。
与ReduceFunction相同,Flink将在窗口的输入元素到达时对其进行增量聚合。
AggregateFunction源码如下:

1、ACC createAccumulator():
创建一个新的累加器,开始一个新的聚合。
<p>除非累加值,否则新的累加器通常是无意义的
通过{
@link #add(Object,Object)}。
<p>累加器是正在运行的聚合的状态。 当一个程序有多个
进行中的聚合(例如,每个键和窗口),状态(每个键和窗口)
是累加器的大小。
@return一个新的累加器,对应于一个空的聚合。
2、ACC add(IN value, ACC accumulator):
将给定的输入值添加到给定的累加器,返回新的累加器值。
<p>为了提高效率,可以修改并返回输入累加器。
@param value要添加的值
@param accumulator将值添加到的累加器
@return具有更新状态的累加器
3、OUT getResult(ACC accumulator):
从累加器获取聚合的结果。
@param accumulator聚合的累加器
@return 最终的聚合结果。
4、ACC merge(ACC a, ACC b):
合并两个累加器,以合并状态返回累加器。
<p>此函数可以重用任何给定的累加器作为合并目标并返回。 假设将不会使用给定的累加器传递给此函数后的更多内容。
@param a 一个要合并的累加器
@param b 另一个要合并的累加器
@return合并状态的累加器
package org.apache.flink.api.common.functions;
import org.apache.flink.annotation.PublicEvolving;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* The {@code AggregateFunction} is a flexible aggregation function, characterized by the
* following features:
*
* <ul>
* <li>The aggregates may use different types for input values, intermediate aggregates,
* and result type, to support a wide range of aggregation types.</li>
*
* <li>Support for distributive aggregations: Different intermediate aggregates can be
* merged together, to allow for pre-aggregation/final-aggregation optimizations.</li>
* </ul>
*
* <p>The {@code AggregateFunction}'s intermediate aggregate (in-progress aggregation state)
* is called the <i>accumulator</i>. Values are added to the accumulator, and final aggregates are
* obtained by finalizing the accumulator state. This supports aggregation functions where the
* intermediate state needs to be different than the aggregated values and the final result type,
* such as for example <i>average</i> (which typically keeps a count and sum).
* Merging intermediate aggregates (partial aggregates) means merging the accumulators.
*
* <p>The AggregationFunction itself is stateless. To allow a single AggregationFunction
* instance to maintain multiple aggregates (such as one aggregate per key), the
* AggregationFunction creates a new accumulator whenever a new aggregation is started.
*
* <p>Aggregation functions must be {@link Serializable} because they are sent around
* between distributed processes during distributed execution.
*
* <h1>Example: Average and Weighted Average</h1>
*
* <pre>{@code
* // the accumulator, which holds the state of the in-flight aggregate
* public class AverageAccumulator {
* long count;
* long sum;
* }
*
* // implementation of an aggregation function for an 'average'
* public class Average implements AggregateFunction<Integer, AverageAccumulator, Double> {
*
* public AverageAccumulator createAccumulator() {
* return new AverageAccumulator();
* }
*
* public AverageAccumulator merge(AverageAccumulator a, AverageAccumulator b) {
* a.count += b.count;
* a.sum += b.sum;
* return a;
* }
*
* public AverageAccumulator add(Integer value, AverageAccumulator acc) {
* acc.sum += value;
* acc.count++;
* return acc;
* }
*
* public Double getResult(AverageAccumulator acc) {
* return acc.sum / (double) acc.count;
* }
* }
*
* // implementation of a weighted average
* // this reuses the same accumulator type as the aggregate function for 'average'
* public class WeightedAverage implements AggregateFunction<Datum, AverageAccumulator, Double> {
*
* public AverageAccumulator createAccumulator() {
* return new AverageAccumulator();
* }
*
* public AverageAccumulator merge(AverageAccumulator a, AverageAccumulator b) {
* a.count += b.count;
* a.sum += b.sum;
* return a;
* }
*
* public AverageAccumulator add(Datum value, AverageAccumulator acc) {
* acc.count += value.getWeight();
* acc.sum += value.getValue();
* return acc;
* }
*
* public Double getResult(AverageAccumulator acc) {
* return acc.sum / (double) acc.count;
* }
* }
* }</pre>
*
* @param <IN> The type of the values that are aggregated (input values)
* @param <ACC> The type of the accumulator (intermediate aggregate state).
* @param <OUT> The type of the aggregated result
*/
@PublicEvolving
public interface AggregateFunction<IN, ACC, OUT> extends Function, Serializable {
/**
* Creates a new accumulator, starting a new aggregate.
*
* <p>The new accumulator is typically meaningless unless a value is added
* via {@link #add(Object, Object)}.
*
* <p>The accumulator is the state of a running aggregation. When a program has multiple
* aggregates in progress (such as per key and window), the state (per key and window)
* is the size of the accumulator.
*
* @return A new accumulator, corresponding to an empty aggregate.
*/
ACC createAccumulator();
/**
* Adds the given input value to the given accumulator, returning the
* new accumulator value.
*
* <p>For efficiency, the input accumulator may be modified and returned.
*
* @param value The value to add
* @param accumulator The accumulator to add the value to
*
* @return The accu




 本文详细介绍了Apache Flink中的窗口操作,包括Keyed Windows和Non-Keyed Windows,讲解了Tumbling window、sliding window、session window、global window和count window等不同类型窗口的特性和应用场景。此外,还阐述了窗口函数如ReduceFunction、AggregateFunction、ProcessWindowFunction以及它们的使用示例,同时讨论了触发器(Trigger)、驱逐器(Evictor)、allowedLateness和sideOutputLateData等功能,提供了丰富的实践案例。
本文详细介绍了Apache Flink中的窗口操作,包括Keyed Windows和Non-Keyed Windows,讲解了Tumbling window、sliding window、session window、global window和count window等不同类型窗口的特性和应用场景。此外,还阐述了窗口函数如ReduceFunction、AggregateFunction、ProcessWindowFunction以及它们的使用示例,同时讨论了触发器(Trigger)、驱逐器(Evictor)、allowedLateness和sideOutputLateData等功能,提供了丰富的实践案例。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 876
876










