limit
limit作用
将查询结果集的一部分取出来。通常使用在分页查询当中

limit怎么用呢?
完整用法:limit startIndex, length
startIndex是起始下标,length是长度。
起始下标从0开始。
缺省用法:limit 5; 这是取前5.
按照薪资降序,取出排名在前5名的员工?
select
ename,sal
from
emp
order by
sal desc
limit 5; //取前5
select
ename,sal
from
emp
order by
sal desc
limit 0,5;
+-------+---------+
| ename | sal |
+-------+---------+
| KING | 5000.00 |
| SCOTT | 3000.00 |
| FORD | 3000.00 |
| JONES | 2975.00 |
| BLAKE | 2850.00 |
+-------+---------+
注意:mysql当中limit在order by之后执行!!!!!!
取出工资排名在[3-5]名的员工?
select
ename,sal
from
emp
order by
sal desc
limit
2, 3;
//2表示起始位置从下标2开始,就是第三条记录。
//3表示长度。
+-------+---------+
| ename | sal |
+-------+---------+
| FORD | 3000.00 |
| JONES | 2975.00 |
| BLAKE | 2850.00 |
+-------+---------+
取出工资排名在[5-9]名的员工?
select
ename,sal
from
emp
order by
sal desc
limit
4, 5;
+--------+---------+
| ename | sal |
+--------+---------+
| BLAKE | 2850.00 |
| CLARK | 2450.00 |
| ALLEN | 1600.00 |
| TURNER | 1500.00 |
| MILLER | 1300.00 |
+--------+---------+
分页
每页显示3条记录
第1页:limit 0,3 [0 1 2]
第2页:limit 3,3 [3 4 5]
第3页:limit 6,3 [6 7 8]
第4页:limit 9,3 [9 10 11]
每页显示pageSize条记录
第pageNo页:limit (pageNo - 1) * pageSize , pageSize
总结
select
...
from
...
where
...
group by
...
having
...
order by
...
limit
...
执行顺序?
1.from
2.where
3.group by
4.having
5.select
6.order by
7.limit..
表的创建
建表的语法格式
create table 表名(
字段名1 数据类型,
字段名2 数据类型,
字段名3 数据类型
);
表名:建议以t_ 或者 tbl_开始,可读性强。见名知意。
字段名:见名知意。
表名和字段名都属于标识符。
关于mysql中的数据类型?
很多数据类型,我们只需要掌握一些常见的数据类型即可。
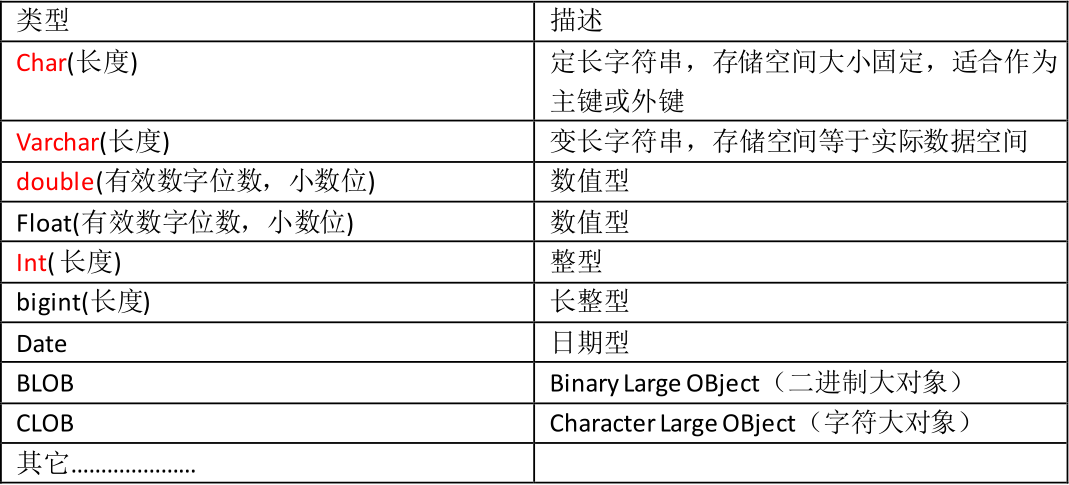
创建一个学生表
学号、姓名、年龄、性别、邮箱地址
create table t_student(
no int,
name varchar(32),
sex char(1),
age int(3),
email varchar(255)
);
删除表
drop table t_student; // 当这张表不存在的时候会报错!
// 如果这张表存在的话,删除
drop table if exists t_student;
插入insert
插入数据
语法格式:
insert into 表名(字段名1,字段名2,字段名3...) values(值1,值2,值3);
注意:字段名和值要一一对应。什么是一一对应?
数量要对应。数据类型要对应。
insert into t_student(no,name,sex,age,email) values(1,'zhangsan','m',20,'zhangsan@123.com');
insert into t_student(email,name,sex,age,no) values('lisi@123.com','lisi','f',20,2);
insert into t_student(no) values(3);
+------+----------+------+------+------------------+
| no | name | sex | age | email |
+------+----------+------+------+------------------+
| 1 | zhangsan | m | 20 | zhangsan@123.com |
| 2 | lisi | f | 20 | lisi@123.com |
| 3 | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL |
+------+----------+------+------+------------------+
insert into t_student(name) values('wangwu');
+------+----------+------+------+------------------+
| no | name | sex | age | email |
+------+----------+------+------+------------------+
| 1 | zhangsan | m | 20 | zhangsan@123.com |
| 2 | lisi | f | 20 | lisi@123.com |
| 3 | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL |
| NULL | wangwu | NULL | NULL | NULL |
+------+----------+------+------+------------------+
注意:insert语句但凡是执行成功了,那么必然会多一条记录。
没有给其它字段指定值的话,默认值是NULL。
insert语句一次插入多条记录
insert into t_user(id,name,birth,create_time) values
(1,'zs','1980-10-11',now()),
(2,'lisi','1981-10-11',now()),
(3,'wangwu','1982-10-11',now());
语法:insert into t_user(字段名1,字段名2) values(),(),(),();
mysql> select * from t_user;
+------+--------+------------+---------------------+
| id | name | birth | create_time |
+------+--------+------------+---------------------+
| 1 | zs | 1980-10-11 | 2020-03-19 09:37:01 |
| 2 | lisi | 1981-10-11 | 2020-03-19 09:37:01 |
| 3 | wangwu | 1982-10-11 | 2020-03-19 09:37:01 |
+------+--------+------------+---------------------+
数组格式化
数字格式化:format
select ename,format(sal, '$999,999') as sal from emp;
+--------+-------+
| ename | sal |
+--------+-------+
| SMITH | 800 |
| ALLEN | 1,600 |
| WARD | 1,250 |
| JONES | 2,975 |
| MARTIN | 1,250 |
| BLAKE | 2,850 |
| CLARK | 2,450 |
| SCOTT | 3,000 |
| KING | 5,000 |
| TURNER | 1,500 |
| ADAMS | 1,100 |
| JAMES | 950 |
| FORD | 3,000 |
| MILLER | 1,300 |
+--------+-------+
插入日期
str_to_date:将字符串varchar类型转换成date类型
date_format:将date类型转换成具有一定格式的varchar字符串类型。
date和datetime两个类型的区别
date是短日期:只包括年月日信息。
datetime是长日期:包括年月日时分秒信息。
drop table if exists t_user;
create table t_user(
id int,
name varchar(32),
birth date,
create_time datetime
);
id是整数
name是字符串
birth是短日期
create_time是这条记录的创建时间:长日期类型
mysql短日期默认格式:%Y-%m-%d
mysql长日期默认格式:%Y-%m-%d %h:%i:%s
在mysql当中怎么获取系统当前时间?
now() 函数,并且获取的时间带有:时分秒信息!!!!是datetime类型的。
insert into t_user(id,name,birth,create_time) values(2,'lisi','1991-10-01',now());
修改update
语法格式:
update 表名 set 字段名1=值1,字段名2=值2,字段名3=值3... where 条件;
注意:没有条件限制会导致所有数据全部更新。
update t_user set name = 'jack', birth = '2000-10-11' where id = 2;
+------+----------+------------+---------------------+
| id | name | birth | create_time |
+------+----------+------------+---------------------+
| 1 | zhangsan | 1990-10-01 | 2020-03-18 15:49:50 |
| 2 | jack | 2000-10-11 | 2020-03-18 15:51:23 |
+------+----------+------------+---------------------+
删除数据 delete
语法格式
delete from 表名 where 条件;
注意:没有条件,整张表的数据会全部删除!
delete from t_user where id = 2;
insert into t_user(id) values(2);
delete from t_user; // 删除所有!
delete语句删除数据的原理
表中的数据被删除了,但是这个数据在硬盘上的真实存储空间不会被释放!!!
这种删除缺点是:删除效率比较低。
这种删除优点是:支持回滚,后悔了可以再恢复数据!!!
快速删除表中的数据
//删除dept_bak表中的数据
delete from dept_bak; //这种删除数据的方式比较慢。
truncate语句删除数据的原理?
这种删除效率比较高,表被一次截断,物理删除。
这种删除缺点:不支持回滚。
这种删除优点:快速。
用法:truncate table dept_bak; (这种操作属于DDL操作。)
大表非常大,上亿条记录时
删除的时候,使用delete,也许需要执行1个小时才能删除完!效率较低。
可以选择使用truncate删除表中的数据。只需要不到1秒钟的时间就删除结束。效率较高。
但是使用truncate之前,必须仔细询问客户是否真的要删除,并警告删除之后不可恢复
快速创建表
mysql> create table emp2 as select * from emp;
原理:
将一个查询结果当做一张表新建!!!!!
这个可以完成表的快速复制!!!!
表创建出来,同时表中的数据也存在了!!!
create table mytable as select empno,ename from emp where job = 'MANAGER';
删除表操作
drop table 表名; // 这不是删除表中的数据,这是把表删除。
约束
什么是约束
约束对应的英语单词:constraint
在创建表的时候,我们可以给表中的字段加上一些约束,来保证这个表中数据的完整性、有效性!!!
约束的作用就是为了保证:表中的数据有效!!
约束包括哪些
非空约束:not null
唯一性约束: unique
主键约束: primary key (简称PK)
外键约束:foreign key(简称FK)
检查约束:check(mysql不支持,oracle支持)
我们这里重点学习四个约束:
not null
unique
primary key
foreign key
非空约束:not null
非空约束not null约束的字段不能为NULL
create table t_vip(
id int,
name varchar(255) not null // not null只有列级约束,没有表级约束!
);
唯一性约束: unique
唯一性约束unique约束的字段不能重复,但是可以为NULL
create table t_vip(
id int,
name varchar(255) unique,
email varchar(255)
);
insert into t_vip(id) values(4);
insert into t_vip(id) values(5);
+------+----------+------------------+
| id | name | email |
+------+----------+------------------+
| 1 | zhangsan | zhangsan@123.com |
| 2 | lisi | lisi@123.com |
| 3 | wangwu | wangwu@123.com |
| 4 | NULL | NULL |
| 5 | NULL | NULL |
+------+----------+------------------+
name字段虽然被unique约束了,但是可以为NULL。
需求:name和email两个字段联合起来具有唯一性
drop table if exists t_vip;
create table t_vip(
id int,
name varchar(255),
email varchar(255),
unique(name,email) // 约束没有添加在列的后面,这种约束被称为表级约束。
);
insert into t_vip(id,name,email) values(1,'zhangsan','zhangsan@123.com');
insert into t_vip(id,name,email) values(2,'zhangsan','zhangsan@sina.com');
select * from t_vip;
name和email两个字段联合起来唯一!!!
insert into t_vip(id,name,email) values(3,'zhangsan','zhangsan@sina.com');
ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry 'zhangsan-zhangsan@sina.com' for key 'name'//报错
什么时候使用表级约束呢?
需要给多个字段联合起来添加某一个约束的时候,需要使用表级约束。
unique 和not null联合
drop table if exists t_vip;
create table t_vip(
id int,
name varchar(255) not null unique
);
mysql> desc t_vip;
+-------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
| name | varchar(255) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
+-------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
//在mysql当中,如果一个字段同时被not null和unique约束的话,
//该字段自动变成主键字段。(注意:oracle中不一样!)
主键约束
主键约束的相关术语
主键约束:就是一种约束。
主键字段:该字段上添加了主键约束,这样的字段叫做:主键字段
主键值:主键字段中的每一个值都叫做:主键值。
什么是主键
主键值是每一行记录的唯一标识。
主键值是每一行记录的身份证号!!!
记住:任何一张表都应该有主键,没有主键,表无效!!
主键的特征
not null + unique(主键值不能是NULL,同时也不能重复!)
给一张表添加主键约束
create table t_vip(
id int primary key, //列级约束
name varchar(255)
);
insert into t_vip(id,name) values(1,'zhangsan');
insert into t_vip(id,name) values(2,'lisi');
//错误:不能重复
insert into t_vip(id,name) values(2,'wangwu');
ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '2' for key 'PRIMARY'
//错误:不能为NULL
insert into t_vip(name) values('zhaoliu');
ERROR 1364 (HY000): Field 'id' doesn't have a default value
主键值建议使用:
int、bigint、char等类型。
不建议使用:varchar来做主键。主键值一般都是数字,一般都是定长的!
主键除了:单一主键和复合主键之外,还可以这样进行分类?
自然主键:主键值是一个自然数,和业务没关系。
业务主键:主键值和业务紧密关联,例如拿银行卡账号做主键值。这就是业务主键!
在实际开发中使用业务主键多,还是使用自然主键多一些?
自然主键使用比较多,因为主键只要做到不重复就行,不需要有意义。
业务主键不好,因为主键一旦和业务挂钩,那么当业务发生变动的时候,
可能会影响到主键值,所以业务主键不建议使用。尽量使用自然主键。
在mysql当中,有一种机制,可以帮助我们自动维护一个主键值?
drop table if exists t_vip;
create table t_vip(
id int primary key auto_increment, //auto_increment表示自增,从1开始,以1递增!
name varchar(255)
);
insert into t_vip(name) values('zhangsan');
insert into t_vip(name) values('zhangsan');
insert into t_vip(name) values('zhangsan');
insert into t_vip(name) values('zhangsan');
insert into t_vip(name) values('zhangsan');
insert into t_vip(name) values('zhangsan');
insert into t_vip(name) values('zhangsan');
insert into t_vip(name) values('zhangsan');
select * from t_vip;
+----+----------+
| id | name |
+----+----------+
| 1 | zhangsan |
| 2 | zhangsan |
| 3 | zhangsan |
| 4 | zhangsan |
| 5 | zhangsan |
| 6 | zhangsan |
| 7 | zhangsan |
| 8 | zhangsan |
+----+----------+
























 2740
2740

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








