计算机网络 传输层 (4,5周)
-
Introduction and Transport-Layer Services
-
Relationship Between Transport and Network Layers
The transport layer provides logical rather than physical communication between application processes
-
Overview of the Transport Layer in the Internet
the Internet makes two distinct transport-layer protocols available to the application layer. One of these protocols is UDP (User Datagram Protocol), which provides an unreliable, connectionless service to the invoking application. The second of these protocols is TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), which provides a reliable, connection-oriented service to the invoking application.
-
-
Multiplexing and Demultiplexing
This job of delivering the data in a transport-layer segment to the correct socket is called demultiplexing. The job of gathering data chunks at the source host from different sockets, encapsulating each data chunk with header information (that will later be used in demultiplexing) to create segments, and passing the segments to the network layer is called multiplexing.
-
Connectionless Transport: UDP
UDP takes messages from the application process, attaches source and destination port number
fields for the multiplexing/demultiplexing service, adds two other small fields, and passes the resulting
segment to the network layer-
UDP Segment Structure
-
UDP Checksum
-
-
Principles of Reliable Data Transfer
- Building a Reliable Data Transfer Protocol
- Pipelined Reliable Data Transfer Protocols
- Go-Back-N (GBN)
- Selective Repeat (SR)
-
Connection-Oriented Transport: TCP
-
The TCP Connection
-
-
连接:三次握手
-
断开:四次挥手
-
-
-
TCP Segment Structure
-
Round-Trip Time Estimation and Timeout
-
Reliable Data Transfer >
- 超时重试
- 估计往返时间,需要TCP通过采样RTT的时间,然后进行加权平均,算出一个值,而且这个值还是要不断变化的,因为网络状况不断的变化。除了采样RTT,还要采样RTT的波动范围,计算出一个估计的超时时间。由于重传时间是不断变化的,我们称为自适应重传算法(Adaptive Retransmission Algorithm)。
- 超时重试
-
Flow Control
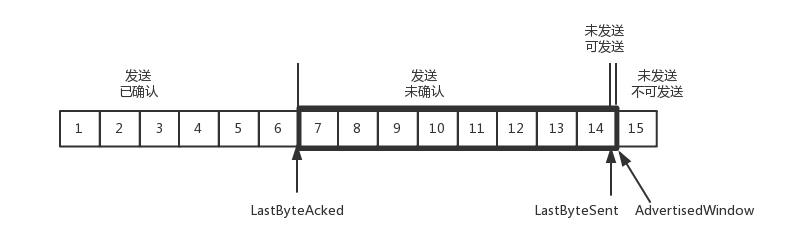
我们再来看流量控制机制,在对于包的确认中,同时会携带一个窗口的大小。
我们先假设窗口不变的情况,窗口始终为9。4的确认来的时候,会右移一个,这个时候第13个包也可以发送了。
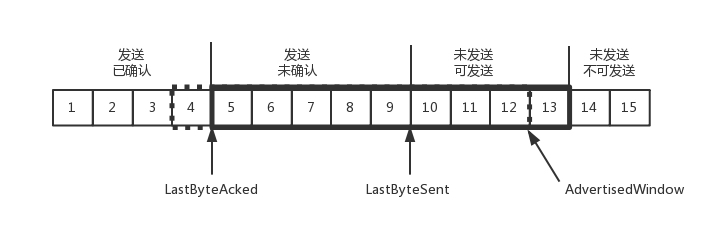
这个时候,假设发送端发送过猛,会将第三部分的10、11、12、13全部发送完毕,之后就停止发送了,未发送可发送部分为0。
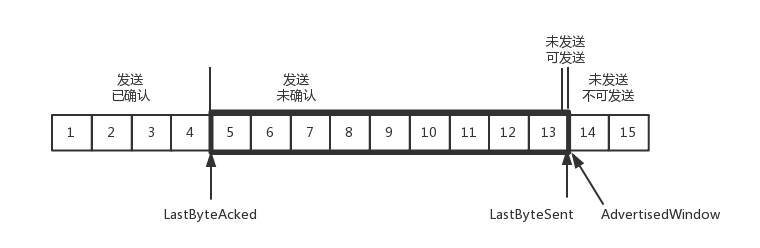
当对于包5的确认到达的时候,在客户端相当于窗口再滑动了一格,这个时候,才可以有更多的包可以发送了,例如第14个包才可以发送。
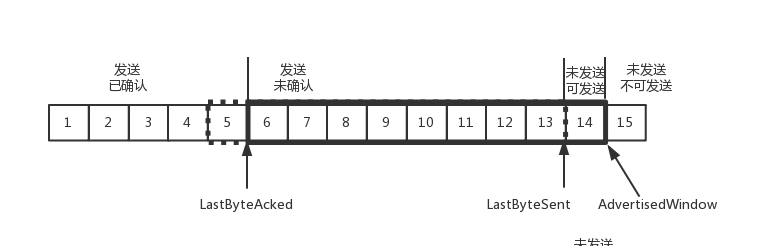
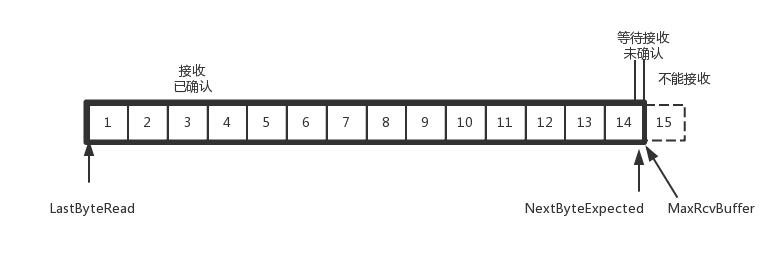
如果接收方实在处理的太慢,导致缓存中没有空间了,可以通过确认信息修改窗口的大小,甚至可以设置为0,则发送方将暂时停止发送。
我们假设一个极端情况,接收端的应用一直不读取缓存中的数据,当数据包6确认后,窗口大小就不能再是9了,就要缩小一个变为8。
这个新的窗口8通过6的确认消息到达发送端的时候,你会发现窗口没有平行右移,而是仅仅左面的边右移了,窗口的大小从9改成了8。
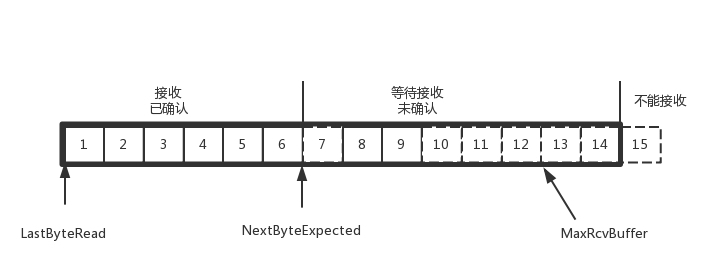
如果接收端还是一直不处理数据,则随着确认的包越来越多,窗口越来越小,直到为0。
当这个窗口通过包14的确认到达发送端的时候,发送端的窗口也调整为0,停止发送。
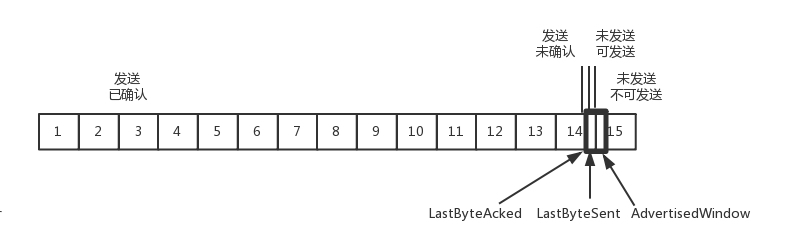
如果这样的话,发送方会定时发送窗口探测数据包,看是否有机会调整窗口的大小。当接收方比较慢的时候,要防止低能窗口综合征,别空出一个字节来就赶快告诉发送方,然后马上又填满了,可以当窗口太小的时候,不更新窗口,直到达到一定大小,或者缓冲区一半为空,才更新窗口。
这就是我们常说的流量控制。
-
TCP Connection Management
-
-
Principles of Congestion Control
-
拥塞控制是通过拥塞窗口来解决的,相当于往管道里面倒水,快了容易溢出,慢了浪费带宽,要摸着石头过河,找到最优值。
-
The Causes and the Costs of Congestion
-
Approaches to Congestion Control
-
-
TCP Congestion Control
-
Fairness
-
Consider K TCP connections, each with a different end-to-end path, but all passing through a bottleneck link with transmission rate R bps. (By bottleneck link, we mean that for each connection, all the other links along the connection’s path are not congested and have abundant transmission capacity as compared with the transmission capacity of the bottleneck link.) Suppose each connection is transferring
a large file and there is no UDP traffic passing through the bottleneck link. A congestion-control mechanism is said to be fair if the average transmission rate of each connection is approximately R/K; average throughput of a connection=1.22⋅MSSRTTL –10 that is, each connection gets an equal share of the link bandwidth.
-
-
Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN): Network-assisted Congestion Control
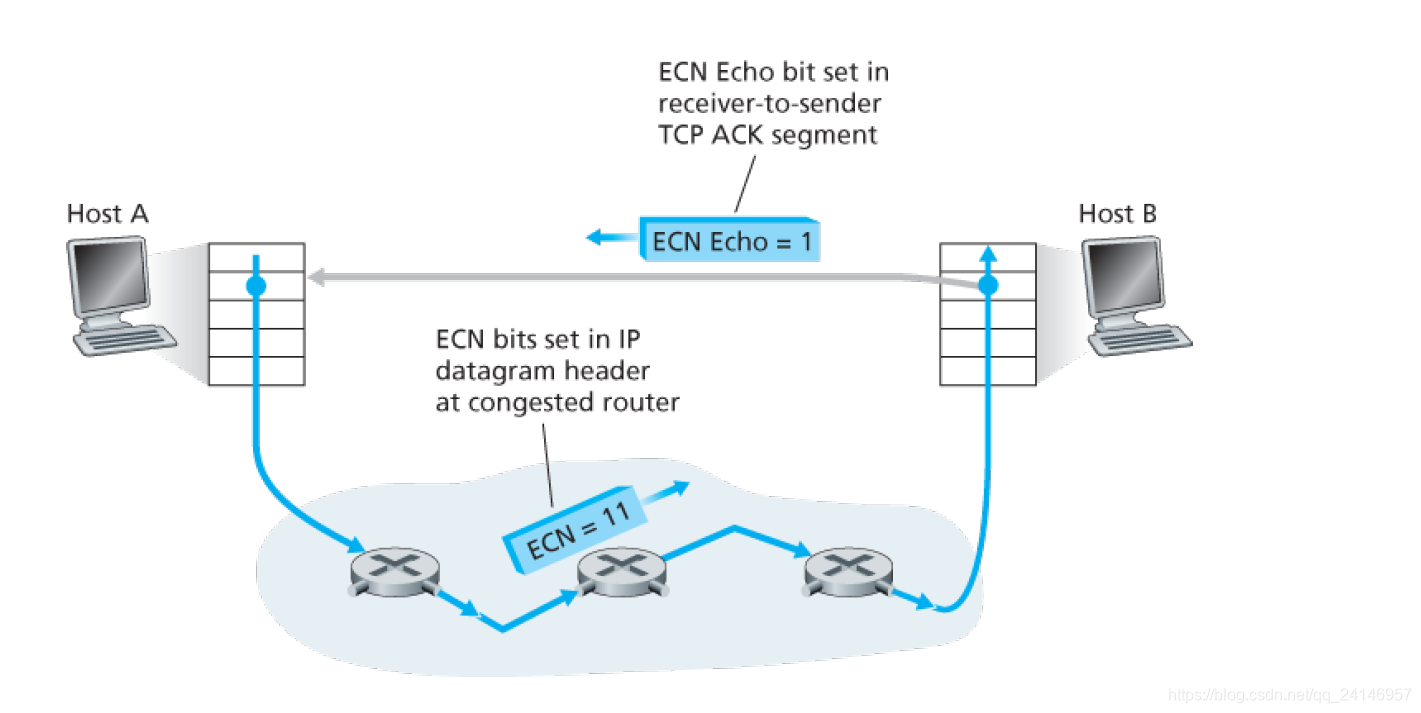
-





 本文详细介绍了计算机网络传输层的原理,包括TCP和UDP两种主要协议。TCP提供可靠、面向连接的服务,而UDP则提供不可靠、无连接的服务。文章还讨论了TCP的三次握手和四次挥手连接过程,以及TCP的流量控制和拥塞控制机制,强调了公平性和网络效率的重要性。
本文详细介绍了计算机网络传输层的原理,包括TCP和UDP两种主要协议。TCP提供可靠、面向连接的服务,而UDP则提供不可靠、无连接的服务。文章还讨论了TCP的三次握手和四次挥手连接过程,以及TCP的流量控制和拥塞控制机制,强调了公平性和网络效率的重要性。

















 6155
6155

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








