上文提到了总体的一个宏观展示,这次我们细细的分析跟踪下框架代码
Android(Linux) led子系统分析:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_23327993/article/details/86520216
先看led子系统注册的入口函数
路劲:kernel/msm-3.18/drivers/leds/led-class.c
/*
* LED Class Core
*
* Copyright (C) 2005 John Lenz <lenz@cs.wisc.edu>
* Copyright (C) 2005-2007 Richard Purdie <rpurdie@openedhand.com>
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 as
* published by the Free Software Foundation.
*/
#define DEBUG
#include <linux/ctype.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/err.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/leds.h>
#include <linux/list.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/spinlock.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include "leds.h"
static struct class *leds_class;
static ssize_t brightness_show(struct device *dev,
struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
struct led_classdev *led_cdev = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
/* no lock needed for this */
led_update_brightness(led_cdev);
return sprintf(buf, "%u\n", led_cdev->brightness);
}
static ssize_t brightness_store(struct device *dev,
struct device_attribute *attr, const char *buf, size_t size)
{
struct led_classdev *led_cdev = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
unsigned long state;
ssize_t ret;
mutex_lock(&led_cdev->led_access);
if (led_sysfs_is_disabled(led_cdev)) {
ret = -EBUSY;
goto unlock;
}
ret = kstrtoul(buf, 10, &state);
if (ret)
goto unlock;
led_cdev->usr_brightness_req = state;
__led_set_brightness(led_cdev, state);
ret = size;
unlock:
mutex_unlock(&led_cdev->led_access);
return ret;
}
static DEVICE_ATTR_RW(brightness);
//static DEVICE_ATTR(brightness, 0666, brightness_show, brightness_store);
static ssize_t max_brightness_show(struct device *dev,
struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
struct led_classdev *led_cdev = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
return sprintf(buf, "%u\n", led_cdev->max_brightness);
}
static ssize_t max_brightness_store(struct device *dev,
struct device_attribute *attr, const char *buf, size_t size)
{
struct led_classdev *led_cdev = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
unsigned long state;
ssize_t ret = -EINVAL;
ret = kstrtoul(buf, 10, &state);
if (ret)
return ret;
led_cdev->max_brightness = state;
led_set_brightness(led_cdev, led_cdev->usr_brightness_req);
return size;
}
static DEVICE_ATTR_RW(max_brightness);
#ifdef CONFIG_LEDS_TRIGGERS
static DEVICE_ATTR(trigger, 0644, led_trigger_show, led_trigger_store);
static struct attribute *led_trigger_attrs[] = {
&dev_attr_trigger.attr,
NULL,
};
static const struct attribute_group led_trigger_group = {
.attrs = led_trigger_attrs,
};
#endif
static struct attribute *led_class_attrs[] = {
&dev_attr_brightness.attr,
&dev_attr_max_brightness.attr,
NULL,
};
static const struct attribute_group led_group = {
.attrs = led_class_attrs,
};
static const struct attribute_group *led_groups[] = {
&led_group,
#ifdef CONFIG_LEDS_TRIGGERS
&led_trigger_group,
#endif
NULL,
};
static void led_timer_function(unsigned long data)
{
struct led_classdev *led_cdev = (void *)data;
unsigned long brightness;
unsigned long delay;
if (!led_cdev->blink_delay_on || !led_cdev->blink_delay_off) {
__led_set_brightness(led_cdev, LED_OFF);
return;
}
if (led_cdev->flags & LED_BLINK_ONESHOT_STOP) {
led_cdev->flags &= ~LED_BLINK_ONESHOT_STOP;
return;
}
brightness = led_get_brightness(led_cdev);
if (!brightness) {
/* Time to switch the LED on. */
brightness = led_cdev->blink_brightness;
delay = led_cdev->blink_delay_on;
} else {
/* Store the current brightness value to be able
* to restore it when the delay_off period is over.
*/
led_cdev->blink_brightness = brightness;
brightness = LED_OFF;
delay = led_cdev->blink_delay_off;
}
__led_set_brightness(led_cdev, brightness);
/* Return in next iteration if led is in one-shot mode and we are in
* the final blink state so that the led is toggled each delay_on +
* delay_off milliseconds in worst case.
*/
if (led_cdev->flags & LED_BLINK_ONESHOT) {
if (led_cdev->flags & LED_BLINK_INVERT) {
if (brightness)
led_cdev->flags |= LED_BLINK_ONESHOT_STOP;
} else {
if (!brightness)
led_cdev->flags |= LED_BLINK_ONESHOT_STOP;
}
}
mod_timer(&led_cdev->blink_timer, jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(delay));
}
static void set_brightness_delayed(struct work_struct *ws)
{
struct led_classdev *led_cdev =
container_of(ws, struct led_classdev, set_brightness_work);
led_stop_software_blink(led_cdev);
__led_set_brightness(led_cdev, led_cdev->delayed_set_value);
}
/**
* led_classdev_suspend - suspend an led_classdev.
* @led_cdev: the led_classdev to suspend.
*/
void led_classdev_suspend(struct led_classdev *led_cdev)
{
led_cdev->flags |= LED_SUSPENDED;
led_cdev->brightness_set(led_cdev, 0);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(led_classdev_suspend);
/**
* led_classdev_resume - resume an led_classdev.
* @led_cdev: the led_classdev to resume.
*/
void led_classdev_resume(struct led_classdev *led_cdev)
{
led_cdev->brightness_set(led_cdev, led_cdev->brightness);
led_cdev->flags &= ~LED_SUSPENDED;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(led_classdev_resume);
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_SLEEP
static int led_suspend(struct device *dev)
{
struct led_classdev *led_cdev = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
if (led_cdev->flags & LED_CORE_SUSPENDRESUME)
led_classdev_suspend(led_cdev);
return 0;
}
static int led_resume(struct device *dev)
{
struct led_classdev *led_cdev = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
if (led_cdev->flags & LED_CORE_SUSPENDRESUME)
led_classdev_resume(led_cdev);
return 0;
}
#endif
static SIMPLE_DEV_PM_OPS(leds_class_dev_pm_ops, led_suspend, led_resume);
/**
* led_classdev_register - register a new object of led_classdev class.
* @parent: The device to register.
* @led_cdev: the led_classdev structure for this device.
*/
int led_classdev_register(struct device *parent, struct led_classdev *led_cdev)
{
led_cdev->dev = device_create_with_groups(leds_class, parent, 0,
led_cdev, led_cdev->groups,
"%s", led_cdev->name);
pr_debug("hogo file:%s,func:%s,line:%d\n", __FILE__,__func__,__LINE__);
if (IS_ERR(led_cdev->dev))
return PTR_ERR(led_cdev->dev);
#ifdef CONFIG_LEDS_TRIGGERS
init_rwsem(&led_cdev->trigger_lock);
#endif
mutex_init(&led_cdev->led_access);
/* add to the list of leds */
down_write(&leds_list_lock);
list_add_tail(&led_cdev->node, &leds_list);
up_write(&leds_list_lock);
if (!led_cdev->max_brightness)
led_cdev->max_brightness = LED_FULL;
led_update_brightness(led_cdev);
INIT_WORK(&led_cdev->set_brightness_work, set_brightness_delayed);
init_timer(&led_cdev->blink_timer);
led_cdev->blink_timer.function = led_timer_function;
led_cdev->blink_timer.data = (unsigned long)led_cdev;
#ifdef CONFIG_LEDS_TRIGGERS
led_trigger_set_default(led_cdev);
#endif
dev_dbg(parent, "Registered led device: %s\n",
led_cdev->name);
pr_debug("hogo Registered led device: %s,file:%s,func:%s,line:%d\n",led_cdev->name,__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__);
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(led_classdev_register);
/**
* led_classdev_unregister - unregisters a object of led_properties class.
* @led_cdev: the led device to unregister
*
* Unregisters a previously registered via led_classdev_register object.
*/
void led_classdev_unregister(struct led_classdev *led_cdev)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_LEDS_TRIGGERS
down_write(&led_cdev->trigger_lock);
if (led_cdev->trigger)
led_trigger_set(led_cdev, NULL);
up_write(&led_cdev->trigger_lock);
#endif
cancel_work_sync(&led_cdev->set_brightness_work);
/* Stop blinking */
led_stop_software_blink(led_cdev);
led_set_brightness(led_cdev, LED_OFF);
device_unregister(led_cdev->dev);
down_write(&leds_list_lock);
list_del(&led_cdev->node);
up_write(&leds_list_lock);
mutex_destroy(&led_cdev->led_access);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(led_classdev_unregister);
static int __init leds_init(void)
{
leds_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "leds");
if (IS_ERR(leds_class))
return PTR_ERR(leds_class);
leds_class->pm = &leds_class_dev_pm_ops;
leds_class->dev_groups = led_groups;
return 0;
}
static void __exit leds_exit(void)
{
class_destroy(leds_class);
}
subsys_initcall(leds_init);
module_exit(leds_exit);
MODULE_AUTHOR("John Lenz, Richard Purdie");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("LED Class Interface");先重点看下模块加载函数leds_init()
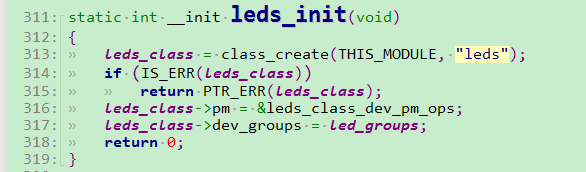
这里可以看到init函数中创建了以leds命名的类,该类创建在 /sys/class/ 下 以 “leds” 命名
如图: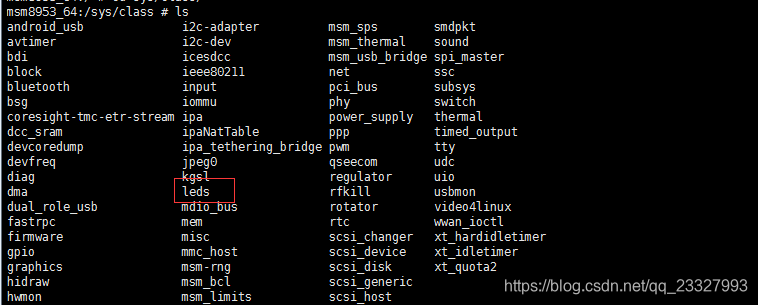
如果创建类成功,则对leds_class 中的成员进行填充,那此处的leds_class 是什么呢,可以跟踪去看看
![]()
原来是个class 结构体,这个结构体定义在哪呢,我们可以看到leds_class.c 中引入了#include <linux/device.h> 头文件,猜想这个结构体应该就定义在这个头文件里面,跟进去看看
kernel/msm-3.18/include/linux/device.h
/*
* device.h - generic, centralized driver model
*
* Copyright (c) 2001-2003 Patrick Mochel <mochel@osdl.org>
* Copyright (c) 2004-2009 Greg Kroah-Hartman <gregkh@suse.de>
* Copyright (c) 2008-2009 Novell Inc.
*
* This file is released under the GPLv2
*
* See Documentation/driver-model/ for more information.
*/
#ifndef _DEVICE_H_
#define _DEVICE_H_
#include <linux/ioport.h>
#include <linux/kobject.h>
#include <linux/klist.h>
#include <linux/list.h>
#include <linux/lockdep.h>
#include <linux/compiler.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/pinctrl/devinfo.h>
#include <linux/pm.h>
#include <linux/atomic.h>
#include <linux/ratelimit.h>
#include <linux/uidgid.h>
#include <linux/gfp.h>
#include <asm/device.h>
struct device;
struct device_private;
struct device_driver;
struct driver_private;
struct module;
struct class;
struct subsys_private;
struct bus_type;
struct device_node;
struct iommu_ops;
struct iommu_group;
struct bus_attribute {
struct attribute attr;
ssize_t (*show)(struct bus_type *bus, char *buf);
ssize_t (*store)(struct bus_type *bus, const char *buf, size_t count);
};
#define BUS_ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, _store) \
struct bus_attribute bus_attr_##_name = __ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, _store)
#define BUS_ATTR_RW(_name) \
struct bus_attribute bus_attr_##_name = __ATTR_RW(_name)
#define BUS_ATTR_RO(_name) \
struct bus_attribute bus_attr_##_name = __ATTR_RO(_name)
extern int __must_check bus_create_file(struct bus_type *,
struct bus_attribute *);
extern void bus_remove_file(struct bus_type *, struct bus_attribute *);
/**
* struct bus_type - The bus type of the device
*
* @name: The name of the bus.
* @dev_name: Used for subsystems to enumerate devices like ("foo%u", dev->id).
* @dev_root: Default device to use as the parent.
* @dev_attrs: Default attributes of the devices on the bus.
* @bus_groups: Default attributes of the bus.
* @dev_groups: Default attributes of the devices on the bus.
* @drv_groups: Default attributes of the device drivers on the bus.
* @match: Called, perhaps multiple times, whenever a new device or driver
* is added for this bus. It should return a nonzero value if the
* given device can be handled by the given driver.
* @uevent: Called when a device is added, removed, or a few other things
* that generate uevents to add the environment variables.
* @probe: Called when a new device or driver add to this bus, and callback
* the specific driver's probe to initial the matched device.
* @remove: Called when a device removed from this bus.
* @shutdown: Called at shut-down time to quiesce the device.
*
* @online: Called to put the device back online (after offlining it).
* @offline: Called to put the device offline for hot-removal. May fail.
*
* @suspend: Called when a device on this bus wants to go to sleep mode.
* @resume: Called to bring a device on this bus out of sleep mode.
* @pm: Power management operations of this bus, callback the specific
* device driver's pm-ops.
* @iommu_ops: IOMMU specific operations for this bus, used to attach IOMMU
* driver implementations to a bus and allow the driver to do
* bus-specific setup
* @p: The private data of the driver core, only the driver core can
* touch this.
* @lock_key: Lock class key for use by the lock validator
*
* A bus is a channel between the processor and one or more devices. For the
* purposes of the device model, all devices are connected via a bus, even if
* it is an internal, virtual, "platform" bus. Buses can plug into each other.
* A USB controller is usually a PCI device, for example. The device model
* represents the actual connections between buses and the devices they control.
* A bus is represented by the bus_type structure. It contains the name, the
* default attributes, the bus' methods, PM operations, and the driver core's
* private data.
*/
struct bus_type {
const char *name;
const char *dev_name;
struct device *dev_root;
struct device_attribute *dev_attrs; /* use dev_groups instead */
const struct attribute_group **bus_groups;
const struct attribute_group **dev_groups;
const struct attribute_group **drv_groups;
int (*match)(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv);
int (*uevent)(struct device *dev, struct kobj_uevent_env *env);
int (*probe)(struct device *dev);
int (*remove)(struct device *dev);
void (*shutdown)(struct device *dev);
int (*online)(struct device *dev);
int (*offline)(struct device *dev);
int (*suspend)(struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume)(struct device *dev);
const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;
const struct iommu_ops *iommu_ops;
struct subsys_private *p;
struct lock_class_key lock_key;
};
extern int __must_check bus_register(struct bus_type *bus);
extern void bus_unregister(struct bus_type *bus);
extern int __must_check bus_rescan_devices(struct bus_type *bus);
/* iterator helpers for buses */
struct subsys_dev_iter {
struct klist_iter ki;
const struct device_type *type;
};
void subsys_dev_iter_init(struct subsys_dev_iter *iter,
struct bus_type *subsys,
struct device *start,
const struct device_type *type);
struct device *subsys_dev_iter_next(struct subsys_dev_iter *iter);
void subsys_dev_iter_exit(struct subsys_dev_iter *iter);
int bus_for_each_dev(struct bus_type *bus, struct device *start, void *data,
int (*fn)(struct device *dev, void *data));
struct device *bus_find_device(struct bus_type *bus, struct device *start,
void *data,
int (*match)(struct device *dev, void *data));
struct device *bus_find_device_by_name(struct bus_type *bus,
struct device *start,
const char *name);
struct device *subsys_find_device_by_id(struct bus_type *bus, unsigned int id,
struct device *hint);
int bus_for_each_drv(struct bus_type *bus, struct device_driver *start,
void *data, int (*fn)(struct device_driver *, void *));
void bus_sort_breadthfirst(struct bus_type *bus,
int (*compare)(const struct device *a,
const struct device *b));
/*
* Bus notifiers: Get notified of addition/removal of devices
* and binding/unbinding of drivers to devices.
* In the long run, it should be a replacement for the platform
* notify hooks.
*/
struct notifier_block;
extern int bus_register_notifier(struct bus_type *bus,
struct notifier_block *nb);
extern int bus_unregister_notifier(struct bus_type *bus,
struct notifier_block *nb);
/* All 4 notifers below get called with the target struct device *
* as an argument. Note that those functions are likely to be called
* with the device lock held in the core, so be careful.
*/
#define BUS_NOTIFY_ADD_DEVICE 0x00000001 /* device added */
#define BUS_NOTIFY_DEL_DEVICE 0x00000002 /* device to be removed */
#define BUS_NOTIFY_REMOVED_DEVICE 0x00000003 /* device removed */
#define BUS_NOTIFY_BIND_DRIVER 0x00000004 /* driver about to be
bound */
#define BUS_NOTIFY_BOUND_DRIVER 0x00000005 /* driver bound to device */
#define BUS_NOTIFY_UNBIND_DRIVER 0x00000006 /* driver about to be
unbound */
#define BUS_NOTIFY_UNBOUND_DRIVER 0x00000007 /* driver is unbound
from the device */
extern struct kset *bus_get_kset(struct bus_type *bus);
extern struct klist *bus_get_device_klist(struct bus_type *bus);
/**
* struct device_driver - The basic device driver structure
* @name: Name of the device driver.
* @bus: The bus which the device of this driver belongs to.
* @owner: The module owner.
* @mod_name: Used for built-in modules.
* @suppress_bind_attrs: Disables bind/unbind via sysfs.
* @of_match_table: The open firmware table.
* @acpi_match_table: The ACPI match table.
* @probe: Called to query the existence of a specific device,
* whether this driver can work with it, and bind the driver
* to a specific device.
* @remove: Called when the device is removed from the system to
* unbind a device from this driver.
* @shutdown: Called at shut-down time to quiesce the device.
* @suspend: Called to put the device to sleep mode. Usually to a
* low power state.
* @resume: Called to bring a device from sleep mode.
* @groups: Default attributes that get created by the driver core
* automatically.
* @pm: Power management operations of the device which matched
* this driver.
* @p: Driver core's private data, no one other than the driver
* core can touch this.
*
* The device driver-model tracks all of the drivers known to the system.
* The main reason for this tracking is to enable the driver core to match
* up drivers with new devices. Once drivers are known objects within the
* system, however, a number of other things become possible. Device drivers
* can export information and configuration variables that are independent
* of any specific device.
*/
struct device_driver {
const char *name;
struct bus_type *bus;
struct module *owner;
const char *mod_name; /* used for built-in modules */
bool suppress_bind_attrs; /* disables bind/unbind via sysfs */
const struct of_device_id *of_match_table;
const struct acpi_device_id *acpi_match_table;
int (*probe) (struct device *dev);
int (*remove) (struct device *dev);
void (*shutdown) (struct device *dev);
int (*suspend) (struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume) (struct device *dev);
const struct attribute_group **groups;
const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;
struct driver_private *p;
};
extern int __must_check driver_register(struct device_driver *drv);
extern void driver_unregister(struct device_driver *drv);
extern struct device_driver *driver_find(const char *name,
struct bus_type *bus);
extern int driver_probe_done(void);
extern void wait_for_device_probe(void);
/* sysfs interface for exporting driver attributes */
struct driver_attribute {
struct attribute attr;
ssize_t (*show)(struct device_driver *driver, char *buf);
ssize_t (*store)(struct device_driver *driver, const char *buf,
size_t count);
};
#define DRIVER_ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, _store) \
struct driver_attribute driver_attr_##_name = __ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, _store)
#define DRIVER_ATTR_RW(_name) \
struct driver_attribute driver_attr_##_name = __ATTR_RW(_name)
#define DRIVER_ATTR_RO(_name) \
struct driver_attribute driver_attr_##_name = __ATTR_RO(_name)
#define DRIVER_ATTR_WO(_name) \
struct driver_attribute driver_attr_##_name = __ATTR_WO(_name)
extern int __must_check driver_create_file(struct device_driver *driver,
const struct driver_attribute *attr);
extern void driver_remove_file(struct device_driver *driver,
const struct driver_attribute *attr);
extern int __must_check driver_for_each_device(struct device_driver *drv,
struct device *start,
void *data,
int (*fn)(struct device *dev,
void *));
struct device *driver_find_device(struct device_driver *drv,
struct device *start, void *data,
int (*match)(struct device *dev, void *data));
/**
* struct subsys_interface - interfaces to device functions
* @name: name of the device function
* @subsys: subsytem of the devices to attach to
* @node: the list of functions registered at the subsystem
* @add_dev: device hookup to device function handler
* @remove_dev: device hookup to device function handler
*
* Simple interfaces attached to a subsystem. Multiple interfaces can
* attach to a subsystem and its devices. Unlike drivers, they do not
* exclusively claim or control devices. Interfaces usually represent
* a specific functionality of a subsystem/class of devices.
*/
struct subsys_interface {
const char *name;
struct bus_type *subsys;
struct list_head node;
int (*add_dev)(struct device *dev, struct subsys_interface *sif);
int (*remove_dev)(struct device *dev, struct subsys_interface *sif);
};
int subsys_interface_register(struct subsys_interface *sif);
void subsys_interface_unregister(struct subsys_interface *sif);
int subsys_system_register(struct bus_type *subsys,
const struct attribute_group **groups);
int subsys_virtual_register(struct bus_type *subsys,
const struct attribute_group **groups);
/**
* struct class - device classes
* @name: Name of the class.
* @owner: The module owner.
* @class_attrs: Default attributes of this class.
* @dev_groups: Default attributes of the devices that belong to the class.
* @dev_kobj: The kobject that represents this class and links it into the hierarchy.
* @dev_uevent: Called when a device is added, removed from this class, or a
* few other things that generate uevents to add the environment
* variables.
* @devnode: Callback to provide the devtmpfs.
* @class_release: Called to release this class.
* @dev_release: Called to release the device.
* @suspend: Used to put the device to sleep mode, usually to a low power
* state.
* @resume: Used to bring the device from the sleep mode.
* @ns_type: Callbacks so sysfs can detemine namespaces.
* @namespace: Namespace of the device belongs to this class.
* @pm: The default device power management operations of this class.
* @p: The private data of the driver core, no one other than the
* driver core can touch this.
*
* A class is a higher-level view of a device that abstracts out low-level
* implementation details. Drivers may see a SCSI disk or an ATA disk, but,
* at the class level, they are all simply disks. Classes allow user space
* to work with devices based on what they do, rather than how they are
* connected or how they work.
*/
struct class {
const char *name;
struct module *owner;
struct class_attribute *class_attrs;
const struct attribute_group **dev_groups;
struct kobject *dev_kobj;
int (*dev_uevent)(struct device *dev, struct kobj_uevent_env *env);
char *(*devnode)(struct device *dev, umode_t *mode);
void (*class_release)(struct class *class);
void (*dev_release)(struct device *dev);
int (*suspend)(struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume)(struct device *dev);
const struct kobj_ns_type_operations *ns_type;
const void *(*namespace)(struct device *dev);
const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;
struct subsys_private *p;
};
struct class_dev_iter {
struct klist_iter ki;
const struct device_type *type;
};
extern struct kobject *sysfs_dev_block_kobj;
extern struct kobject *sysfs_dev_char_kobj;
extern int __must_check __class_register(struct class *class,
struct lock_class_key *key);
extern void class_unregister(struct class *class);
/* This is a #define to keep the compiler from merging different
* instances of the __key variable */
#define class_register(class) \
({ \
static struct lock_class_key __key; \
__class_register(class, &__key); \
})
struct class_compat;
struct class_compat *class_compat_register(const char *name);
void class_compat_unregister(struct class_compat *cls);
int class_compat_create_link(struct class_compat *cls, struct device *dev,
struct device *device_link);
void class_compat_remove_link(struct class_compat *cls, struct device *dev,
struct device *device_link);
extern void class_dev_iter_init(struct class_dev_iter *iter,
struct class *class,
struct device *start,
const struct device_type *type);
extern struct device *class_dev_iter_next(struct class_dev_iter *iter);
extern void class_dev_iter_exit(struct class_dev_iter *iter);
extern int class_for_each_device(struct class *class, struct device *start,
void *data,
int (*fn)(struct device *dev, void *data));
extern struct device *class_find_device(struct class *class,
struct device *start, const void *data,
int (*match)(struct device *, const void *));
struct class_attribute {
struct attribute attr;
ssize_t (*show)(struct class *class, struct class_attribute *attr,
char *buf);
ssize_t (*store)(struct class *class, struct class_attribute *attr,
const char *buf, size_t count);
};
#define CLASS_ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, _store) \
struct class_attribute class_attr_##_name = __ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, _store)
#define CLASS_ATTR_RW(_name) \
struct class_attribute class_attr_##_name = __ATTR_RW(_name)
#define CLASS_ATTR_RO(_name) \
struct class_attribute class_attr_##_name = __ATTR_RO(_name)
extern int __must_check class_create_file_ns(struct class *class,
const struct class_attribute *attr,
const void *ns);
extern void class_remove_file_ns(struct class *class,
const struct class_attribute *attr,
const void *ns);
static inline int __must_check class_create_file(struct class *class,
const struct class_attribute *attr)
{
return class_create_file_ns(class, attr, NULL);
}
static inline void class_remove_file(struct class *class,
const struct class_attribute *attr)
{
return class_remove_file_ns(class, attr, NULL);
}
/* Simple class attribute that is just a static string */
struct class_attribute_string {
struct class_attribute attr;
char *str;
};
/* Currently read-only only */
#define _CLASS_ATTR_STRING(_name, _mode, _str) \
{ __ATTR(_name, _mode, show_class_attr_string, NULL), _str }
#define CLASS_ATTR_STRING(_name, _mode, _str) \
struct class_attribute_string class_attr_##_name = \
_CLASS_ATTR_STRING(_name, _mode, _str)
extern ssize_t show_class_attr_string(struct class *class, struct class_attribute *attr,
char *buf);
struct class_interface {
struct list_head node;
struct class *class;
int (*add_dev) (struct device *, struct class_interface *);
void (*remove_dev) (struct device *, struct class_interface *);
};
extern int __must_check class_interface_register(struct class_interface *);
extern void class_interface_unregister(struct class_interface *);
extern struct class * __must_check __class_create(struct module *owner,
const char *name,
struct lock_class_key *key);
extern void class_destroy(struct class *cls);
/* This is a #define to keep the compiler from merging different
* instances of the __key variable */
#define class_create(owner, name) \
({ \
static struct lock_class_key __key; \
__class_create(owner, name, &__key); \
})
/*
* The type of device, "struct device" is embedded in. A class
* or bus can contain devices of different types
* like "partitions" and "disks", "mouse" and "event".
* This identifies the device type and carries type-specific
* information, equivalent to the kobj_type of a kobject.
* If "name" is specified, the uevent will contain it in
* the DEVTYPE variable.
*/
struct device_type {
const char *name;
const struct attribute_group **groups;
int (*uevent)(struct device *dev, struct kobj_uevent_env *env);
char *(*devnode)(struct device *dev, umode_t *mode,
kuid_t *uid, kgid_t *gid);
void (*release)(struct device *dev);
const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;
};
/* interface for exporting device attributes */
struct device_attribute {
struct attribute attr;
ssize_t (*show)(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr,
char *buf);
ssize_t (*store)(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr,
const char *buf, size_t count);
};
struct dev_ext_attribute {
struct device_attribute attr;
void *var;
};
ssize_t device_show_ulong(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr,
char *buf);
ssize_t device_store_ulong(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr,
const char *buf, size_t count);
ssize_t device_show_int(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr,
char *buf);
ssize_t device_store_int(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr,
const char *buf, size_t count);
ssize_t device_show_bool(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr,
char *buf);
ssize_t device_store_bool(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr,
const char *buf, size_t count);
#define DEVICE_ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, _store) \
struct device_attribute dev_attr_##_name = __ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, _store)
#define DEVICE_ATTR_RW(_name) \
struct device_attribute dev_attr_##_name = __ATTR_RW(_name)
#define DEVICE_ATTR_RO(_name) \
struct device_attribute dev_attr_##_name = __ATTR_RO(_name)
#define DEVICE_ATTR_WO(_name) \
struct device_attribute dev_attr_##_name = __ATTR_WO(_name)
#define DEVICE_ULONG_ATTR(_name, _mode, _var) \
struct dev_ext_attribute dev_attr_##_name = \
{ __ATTR(_name, _mode, device_show_ulong, device_store_ulong), &(_var) }
#define DEVICE_INT_ATTR(_name, _mode, _var) \
struct dev_ext_attribute dev_attr_##_name = \
{ __ATTR(_name, _mode, device_show_int, device_store_int), &(_var) }
#define DEVICE_BOOL_ATTR(_name, _mode, _var) \
struct dev_ext_attribute dev_attr_##_name = \
{ __ATTR(_name, _mode, device_show_bool, device_store_bool), &(_var) }
#define DEVICE_ATTR_IGNORE_LOCKDEP(_name, _mode, _show, _store) \
struct device_attribute dev_attr_##_name = \
__ATTR_IGNORE_LOCKDEP(_name, _mode, _show, _store)
extern int device_create_file(struct device *device,
const struct device_attribute *entry);
extern void device_remove_file(struct device *dev,
const struct device_attribute *attr);
extern bool device_remove_file_self(struct device *dev,
const struct device_attribute *attr);
extern int __must_check device_create_bin_file(struct device *dev,
const struct bin_attribute *attr);
extern void device_remove_bin_file(struct device *dev,
const struct bin_attribute *attr);
/* device resource management */
typedef void (*dr_release_t)(struct device *dev, void *res);
typedef int (*dr_match_t)(struct device *dev, void *res, void *match_data);
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_DEVRES
extern void *__devres_alloc(dr_release_t release, size_t size, gfp_t gfp,
const char *name);
#define devres_alloc(release, size, gfp) \
__devres_alloc(release, size, gfp, #release)
#else
extern void *devres_alloc(dr_release_t release, size_t size, gfp_t gfp);
#endif
extern void devres_for_each_res(struct device *dev, dr_release_t release,
dr_match_t match, void *match_data,
void (*fn)(struct device *, void *, void *),
void *data);
extern void devres_free(void *res);
extern void devres_add(struct device *dev, void *res);
extern void *devres_find(struct device *dev, dr_release_t release,
dr_match_t match, void *match_data);
extern void *devres_get(struct device *dev, void *new_res,
dr_match_t match, void *match_data);
extern void *devres_remove(struct device *dev, dr_release_t release,
dr_match_t match, void *match_data);
extern int devres_destroy(struct device *dev, dr_release_t release,
dr_match_t match, void *match_data);
extern int devres_release(struct device *dev, dr_release_t release,
dr_match_t match, void *match_data);
/* devres group */
extern void * __must_check devres_open_group(struct device *dev, void *id,
gfp_t gfp);
extern void devres_close_group(struct device *dev, void *id);
extern void devres_remove_group(struct device *dev, void *id);
extern int devres_release_group(struct device *dev, void *id);
/* managed devm_k.alloc/kfree for device drivers */
extern void *devm_kmalloc(struct device *dev, size_t size, gfp_t gfp);
extern char *devm_kvasprintf(struct device *dev, gfp_t gfp, const char *fmt,
va_list ap);
extern __printf(3, 4)
char *devm_kasprintf(struct device *dev, gfp_t gfp, const char *fmt, ...);
static inline void *devm_kzalloc(struct device *dev, size_t size, gfp_t gfp)
{
return devm_kmalloc(dev, size, gfp | __GFP_ZERO);
}
static inline void *devm_kmalloc_array(struct device *dev,
size_t n, size_t size, gfp_t flags)
{
if (size != 0 && n > SIZE_MAX / size)
return NULL;
return devm_kmalloc(dev, n * size, flags);
}
static inline void *devm_kcalloc(struct device *dev,
size_t n, size_t size, gfp_t flags)
{
return devm_kmalloc_array(dev, n, size, flags | __GFP_ZERO);
}
extern void devm_kfree(struct device *dev, void *p);
extern char *devm_kstrdup(struct device *dev, const char *s, gfp_t gfp);
extern void *devm_kmemdup(struct device *dev, const void *src, size_t len,
gfp_t gfp);
extern unsigned long devm_get_free_pages(struct device *dev,
gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order);
extern void devm_free_pages(struct device *dev, unsigned long addr);
void __iomem *devm_ioremap_resource(struct device *dev, struct resource *res);
/* allows to add/remove a custom action to devres stack */
int devm_add_action(struct device *dev, void (*action)(void *), void *data);
void devm_remove_action(struct device *dev, void (*action)(void *), void *data);
struct device_dma_parameters {
/*
* a low level driver may set these to teach IOMMU code about
* sg limitations.
*/
unsigned int max_segment_size;
unsigned long segment_boundary_mask;
};
struct acpi_device;
struct acpi_dev_node {
#ifdef CONFIG_ACPI
struct acpi_device *companion;
#endif
};
/**
* struct device - The basic device structure
* @parent: The device's "parent" device, the device to which it is attached.
* In most cases, a parent device is some sort of bus or host
* controller. If parent is NULL, the device, is a top-level device,
* which is not usually what you want.
* @p: Holds the private data of the driver core portions of the device.
* See the comment of the struct device_private for detail.
* @kobj: A top-level, abstract class from which other classes are derived.
* @init_name: Initial name of the device.
* @type: The type of device.
* This identifies the device type and carries type-specific
* information.
* @mutex: Mutex to synchronize calls to its driver.
* @bus: Type of bus device is on.
* @driver: Which driver has allocated this
* @platform_data: Platform data specific to the device.
* Example: For devices on custom boards, as typical of embedded
* and SOC based hardware, Linux often uses platform_data to point
* to board-specific structures describing devices and how they
* are wired. That can include what ports are available, chip
* variants, which GPIO pins act in what additional roles, and so
* on. This shrinks the "Board Support Packages" (BSPs) and
* minimizes board-specific #ifdefs in drivers.
* @driver_data: Private pointer for driver specific info.
* @power: For device power management.
* See Documentation/power/devices.txt for details.
* @pm_domain: Provide callbacks that are executed during system suspend,
* hibernation, system resume and during runtime PM transitions
* along with subsystem-level and driver-level callbacks.
* @pins: For device pin management.
* See Documentation/pinctrl.txt for details.
* @msi_domain: The generic MSI domain this device is using.
* @numa_node: NUMA node this device is close to.
* @dma_mask: Dma mask (if dma'ble device).
* @coherent_dma_mask: Like dma_mask, but for alloc_coherent mapping as not all
* hardware supports 64-bit addresses for consistent allocations
* such descriptors.
* @dma_pfn_offset: offset of DMA memory range relatively of RAM
* @dma_parms: A low level driver may set these to teach IOMMU code about
* segment limitations.
* @dma_pools: Dma pools (if dma'ble device).
* @dma_mem: Internal for coherent mem override.
* @cma_area: Contiguous memory area for dma allocations
* @archdata: For arch-specific additions.
* @of_node: Associated device tree node.
* @acpi_node: Associated ACPI device node.
* @devt: For creating the sysfs "dev".
* @id: device instance
* @devres_lock: Spinlock to protect the resource of the device.
* @devres_head: The resources list of the device.
* @knode_class: The node used to add the device to the class list.
* @class: The class of the device.
* @groups: Optional attribute groups.
* @release: Callback to free the device after all references have
* gone away. This should be set by the allocator of the
* device (i.e. the bus driver that discovered the device).
* @iommu_group: IOMMU group the device belongs to.
*
* @offline_disabled: If set, the device is permanently online.
* @offline: Set after successful invocation of bus type's .offline().
*
* At the lowest level, every device in a Linux system is represented by an
* instance of struct device. The device structure contains the information
* that the device model core needs to model the system. Most subsystems,
* however, track additional information about the devices they host. As a
* result, it is rare for devices to be represented by bare device structures;
* instead, that structure, like kobject structures, is usually embedded within
* a higher-level representation of the device.
*/
struct device {
struct device *parent;
struct device_private *p;
struct kobject kobj;
const char *init_name; /* initial name of the device */
const struct device_type *type;
struct mutex mutex; /* mutex to synchronize calls to
* its driver.
*/
struct bus_type *bus; /* type of bus device is on */
struct device_driver *driver; /* which driver has allocated this
device */
void *platform_data; /* Platform specific data, device
core doesn't touch it */
void *driver_data; /* Driver data, set and get with
dev_set/get_drvdata */
struct dev_pm_info power;
struct dev_pm_domain *pm_domain;
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_MSI_IRQ_DOMAIN
struct irq_domain *msi_domain;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PINCTRL
struct dev_pin_info *pins;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
int numa_node; /* NUMA node this device is close to */
#endif
u64 *dma_mask; /* dma mask (if dma'able device) */
u64 coherent_dma_mask;/* Like dma_mask, but for
alloc_coherent mappings as
not all hardware supports
64 bit addresses for consistent
allocations such descriptors. */
unsigned long dma_pfn_offset;
struct device_dma_parameters *dma_parms;
struct list_head dma_pools; /* dma pools (if dma'ble) */
struct dma_coherent_mem *dma_mem; /* internal for coherent mem
override */
#ifdef CONFIG_DMA_CMA
struct cma *cma_area; /* contiguous memory area for dma
allocations */
#endif
struct removed_region *removed_mem;
/* arch specific additions */
struct dev_archdata archdata;
struct device_node *of_node; /* associated device tree node */
struct acpi_dev_node acpi_node; /* associated ACPI device node */
dev_t devt; /* dev_t, creates the sysfs "dev" */
u32 id; /* device instance */
spinlock_t devres_lock;
struct list_head devres_head;
struct klist_node knode_class;
struct class *class;
const struct attribute_group **groups; /* optional groups */
void (*release)(struct device *dev);
struct iommu_group *iommu_group;
bool offline_disabled:1;
bool offline:1;
};
static inline struct device *kobj_to_dev(struct kobject *kobj)
{
return container_of(kobj, struct device, kobj);
}
/* Get the wakeup routines, which depend on struct device */
#include <linux/pm_wakeup.h>
static inline const char *dev_name(const struct device *dev)
{
/* Use the init name until the kobject becomes available */
if (dev->init_name)
return dev->init_name;
return kobject_name(&dev->kobj);
}
extern __printf(2, 3)
int dev_set_name(struct device *dev, const char *name, ...);
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
static inline int dev_to_node(struct device *dev)
{
return dev->numa_node;
}
static inline void set_dev_node(struct device *dev, int node)
{
dev->numa_node = node;
}
#else
static inline int dev_to_node(struct device *dev)
{
return -1;
}
static inline void set_dev_node(struct device *dev, int node)
{
}
#endif
static inline struct irq_domain *dev_get_msi_domain(const struct device *dev)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_MSI_IRQ_DOMAIN
return dev->msi_domain;
#else
return NULL;
#endif
}
static inline void dev_set_msi_domain(struct device *dev, struct irq_domain *d)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_MSI_IRQ_DOMAIN
dev->msi_domain = d;
#endif
}
static inline void *dev_get_drvdata(const struct device *dev)
{
return dev->driver_data;
}
static inline void dev_set_drvdata(struct device *dev, void *data)
{
dev->driver_data = data;
}
static inline struct pm_subsys_data *dev_to_psd(struct device *dev)
{
return dev ? dev->power.subsys_data : NULL;
}
static inline unsigned int dev_get_uevent_suppress(const struct device *dev)
{
return dev->kobj.uevent_suppress;
}
static inline void dev_set_uevent_suppress(struct device *dev, int val)
{
dev->kobj.uevent_suppress = val;
}
static inline int device_is_registered(struct device *dev)
{
return dev->kobj.state_in_sysfs;
}
static inline void device_enable_async_suspend(struct device *dev)
{
if (!dev->power.is_prepared)
dev->power.async_suspend = true;
}
static inline void device_disable_async_suspend(struct device *dev)
{
if (!dev->power.is_prepared)
dev->power.async_suspend = false;
}
static inline bool device_async_suspend_enabled(struct device *dev)
{
return !!dev->power.async_suspend;
}
static inline void pm_suspend_ignore_children(struct device *dev, bool enable)
{
dev->power.ignore_children = enable;
}
static inline void dev_pm_syscore_device(struct device *dev, bool val)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_SLEEP
dev->power.syscore = val;
#endif
}
static inline void device_lock(struct device *dev)
{
mutex_lock(&dev->mutex);
}
static inline int device_trylock(struct device *dev)
{
return mutex_trylock(&dev->mutex);
}
static inline void device_unlock(struct device *dev)
{
mutex_unlock(&dev->mutex);
}
void driver_init(void);
/*
* High level routines for use by the bus drivers
*/
extern int __must_check device_register(struct device *dev);
extern void device_unregister(struct device *dev);
extern void device_initialize(struct device *dev);
extern int __must_check device_add(struct device *dev);
extern void device_del(struct device *dev);
extern int device_for_each_child(struct device *dev, void *data,
int (*fn)(struct device *dev, void *data));
extern struct device *device_find_child(struct device *dev, void *data,
int (*match)(struct device *dev, void *data));
extern int device_rename(struct device *dev, const char *new_name);
extern int device_move(struct device *dev, struct device *new_parent,
enum dpm_order dpm_order);
extern const char *device_get_devnode(struct device *dev,
umode_t *mode, kuid_t *uid, kgid_t *gid,
const char **tmp);
static inline bool device_supports_offline(struct device *dev)
{
return dev->bus && dev->bus->offline && dev->bus->online;
}
extern void lock_device_hotplug(void);
extern void unlock_device_hotplug(void);
extern int lock_device_hotplug_sysfs(void);
extern int device_offline(struct device *dev);
extern int device_online(struct device *dev);
/*
* Root device objects for grouping under /sys/devices
*/
extern struct device *__root_device_register(const char *name,
struct module *owner);
/* This is a macro to avoid include problems with THIS_MODULE */
#define root_device_register(name) \
__root_device_register(name, THIS_MODULE)
extern void root_device_unregister(struct device *root);
static inline void *dev_get_platdata(const struct device *dev)
{
return dev->platform_data;
}
/*
* Manual binding of a device to driver. See drivers/base/bus.c
* for information on use.
*/
extern int __must_check device_bind_driver(struct device *dev);
extern void device_release_driver(struct device *dev);
extern int __must_check device_attach(struct device *dev);
extern int __must_check driver_attach(struct device_driver *drv);
extern int __must_check device_reprobe(struct device *dev);
/*
* Easy functions for dynamically creating devices on the fly
*/
extern struct device *device_create_vargs(struct class *cls,
struct device *parent,
dev_t devt,
void *drvdata,
const char *fmt,
va_list vargs);
extern __printf(5, 6)
struct device *device_create(struct class *cls, struct device *parent,
dev_t devt, void *drvdata,
const char *fmt, ...);
extern __printf(6, 7)
struct device *device_create_with_groups(struct class *cls,
struct device *parent, dev_t devt, void *drvdata,
const struct attribute_group **groups,
const char *fmt, ...);
extern void device_destroy(struct class *cls, dev_t devt);
/*
* Platform "fixup" functions - allow the platform to have their say
* about devices and actions that the general device layer doesn't
* know about.
*/
/* Notify platform of device discovery */
extern int (*platform_notify)(struct device *dev);
extern int (*platform_notify_remove)(struct device *dev);
/*
* get_device - atomically increment the reference count for the device.
*
*/
extern struct device *get_device(struct device *dev);
extern void put_device(struct device *dev);
#ifdef CONFIG_DEVTMPFS
extern int devtmpfs_create_node(struct device *dev);
extern int devtmpfs_delete_node(struct device *dev);
extern int devtmpfs_mount(const char *mntdir);
#else
static inline int devtmpfs_create_node(struct device *dev) { return 0; }
static inline int devtmpfs_delete_node(struct device *dev) { return 0; }
static inline int devtmpfs_mount(const char *mountpoint) { return 0; }
#endif
/* drivers/base/power/shutdown.c */
extern void device_shutdown(void);
/* debugging and troubleshooting/diagnostic helpers. */
extern const char *dev_driver_string(const struct device *dev);
#ifdef CONFIG_PRINTK
extern __printf(3, 0)
int dev_vprintk_emit(int level, const struct device *dev,
const char *fmt, va_list args);
extern __printf(3, 4)
int dev_printk_emit(int level, const struct device *dev, const char *fmt, ...);
extern __printf(3, 4)
int dev_printk(const char *level, const struct device *dev,
const char *fmt, ...);
extern __printf(2, 3)
int dev_emerg(const struct device *dev, const char *fmt, ...);
extern __printf(2, 3)
int dev_alert(const struct device *dev, const char *fmt, ...);
extern __printf(2, 3)
int dev_crit(const struct device *dev, const char *fmt, ...);
extern __printf(2, 3)
int dev_err(const struct device *dev, const char *fmt, ...);
extern __printf(2, 3)
int dev_warn(const struct device *dev, const char *fmt, ...);
extern __printf(2, 3)
int dev_notice(const struct device *dev, const char *fmt, ...);
extern __printf(2, 3)
int _dev_info(const struct device *dev, const char *fmt, ...);
#else
static inline __printf(3, 0)
int dev_vprintk_emit(int level, const struct device *dev,
const char *fmt, va_list args)
{ return 0; }
static inline __printf(3, 4)
int dev_printk_emit(int level, const struct device *dev, const char *fmt, ...)
{ return 0; }
static inline int __dev_printk(const char *level, const struct device *dev,
struct va_format *vaf)
{ return 0; }
static inline __printf(3, 4)
int dev_printk(const char *level, const struct device *dev,
const char *fmt, ...)
{ return 0; }
static inline __printf(2, 3)
int dev_emerg(const struct device *dev, const char *fmt, ...)
{ return 0; }
static inline __printf(2, 3)
int dev_crit(const struct device *dev, const char *fmt, ...)
{ return 0; }
static inline __printf(2, 3)
int dev_alert(const struct device *dev, const char *fmt, ...)
{ return 0; }
static inline __printf(2, 3)
int dev_err(const struct device *dev, const char *fmt, ...)
{ return 0; }
static inline __printf(2, 3)
int dev_warn(const struct device *dev, const char *fmt, ...)
{ return 0; }
static inline __printf(2, 3)
int dev_notice(const struct device *dev, const char *fmt, ...)
{ return 0; }
static inline __printf(2, 3)
int _dev_info(const struct device *dev, const char *fmt, ...)
{ return 0; }
#endif
/*
* Stupid hackaround for existing uses of non-printk uses dev_info
*
* Note that the definition of dev_info below is actually _dev_info
* and a macro is used to avoid redefining dev_info
*/
#define dev_info(dev, fmt, arg...) _dev_info(dev, fmt, ##arg)
#if defined(CONFIG_DYNAMIC_DEBUG)
#define dev_dbg(dev, format, ...) \
do { \
dynamic_dev_dbg(dev, format, ##__VA_ARGS__); \
} while (0)
#elif defined(DEBUG)
#define dev_dbg(dev, format, arg...) \
dev_printk(KERN_DEBUG, dev, format, ##arg)
#else
#define dev_dbg(dev, format, arg...) \
({ \
if (0) \
dev_printk(KERN_DEBUG, dev, format, ##arg); \
0; \
})
#endif
#define dev_level_ratelimited(dev_level, dev, fmt, ...) \
do { \
static DEFINE_RATELIMIT_STATE(_rs, \
DEFAULT_RATELIMIT_INTERVAL, \
DEFAULT_RATELIMIT_BURST); \
if (__ratelimit(&_rs)) \
dev_level(dev, fmt, ##__VA_ARGS__); \
} while (0)
#define dev_emerg_ratelimited(dev, fmt, ...) \
dev_level_ratelimited(dev_emerg, dev, fmt, ##__VA_ARGS__)
#define dev_alert_ratelimited(dev, fmt, ...) \
dev_level_ratelimited(dev_alert, dev, fmt, ##__VA_ARGS__)
#define dev_crit_ratelimited(dev, fmt, ...) \
dev_level_ratelimited(dev_crit, dev, fmt, ##__VA_ARGS__)
#define dev_err_ratelimited(dev, fmt, ...) \
dev_level_ratelimited(dev_err, dev, fmt, ##__VA_ARGS__)
#define dev_warn_ratelimited(dev, fmt, ...) \
dev_level_ratelimited(dev_warn, dev, fmt, ##__VA_ARGS__)
#define dev_notice_ratelimited(dev, fmt, ...) \
dev_level_ratelimited(dev_notice, dev, fmt, ##__VA_ARGS__)
#define dev_info_ratelimited(dev, fmt, ...) \
dev_level_ratelimited(dev_info, dev, fmt, ##__VA_ARGS__)
#if defined(CONFIG_DYNAMIC_DEBUG)
/* descriptor check is first to prevent flooding with "callbacks suppressed" */
#define dev_dbg_ratelimited(dev, fmt, ...) \
do { \
static DEFINE_RATELIMIT_STATE(_rs, \
DEFAULT_RATELIMIT_INTERVAL, \
DEFAULT_RATELIMIT_BURST); \
DEFINE_DYNAMIC_DEBUG_METADATA(descriptor, fmt); \
if (unlikely(descriptor.flags & _DPRINTK_FLAGS_PRINT) && \
__ratelimit(&_rs)) \
__dynamic_dev_dbg(&descriptor, dev, fmt, \
##__VA_ARGS__); \
} while (0)
#elif defined(DEBUG)
#define dev_dbg_ratelimited(dev, fmt, ...) \
do { \
static DEFINE_RATELIMIT_STATE(_rs, \
DEFAULT_RATELIMIT_INTERVAL, \
DEFAULT_RATELIMIT_BURST); \
if (__ratelimit(&_rs)) \
dev_printk(KERN_DEBUG, dev, fmt, ##__VA_ARGS__); \
} while (0)
#else
#define dev_dbg_ratelimited(dev, fmt, ...) \
no_printk(KERN_DEBUG pr_fmt(fmt), ##__VA_ARGS__)
#endif
#ifdef VERBOSE_DEBUG
#define dev_vdbg dev_dbg
#else
#define dev_vdbg(dev, format, arg...) \
({ \
if (0) \
dev_printk(KERN_DEBUG, dev, format, ##arg); \
0; \
})
#endif
/*
* dev_WARN*() acts like dev_printk(), but with the key difference of
* using WARN/WARN_ONCE to include file/line information and a backtrace.
*/
#define dev_WARN(dev, format, arg...) \
WARN(1, "%s %s: " format, dev_driver_string(dev), dev_name(dev), ## arg);
#define dev_WARN_ONCE(dev, condition, format, arg...) \
WARN_ONCE(condition, "%s %s: " format, \
dev_driver_string(dev), dev_name(dev), ## arg)
/* Create alias, so I can be autoloaded. */
#define MODULE_ALIAS_CHARDEV(major,minor) \
MODULE_ALIAS("char-major-" __stringify(major) "-" __stringify(minor))
#define MODULE_ALIAS_CHARDEV_MAJOR(major) \
MODULE_ALIAS("char-major-" __stringify(major) "-*")
#ifdef CONFIG_SYSFS_DEPRECATED
extern long sysfs_deprecated;
#else
#define sysfs_deprecated 0
#endif
/**
* module_driver() - Helper macro for drivers that don't do anything
* special in module init/exit. This eliminates a lot of boilerplate.
* Each module may only use this macro once, and calling it replaces
* module_init() and module_exit().
*
* @__driver: driver name
* @__register: register function for this driver type
* @__unregister: unregister function for this driver type
* @...: Additional arguments to be passed to __register and __unregister.
*
* Use this macro to construct bus specific macros for registering
* drivers, and do not use it on its own.
*/
#define module_driver(__driver, __register, __unregister, ...) \
static int __init __driver##_init(void) \
{ \
return __register(&(__driver) , ##__VA_ARGS__); \
} \
module_init(__driver##_init); \
static void __exit __driver##_exit(void) \
{ \
__unregister(&(__driver) , ##__VA_ARGS__); \
} \
module_exit(__driver##_exit);
#endif /* _DEVICE_H_ */找到struct class 结构体定义的地方

这里可以看到这个结构体里有许多成员,有些成员本身也是结构体类型,这里就不再详细赘述了,感兴趣的朋友可以慢慢跟进去阅读。我们回到上面的leds_class.c,刚刚讲leds_init(),先看看看该C文件里面的其他函数
看到这里,发现该C文件中有许多被static修饰的函数,这些函数都是干嘛用的呢?有没有人回想到前面讲过的leds目录结构,
然后结合到C文件里的这种类型的语句,是否会想到什么?
static DEVICE_ATTR(trigger, 0644, led_trigger_show, led_trigger_store);哦,应该是对应用户操作文件的函数吧,这里解释下这种语句的意思,看起来应该很好理解,
参数1:leds目录下文件名为trigger的文件
参数2:0644 文件操作权限
参数3,4:对应操作文件联系到的函数 ,这里在详细说明下 show(显示 cat) store(设置 echo)
那去验证下吧,经过cat echo 的操作
当博主先后对max_brightness文件进行cat -> echo -> cat 操作,效果如图
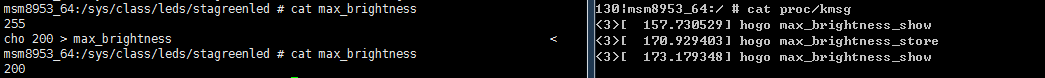
这样是不是证明我们刚刚的推断是正确的,nice
到目前为止,leds_class.c中还有一个很重要的最外函数led_classdev_register,这个函数可以注册一个led实例,为了让外部使用这个函数,在/kernel/msm-3.18/include/linux/leds.h中,特意使用了extern 修饰该函数
extern int led_classdev_register(struct device *parent,
struct led_classdev *led_cdev);讲到这,函数内有两个参数:
参数1:struct device,定义在/kernel/msm-3.18/include/linux/devices.h中,这里不做详细赘述
参数2:struct led_classdev,定义在/kernel/msm-3.18/include/linux/leds.h中,这里简单对该结构体作下分析。
struct led_classdev {
const char *name; //名字
enum led_brightness brightness; //亮度
enum led_brightness max_brightness; //最大亮度
enum led_brightness usr_brightness_req;
int flags; //标志 只支持 LED_SUSPENDED LED_CORE_SUSPENDRESUME LED_BLINK_ONESHOT等
/* Lower 16 bits reflect status */
#define LED_SUSPENDED (1 << 0)
/* Upper 16 bits reflect control information */
#define LED_CORE_SUSPENDRESUME (1 << 16)
#define LED_BLINK_ONESHOT (1 << 17)
#define LED_BLINK_ONESHOT_STOP (1 << 18)
#define LED_BLINK_INVERT (1 << 19)
#define LED_SYSFS_DISABLE (1 << 20)
/* Set LED brightness level */
/* Must not sleep, use a workqueue if needed */ //设置LED亮度等级*//*不能休眠,如果需要使用工作队列*/
void (*brightness_set)(struct led_classdev *led_cdev,
enum led_brightness brightness);
/* Get LED brightness level 获取LED亮度等级 */
enum led_brightness (*brightness_get)(struct led_classdev *led_cdev);
/*
* Activate hardware accelerated blink, delays are in milliseconds
* and if both are zero then a sensible default should be chosen.
* The call should adjust the timings in that case and if it can't
* match the values specified exactly.
* Deactivate blinking again when the brightness is set to a fixed
* value via the brightness_set() callback.
*/ /* 激活硬件加速的闪烁 */
int (*blink_set)(struct led_classdev *led_cdev,
unsigned long *delay_on,
unsigned long *delay_off);
struct device *dev;
const struct attribute_group **groups;
struct list_head node; /* LED Device list */ /* 所有已经注册的led_classdev使用这个节点串联起来 */
const char *default_trigger; /* Trigger to use 默认使用的触发器*/
unsigned long blink_delay_on, blink_delay_off;
struct timer_list blink_timer;
int blink_brightness;
struct work_struct set_brightness_work;
int delayed_set_value;
#ifdef CONFIG_LEDS_TRIGGERS //如果配置内核时使能了触发器功能,才会编译下面一段
/* Protects the trigger data below 保护下面的触发器数据*/
struct rw_semaphore trigger_lock;
struct led_trigger *trigger;
struct list_head trig_list;
void *trigger_data;
/* true if activated - deactivate routine uses it to do cleanup 如果激活-禁用例程使用它来做清理 */
bool activated;
#endif
/* Ensures consistent access to the LED Flash Class device 确保对LED Flash类设备的一致访问 */
struct mutex led_access;
};现在再来看看led_classdev_register这个函数的实现,当外部使用led子系统框架进行led实例驱动注册的时候,这个函数做了什么?
/**
* led_classdev_register - register a new object of led_classdev class.
* @parent: The device to register.
* @led_cdev: the led_classdev structure for this device.
*/
int led_classdev_register(struct device *parent, struct led_classdev *led_cdev)
{
/* 创建一个struct device,他的父设备是parent,drvdata是led_cdev,名字是led_cdev->name,类别是 leds_class*/
led_cdev->dev = device_create_with_groups(leds_class, parent, 0,
led_cdev, led_cdev->groups,
"%s", led_cdev->name);
if (IS_ERR(led_cdev->dev))
return PTR_ERR(led_cdev->dev);
#ifdef CONFIG_LEDS_TRIGGERS
init_rwsem(&led_cdev->trigger_lock); //初始化led_cdev的触发器自旋锁
#endif
mutex_init(&led_cdev->led_access); //初始化mutex锁
/* add to the list of leds */
down_write(&leds_list_lock); //获取写锁
list_add_tail(&led_cdev->node, &leds_list); //将新的led加入链表,全局链表是leds_list
up_write(&leds_list_lock); //释放读锁
if (!led_cdev->max_brightness)
led_cdev->max_brightness = LED_FULL; //如果该led中的最大亮度值为0 则填充为255 LED_FULL = 255
led_update_brightness(led_cdev); //获取led当前的亮度更新led_cdev的brightness成员
INIT_WORK(&led_cdev->set_brightness_work, set_brightness_delayed);
init_timer(&led_cdev->blink_timer);// 初始化内核定时器
//填充指定的内核定时器
led_cdev->blink_timer.function = led_timer_function;
led_cdev->blink_timer.data = (unsigned long)led_cdev;
#ifdef CONFIG_LEDS_TRIGGERS
led_trigger_set_default(led_cdev); //为led_cdev设置默认的触发器
#endif
dev_dbg(parent, "Registered led device: %s\n",
led_cdev->name);
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(led_classdev_register);
那接下来看看brightness 同级目录下的 trigger
这个对应的cat echo 应该也是有两个对应的函数,那函数实现在哪呢?
这时引入前面提到的一个文件:kernel/msm-3.18/drivers/leds/led-triggers.c
看到这里,先介绍之前遇到但没有说明的一个结构体,
struct led_trigger:定义在/kernel/msm-3.18/include/linux/leds.h中,这里简单对该结构体作下分析。
struct led_trigger {
/* Trigger Properties */
const char *name; //触发器名字
void (*activate)(struct led_classdev *led_cdev); //激活led。led_classdev和触发器建立连接时会调用这个方法。
void (*deactivate)(struct led_classdev *led_cdev); //取消激活。led_classdev和触发器取消连接时会调用这个方法。
/* LEDs under control by this trigger (for simple triggers) */ /* 本触发器控制之下的led链表 */
rwlock_t leddev_list_lock; //保护链表的锁
struct list_head led_cdevs; //链表头
/* Link to next registered trigger *//* 连接下一个已注册触发器的链表节点 ,所有已注册的触发器都会被加入一个全局链表*/
struct list_head next_trig;
};现在在回到led-triggers.c,可以看到led_trigger_store和led_trigger_show函数,那这两个就是对于trigger文件的cat和echo 操作直接进入的函数了,同样我们也可以验证一下。

这里我们可以在细看下led_trigger_store函数中的处理:
ssize_t led_trigger_store(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr,
const char *buf, size_t count)
{
struct led_classdev *led_cdev = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
char trigger_name[TRIG_NAME_MAX];
struct led_trigger *trig;
size_t len;
int ret = count;
pr_err("hogo led_trigger_store\n");
mutex_lock(&led_cdev->led_access);
if (led_sysfs_is_disabled(led_cdev)) {
ret = -EBUSY;
goto unlock;
}
trigger_name[sizeof(trigger_name) - 1] = '\0';
strncpy(trigger_name, buf, sizeof(trigger_name) - 1);
len = strlen(trigger_name);
if (len && trigger_name[len - 1] == '\n')
trigger_name[len - 1] = '\0';
if (!strcmp(trigger_name, "none")) {
led_trigger_remove(led_cdev);
goto unlock;
}
down_read(&triggers_list_lock);
list_for_each_entry(trig, &trigger_list, next_trig) {
if (!strcmp(trigger_name, trig->name)) {
down_write(&led_cdev->trigger_lock);
led_trigger_set(led_cdev, trig);
up_write(&led_cdev->trigger_lock);
up_read(&triggers_list_lock);
goto unlock;
}
}
up_read(&triggers_list_lock);
unlock:
mutex_unlock(&led_cdev->led_access);
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(led_trigger_store);从上面的执行过程看,
当用户对trigger输入 none 时,触发器会被remove,同时会与led_classdev断开连接,触发deactivate方法
当用户对trigger输入 非 none时,触发器它会寻找所有已注册的触发器,找到同名的并设置为当前led的触发器。然后与led_classdev建立连接,建立连接的时候会调用触发器的activate方法
说到这,还要补充点之前没有说到的,led_classdev注册的时候也会调用led_trigger_set_default来遍历所有已注册的触发器,找到和led_classdev.default_trigger同名的触发器则将它设为自己的触发器。
那到现在我们可以看看activate和deactivate方法了,那么问题来了,这两个方法实现在哪里呢?
刚开始博主一脸懵逼,看网上说的leds/xxx 目录下trigger可以控制led山所,同时会有 delay_on,delay_off存在可以控制闪烁的频率,但路并不是那么顺啊,博主并没有看到啊,原来,是这么回事,怎么回事?经过之前的一些分析,有没有可以想到是什么原因呢?
原因是这样的,首先led闪烁需要led_classdev(led实例与一个已经注册的trigger进行连接,并且连接成功),才会调用blink相关的函数去控制led闪烁。那么博主的问题是啥呢?
博主所调试的平台代码,在kernel/msm-3.18/drivers/leds/trigger/下有一个 ledtrig-timer.c的文件,我们先看看里面的内容:
/*
* LED Kernel Timer Trigger
*
* Copyright 2005-2006 Openedhand Ltd.
*
* Author: Richard Purdie <rpurdie@openedhand.com>
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 as
* published by the Free Software Foundation.
*
*/
#define DEBUG
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/ctype.h>
#include <linux/leds.h>
static ssize_t led_delay_on_show(struct device *dev,
struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
struct led_classdev *led_cdev = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
return sprintf(buf, "%lu\n", led_cdev->blink_delay_on);
}
static ssize_t led_delay_on_store(struct device *dev,
struct device_attribute *attr, const char *buf, size_t size)
{
struct led_classdev *led_cdev = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
unsigned long state;
ssize_t ret = -EINVAL;
ret = kstrtoul(buf, 10, &state);
if (ret)
return ret;
led_blink_set(led_cdev, &state, &led_cdev->blink_delay_off);
led_cdev->blink_delay_on = state;
return size;
}
static ssize_t led_delay_off_show(struct device *dev,
struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
struct led_classdev *led_cdev = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
return sprintf(buf, "%lu\n", led_cdev->blink_delay_off);
}
static ssize_t led_delay_off_store(struct device *dev,
struct device_attribute *attr, const char *buf, size_t size)
{
struct led_classdev *led_cdev = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
unsigned long state;
ssize_t ret = -EINVAL;
ret = kstrtoul(buf, 10, &state);
if (ret)
return ret;
led_blink_set(led_cdev, &led_cdev->blink_delay_on, &state);
led_cdev->blink_delay_off = state;
return size;
}
static DEVICE_ATTR(delay_on, 0644, led_delay_on_show, led_delay_on_store);
static DEVICE_ATTR(delay_off, 0644, led_delay_off_show, led_delay_off_store);
static void timer_trig_activate(struct led_classdev *led_cdev)
{
int rc;
led_cdev->trigger_data = NULL;
rc = device_create_file(led_cdev->dev, &dev_attr_delay_on);
if (rc)
return;
rc = device_create_file(led_cdev->dev, &dev_attr_delay_off);
if (rc)
goto err_out_delayon;
led_blink_set(led_cdev, &led_cdev->blink_delay_on,
&led_cdev->blink_delay_off);
led_cdev->activated = true;
return;
err_out_delayon:
device_remove_file(led_cdev->dev, &dev_attr_delay_on);
}
static void timer_trig_deactivate(struct led_classdev *led_cdev)
{
if (led_cdev->activated) {
device_remove_file(led_cdev->dev, &dev_attr_delay_on);
device_remove_file(led_cdev->dev, &dev_attr_delay_off);
led_cdev->activated = false;
}
/* Stop blinking */
led_set_brightness(led_cdev, LED_OFF);
}
static struct led_trigger timer_led_trigger = {
.name = "timer",
.activate = timer_trig_activate,
.deactivate = timer_trig_deactivate,
};
static int __init timer_trig_init(void)
{
return led_trigger_register(&timer_led_trigger);
}
static void __exit timer_trig_exit(void)
{
led_trigger_unregister(&timer_led_trigger);
}
module_init(timer_trig_init);
module_exit(timer_trig_exit);
MODULE_AUTHOR("Richard Purdie <rpurdie@openedhand.com>");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Timer LED trigger");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");看完这个文件中代码,博主心中卧槽了一声,这不就是坑了我好久的问题吗,但问题是为啥对trigger文件进行相关操作后没有进入这里的一些函数呢?
想来想去,只可能是这个文件没有参与编译,导致名为 timer 的触发器没有注册成功,那么led_classdev就无法与这个触发器进行连接,无法连接也就无法触发这里面的一系列函数了,经过一波思考,然后立马打开内核编译配置文件,再次心中卧槽了一下,还真是没编译,然后宏编译添加进去,make 一波,重新烧录boot.img ,哦豁,
![]()
东西出来了,然后再次对trigger 进行echo 操作,哦豁,灯闪起来了,查看下闪烁频率,默认的是500ms,echo ms > delay_on/delay_off 查看灯闪频率,哟,修改成功,很nice.
ps:
参考:
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_20678703/article/details/49301193
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/hanp_linux/article/details/79037610
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/Fred_Wu/article/details/51149987
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/u013256018/article/details/48682883

























 894
894

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










