Iterator是一个接口,里边有4个方法:
hasNext();next();remove();forEachRemaining();
我们一般可以用Iterator来遍历JSONArray,那是因为,JSONArray类实现了List接口,而List接口继承了Iterable
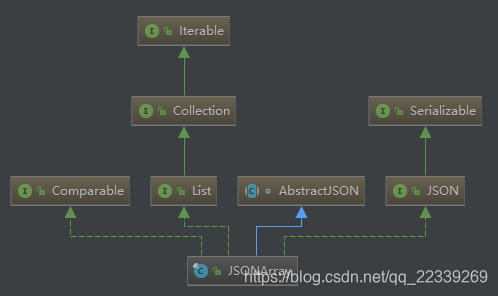
而Iterbale接口中,有Iterator<T> iterator()方法,List也拥有Iterator<T> iterator()方法,所以JSONArray必须实现Iterator<T> iterator()方法,如图:
public Iterator iterator() {
return new JSONArray.JSONArrayListIterator();
}JSONArray的Iterator<T> iterator()方法是借助JSONArrayListIterator类实现的。(JSONArrayListIterator类实现了ListIterator接口,而ListIterator接口正是继承了Iterbale接口,因此ListIterator也拥有Iterator<T> iterator()抽象方法,作为ListIterator的实现类,JSONArrayListIterator必须实现Iterator<T> iterator()抽象方法)
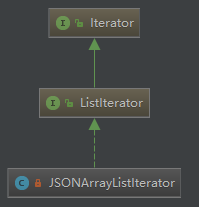
来看看它具体是怎样实现的:
private class JSONArrayListIterator implements ListIterator {
int currentIndex = 0;
int lastIndex = -1;
JSONArrayListIterator() {
}
JSONArrayListIterator(int index) {
this.currentIndex = index;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return this.currentIndex != JSONArray.this.size();
}
public Object next() {
try {
Object next = JSONArray.this.get(this.currentIndex);
this.lastIndex = this.currentIndex++;
return next;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException var2) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
public void remove() {
if (this.lastIndex == -1) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
} else {
try {
JSONArray.this.remove(this.lastIndex);
if (this.lastIndex < this.currentIndex) {
--this.currentIndex;
}
this.lastIndex = -1;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException var2) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return this.currentIndex != 0;
}
public Object previous() {
try {
int index = this.currentIndex - 1;
Object previous = JSONArray.this.get(index);
this.lastIndex = this.currentIndex = index;
return previous;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException var3) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
public int nextIndex() {
return this.currentIndex;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return this.currentIndex - 1;
}
public void set(Object obj) {
if (this.lastIndex == -1) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
} else {
try {
JSONArray.this.set(this.lastIndex, obj);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException var3) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
public void add(Object obj) {
try {
JSONArray.this.add(this.currentIndex++, obj);
this.lastIndex = -1;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException var3) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}了然了。。。
因此,我们可以用下面的代码遍历JSONArray
Person person = new Person("wang","18","man");
Person person1 = new Person("li","17","man");
List<Person> people = new ArrayList<>();
people.add(person);
people.add(person1);
JSONArray jsonArray = JSONArray.fromObject(people);
Iterator iterator2 = jsonArray.iterator();
while (iterator2.hasNext())
{
// System.out.println(iterator2.next().toString());
System.out.println(((JSONObject)iterator2.next()).get("age").toString());
}用下面的代码遍历JSONObject
//遍历JSONObject
JSON json = net.sf.json.JSONObject.fromObject(person);
Iterator iterator = ((JSONObject) json).keys();
while (iterator.hasNext())
{
String key = iterator.next().toString();
Object obj = ((JSONObject) json).get(key);
}





 本文详细解析了如何使用Iterator遍历JSONArray和JSONObject,通过实现ListIterator接口,利用JSONArrayListIterator类,展示了遍历过程中的核心代码片段。
本文详细解析了如何使用Iterator遍历JSONArray和JSONObject,通过实现ListIterator接口,利用JSONArrayListIterator类,展示了遍历过程中的核心代码片段。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








