模拟秒杀
思路
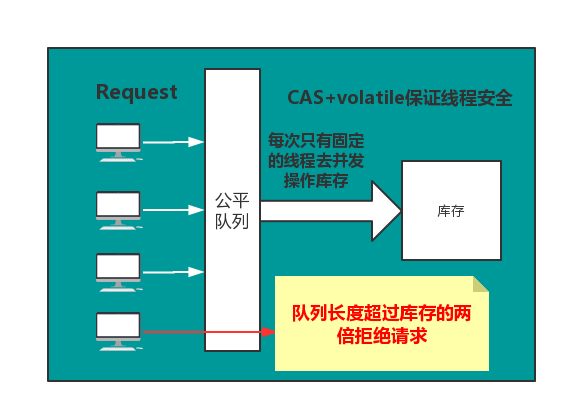
- 对每个秒杀请求入队操作
- 当库存为N时,队列的长度超过N时,可以考虑拒绝后续请求,直接响应客户端秒杀结束
- 为了减轻库存处理的压力,验证并发量,这里通过信号量来控制线程安全。
编码
- 通过Semaphore来控制并发量
- 通过CAS来控制更新库存,保证线程安全
public class Knock {
private static final Unsafe unsafe;
private static final long totalOffset;
private static volatile Knock knock;
private volatile int total;
private Semaphore semaphore;
static {
try {
Field field = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
field.setAccessible(true);
unsafe = (Unsafe) field.get(null);
totalOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(Knock.class.getDeclaredField("total"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new Error(e);
}
}
private Knock(int total, int threadsPerTime) {
this.total = total;
semaphore = new Semaphore(threadsPerTime, true);
}
public static Knock getInstance(int total, int threadsPerTime) {
if (null != knock) {
return knock;
}
synchronized (Knock.class) {
if (null == knock) {
knock = new Knock(total, threadsPerTime);
}
}
return knock;
}
public int getTotal() {
return total;
}
public boolean casTotal(int except) {
for (; ; ) {
if (total > 0) {
int update = total - 1;
if (unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, totalOffset, except, update)) {
return true;
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
public void doKnock(int need) {
if (semaphore.getQueueLength() > (total << 1) || total == 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getId() + ":已售罄!");
return;
}
try {
semaphore.acquire(need);
if (total == 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getId() + "已售罄!");
return;
}
int expect = total;
if (casTotal(expect)) {
int current = expect - 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getId() + "当前剩余:" + current);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
semaphore.release(need);
}
}
}
测试,通过CPU核心数,去控制并发的线程,提高QPS
public class KTest {
static class T extends Thread {
private Knock knock;
private int need;
public T(Knock knock, int need) {
this.knock = knock;
this.need = need;
}
@Override
public void run() {
knock.doKnock(need);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int availableProcessors = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
long s = System.currentTimeMillis();
Knock knock = Knock.getInstance(1100, availableProcessors*2);
for (int i = 0; i < 2000; i++) {
T t = new T(knock, 1);
try {
t.start();
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
long e = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(knock.getTotal() + "======================"+(e-s));
}
}



























 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








