scikit-image图像数据处理
Color 模块和exposure模块
1.基本操作
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage import data
color_image = data.chelsea()
print(color_image.shape)
plt.imshow(color_image)
answer:
(300, 451, 3)

2.分割和索引
red_channel = color_image[:, :, 0] # 红色通道
plt.imshow(red_channel, cmap='gray')
print(red_channel.shape)
answer:
(300, 451)

色彩空间 RGB,HSV,Gray
- RGB转gray -- skimage.color.rgb2gray()
import skimage gray_img = skimage.color.rgb2gray(color_image) plt.imshow(gray_img, cmap='gray') print(gray_img.shape) answer: (300,451)
颜色直方图
- 能快速描绘图像整体像素值分布的统计信息
- skimage.exposure.histogram
- 可以根据直方图选定阈值用于调节图像对比度
- 对比度:
- 增强图像数据的对比度有利于特征的提取,不论是从肉眼还是算法来看都有帮助
- 更改对比度范围
- skimage.exposure.rescale_intensity(image,in_range=(min,max)),原图中小于min的像素值设为0,大鱼max的为255
- 直方图均衡化
- 自动调整图像对比度 skimage.exposure.equalize_hist(image),处理好数据范围变为【0,1】
-
from skimage import data from skimage import exposure # 灰度图颜色直方图 image = data.camera() #print(image.shape) hist, bin_centers = exposure.histogram(image) #bin_centers是像素值的范围,这里输出是0-255 print(bin_centers) fig, ax = plt.subplots(ncols=1) ax.fill_between(bin_centers, hist)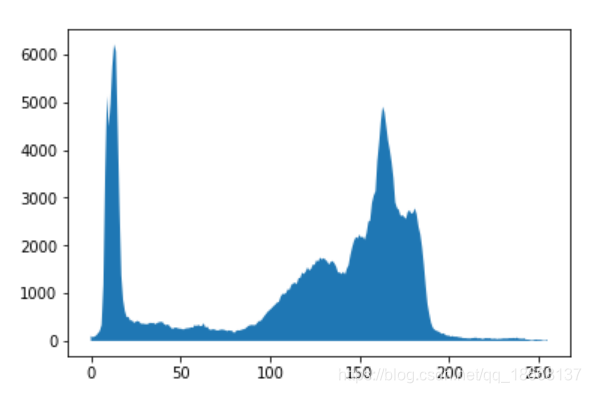
-
彩色图像直方图
-
# 彩色图像直方图 cat = data.chelsea() # R通道 hist_r, bin_centers_r = exposure.histogram(cat[:,:,0]) # G通道 hist_g, bin_centers_g = exposure.histogram(cat[:,:,1]) # B通道 hist_b, bin_centers_b = exposure.histogram(cat[:,:,2]) fig, (ax_r, ax_g, ax_b) = plt.subplots(ncols=3, figsize=(10, 5)) #ax = plt.gca() ax_r.fill_between(bin_centers_r, hist_r) ax_g.fill_between(bin_centers_g, hist_g) ax_b.fill_between(bin_centers_b, hist_b)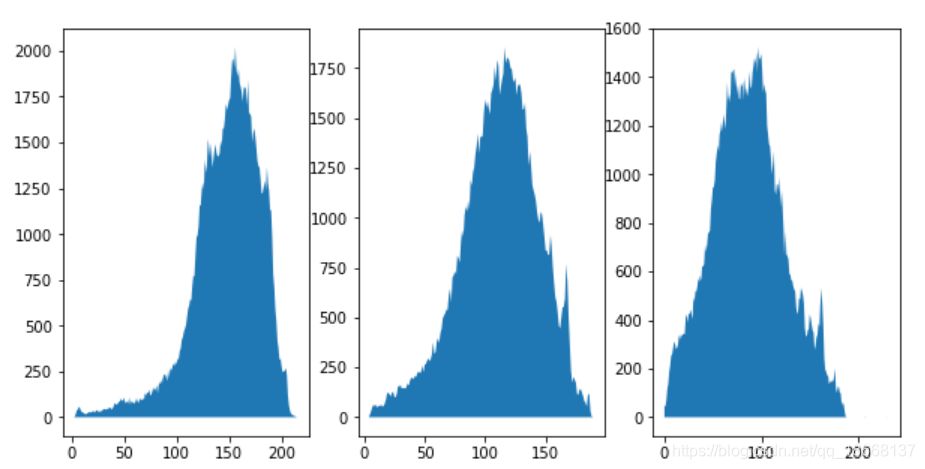
对比度
# 原图像
image = data.camera()
hist, bin_centers = exposure.histogram(image)
# 改变对比度
# image中小于10的像素值设为0,大于180的像素值设为255
high_contrast = exposure.rescale_intensity(image, in_range=(10, 180))
hist2, bin_centers2 = exposure.histogram(high_contrast)
# 图像对比
fig, (ax_1, ax_2) = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=(10, 5))
ax_1.imshow(image, cmap='gray')
ax_2.imshow(high_contrast, cmap='gray')
fig, (ax_hist1, ax_hist2) = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=(10, 5))
ax_hist1.fill_between(bin_centers, hist)
ax_hist2.fill_between(bin_centers2, hist2)
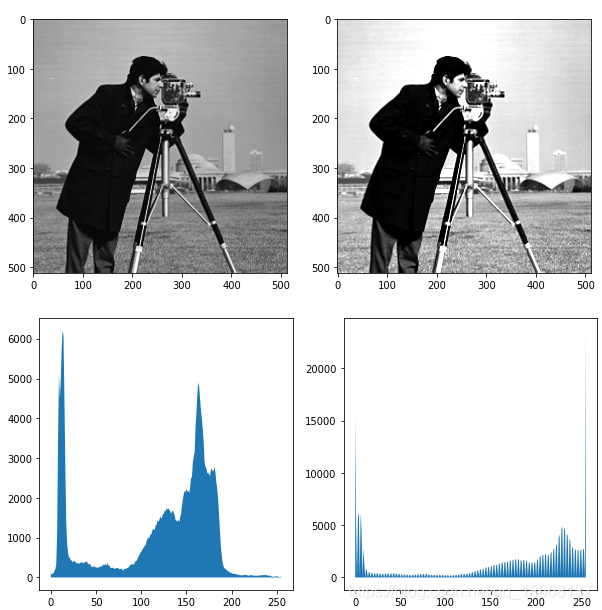
自动直方图均衡化
# 直方图均衡化
equalized = exposure.equalize_hist(image)
hist3, bin_centers3 = exposure.histogram(equalized)
# 图像对比
fig, (ax_1, ax_2) = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=(10, 5))
ax_1.imshow(image, cmap='gray')
ax_2.imshow(equalized, cmap='gray')
fig, (ax_hist1, ax_hist2) = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=(10, 5))
ax_hist1.fill_between(bin_centers, hist)
ax_hist2.fill_between(bin_centers3, hist3)
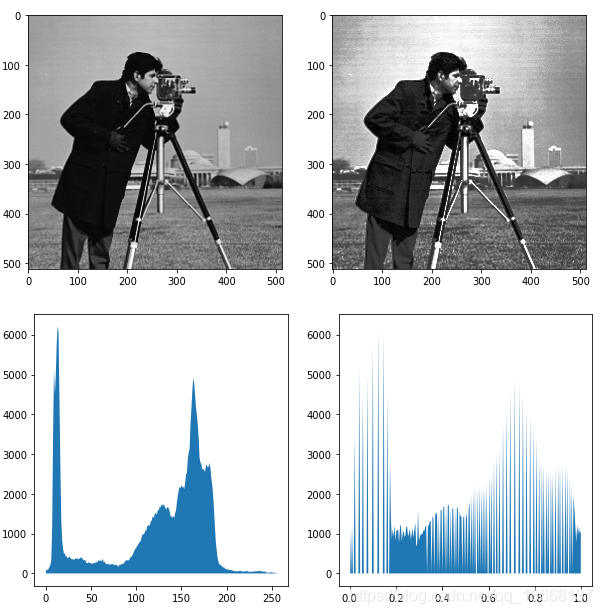
图像滤波
- 滤波可以去除图像中的噪声点,由此增强图像的特征
- 中值滤波
- skimage.filters.rank.median
from skimage import data
from skimage.morphology import disk
from skimage.filters.rank import median
img = data.camera()
med1 = median(img, disk(3)) # 3x3中值滤波
med2 = median(img, disk(5)) # 5x5中值滤波
# 图像对比
fig, (ax_1, ax_2, ax_3) = plt.subplots(ncols=3, figsize=(15, 10))
ax_1.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
ax_2.imshow(med1, cmap='gray')
ax_3.imshow(med2, cmap='gray')

- 高斯滤波
- skimage.filters.gaussian
from skimage import data
from skimage.morphology import disk
from skimage.filters import gaussian
img = data.camera()
gas1 = gaussian(img, sigma=3) # sigma=3
gas2 = gaussian(img, sigma=5) # sigma=5
# 图像对比
fig, (ax_1, ax_2, ax_3) = plt.subplots(ncols=3, figsize=(15, 10))
ax_1.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
ax_2.imshow(gas1, cmap='gray')
ax_3.imshow(gas2, cmap='gray')






 本文详细介绍scikit-image库在图像处理中的应用,包括色彩空间转换、直方图操作、对比度增强及图像滤波等核心功能。通过具体实例,展示如何使用Color模块和exposure模块进行图像分割、色彩通道操作、直方图均衡化和滤波处理。
本文详细介绍scikit-image库在图像处理中的应用,包括色彩空间转换、直方图操作、对比度增强及图像滤波等核心功能。通过具体实例,展示如何使用Color模块和exposure模块进行图像分割、色彩通道操作、直方图均衡化和滤波处理。
















 716
716

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








