Given a root node reference of a BST and a key, delete the node with the given key in the BST. Return the root node reference (possibly updated) of the BST.
Basically, the deletion can be divided into two stages:
- Search for a node to remove.
- If the node is found, delete the node.
Example 1:
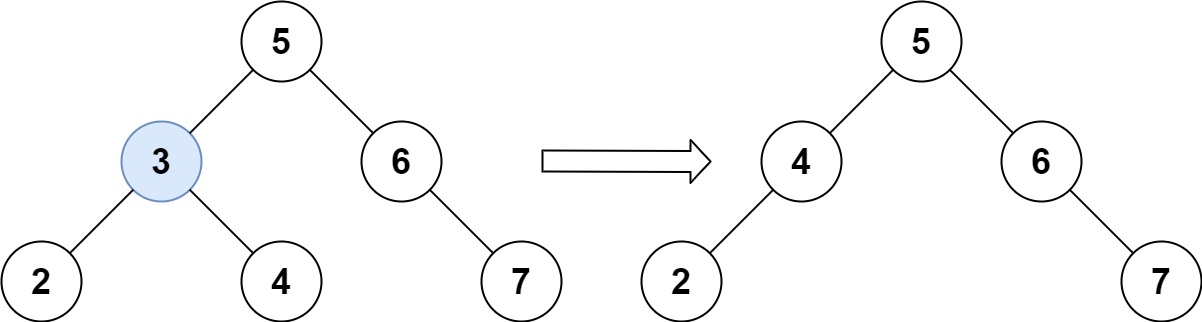
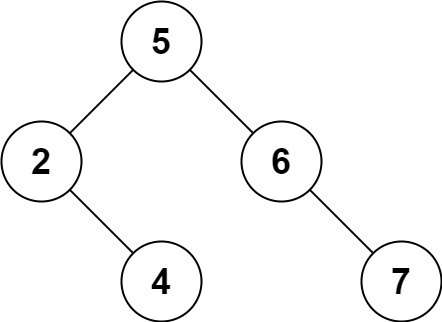
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 3 Output: [5,4,6,2,null,null,7] Explanation: Given key to delete is 3. So we find the node with value 3 and delete it. One valid answer is [5,4,6,2,null,null,7], shown in the above BST. Please notice that another valid answer is [5,2,6,null,4,null,7] and it's also accepted.
Example 2:
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 0 Output: [5,3,6,2,4,null,7] Explanation: The tree does not contain a node with value = 0.
Example 3:
Input: root = [], key = 0 Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 10^4]. -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5- Each node has a unique value.
rootis a valid binary search tree.-10^5 <= key <= 10^5
Follow up: Could you solve it with time complexity O(height of tree)?
【C++】
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* deleteNode(TreeNode* root, int key) {
if (root == nullptr) {return nullptr;}
if (root->val == key) {
if(root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) {
delete root;
return nullptr;
}
if (root->left && root->right == nullptr) {
TreeNode* temp = root->left;
delete root;
return temp;
}
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right) {
TreeNode* temp = root->right;
delete root;
return temp;
}
if(root->left && root->right) {
TreeNode* cur = root->right;
while (cur->left != nullptr) {cur = cur->left;}
int newval = cur->val;
root->val = newval;
root->right = deleteNode(root->right, newval);
return root;
}
}
if (root->val > key) {root->left = deleteNode(root->left, key);}
else {root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key);}
return root;
}
};【Java】
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if (root == null) {return null;}
if (root.val == key) {
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return null;
}
if (root.left != null && root.right == null) {
return root.left;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right != null) {
return root.right;
}
if (root.left != null && root.right != null) {
TreeNode cur = root.right;
while (cur.left != null) {cur = cur.left;}
int newval = cur.val;
root.val = newval;
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, newval);
return root;
}
}
if (root.val > key) {root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);}
else {root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);}
return root;
}
}







 https://leetcode.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-bst/
https://leetcode.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-bst/
















 273
273

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










