Given the root of a Binary Search Tree and a target number k, return true if there exist two elements in the BST such that their sum is equal to the given target.
Example 1:
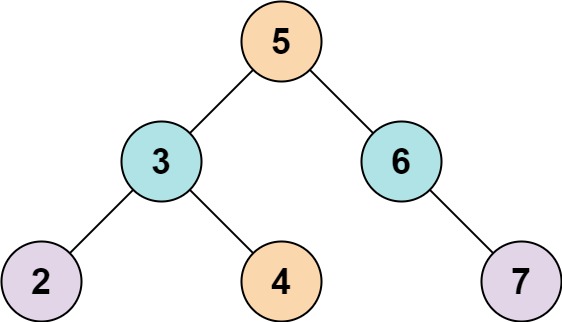
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], k = 9 Output: true
Example 2:
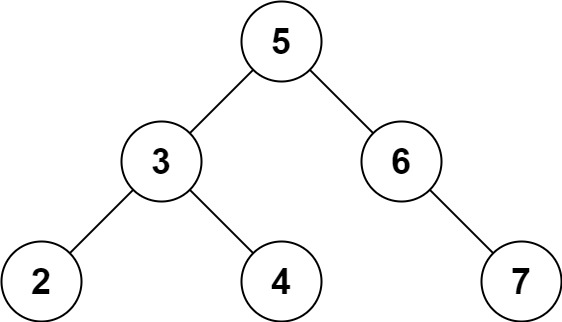
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], k = 28 Output: false
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 10^4]. -10^4 <= Node.val <= 10^4rootis guaranteed to be a valid binary search tree.-10^5 <= k <= 10^5
【C++】
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool findTarget(TreeNode* root, int k) {
vector<int> nums;
inOrder(root, nums);
int i = 0, j = nums.size() - 1;
while (i < j) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[j];
if (sum == k) return true;
if (sum < k) i++;
else j--;
}
return false;
}
void inOrder(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& nums) {
if(!root ) return;
inOrder(root->left, nums);
nums.push_back(root->val);
inOrder(root->right, nums);
}
};【Java】
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean findTarget(TreeNode root, int k) {
List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>();
inOrder(root, nums);
int i = 0, j = nums.size() - 1;
while (i < j) {
int sum = nums.get(i) + nums.get(j);
if (sum == k) return true;
if (sum < k) i++;
else j--;
}
return false;
}
void inOrder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> nums) {
if (root == null) return;
inOrder(root.left, nums);
nums.add(root.val);
inOrder(root.right, nums);
}
}







 https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum-iv-input-is-a-bst/
https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum-iv-input-is-a-bst/ https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_15711195/article/details/122143418
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_15711195/article/details/122143418

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










