先看下测试的代码
public class TestThreadLocal {
static ThreadLocal<String> shareVal = new ThreadLocal<String>();
public static void main(String[] args){
shareVal.set("main_a");
System.out.println("子线程启动前:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"_"+shareVal.get());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);//保证主线程 shareVal 的值修改
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
creatThread().start();
creatThread().start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);//保证子线程启动
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("子线程启动后:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"_"+shareVal.get());
}
public static Thread creatThread(){
return new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"子线程启动前值为:"+shareVal.get());
int i = new Random().nextInt();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"set__"+i);
shareVal.set(" i= "+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" get_"+shareVal.get());
}
});
}
}
结果如下:

我们在ThreadLoacl类型变量shareVal初始化时,重写 initialValue 给初始值,如下:
public class TestThreadLocal {
static ThreadLocal<String> shareVal = new ThreadLocal<String>(){
@Override
protected String initialValue() {
return " init_Vale";
}
};
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("主线程修改前:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"_"+shareVal.get());
shareVal.set("main_a");
System.out.println("子线程启动前:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"_"+shareVal.get());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);//保证主线程 shareVal 的值修改
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
creatThread().start();
creatThread().start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);//保证子线程启动
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("子线程启动后:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"_"+shareVal.get());
}
public static Thread creatThread(){
return new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"子线程启动前值为:"+shareVal.get());
int i = new Random().nextInt();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"set__"+i);
shareVal.set(" i= "+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" get_"+shareVal.get());
}
});
}
}
结果如下:
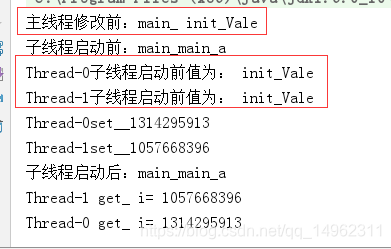
对比可以可以得到,ThreadLocal类,每个线程都会复制一个副本到线程本地中,即从进程的堆中将ThreadLoacl 的值复制到每个线程的栈中。然后线程修改只会修改本地的值,而不会互相影响产生脏读等错误。
每个线程Thread 类中都有 一个ThreadLocal.ThreadLocals成员变量ThreadLocalMap,这个是Map,key为线程自己this,value为 传入的实际值。
有趣可以看下源码。








 本文通过具体示例代码,深入探讨了Java中ThreadLocal的工作原理。展示了如何利用ThreadLocal实现线程间的变量隔离,避免脏读等问题。通过对比不同场景下的运行结果,详细解释了ThreadLocal如何在每个线程中创建变量副本。
本文通过具体示例代码,深入探讨了Java中ThreadLocal的工作原理。展示了如何利用ThreadLocal实现线程间的变量隔离,避免脏读等问题。通过对比不同场景下的运行结果,详细解释了ThreadLocal如何在每个线程中创建变量副本。
















 1540
1540

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








