本章为系列指南的第五章,讲述STM32F407上MAC层以及其DMA的配置。我们在第一章知识储备章节说到,STM32F407会在168MHz主频之外分配一定的时间释放总线数据用来处理DMA,这其中就包含MAC层的DMA,复习一下STM32F4的总线架构图,(图片来自RM0090ST中文STM32F4手册P50):
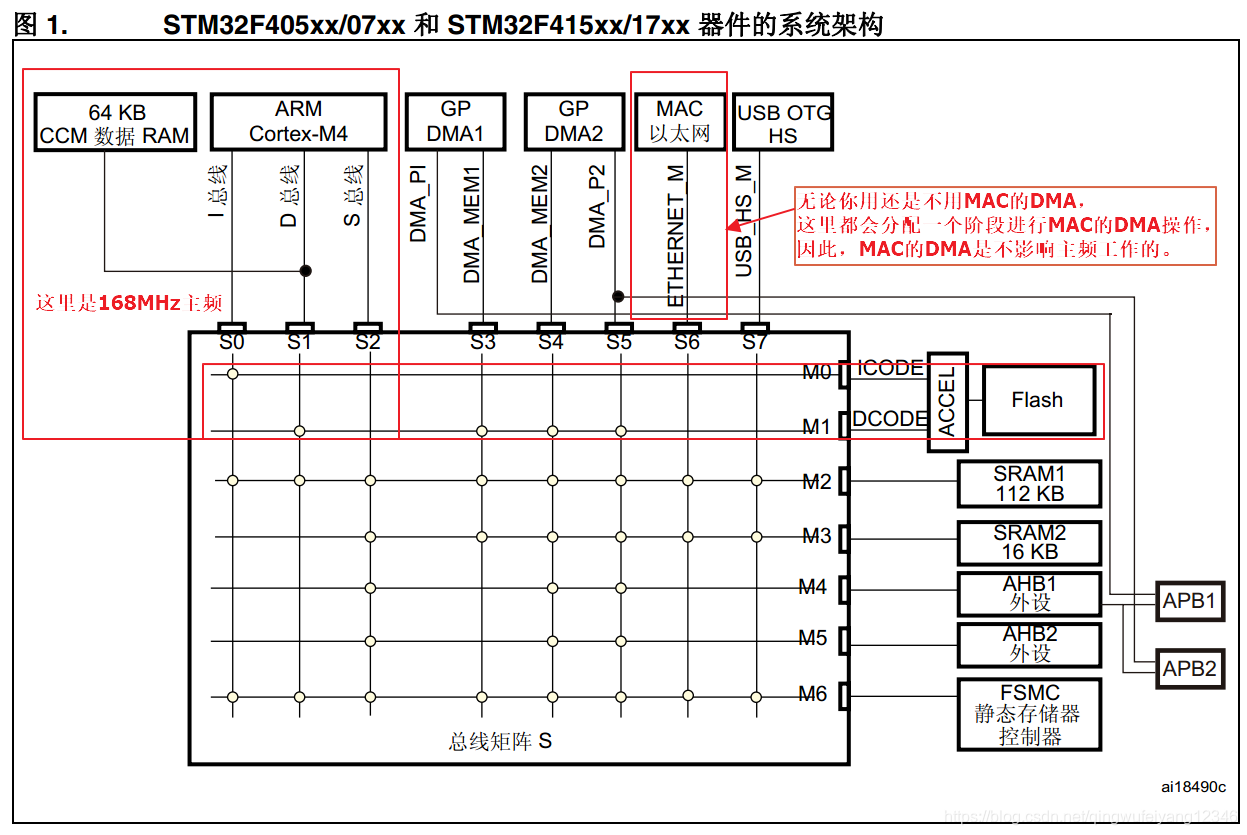
我们看到,在上图红框标注的的S6阶段,就是MAC层的DMA总线,CPU会在核心逻辑之外,有专门的时间片轮转周期处理这一阶段的DMA,所有的数据读写都是DMA来控制,不需要我们在核心逻辑中编写。
本章的要解决的任务只有一个:能编写一个自己构建的DP83848Init()函数,就像任何类似的UARTInit(),DelayInit()等函数一样,在main()函数初始化阶段调用,完成一系列启动网卡的操作。这个任务看似简单,其实比较复杂,因此本章篇幅也会比较多。这个函数包含多个子任务:
GPIO的初始化
MAC层及DMA配置
中断配置
网络服务启动
一、GPIO初始化
这个我们在上一章已经完成了。
二、MAC层初始化
2.1 编码
首先编写以下函数:
static void ETH_MACDMA_Config(void) {
ETH_InitTypeDef ETH_InitStructure;
/* Enable ETHERNET clock */
RCC_AHB1PeriphClockCmd(RCC_AHB1Periph_ETH_MAC | RCC_AHB1Periph_ETH_MAC_Tx | RCC_AHB1Periph_ETH_MAC_Rx, ENABLE);
ETH_DeInit(); /* Reset ETHERNET on AHB Bus */
ETH_SoftwareReset(); /* Software reset */
while (ETH_GetSoftwareResetStatus() == SET); /* Wait for software reset */
/* ETHERNET Configuration
* Call ETH_StructInit to get a default structure
* if you don't like to configure all ETH_InitStructure parameter
*/
ETH_StructInit(Ð_InitStructure);
/* Fill ETH_InitStructure parametrs */
/*------------------------ MAC -----------------------------------*/
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_AutoNegotiation = ETH_AutoNegotiation_Enable; /* 10M/100M自适应 */
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_LoopbackMode = ETH_LoopbackMode_Disable;
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_RetryTransmission = ETH_RetryTransmission_Disable;
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_AutomaticPadCRCStrip = ETH_AutomaticPadCRCStrip_Disable;
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_ReceiveAll = ETH_ReceiveAll_Enable; /* 混杂模式 */
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_BroadcastFramesReception = ETH_BroadcastFramesReception_Enable;
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_PromiscuousMode = ETH_PromiscuousMode_Disable;
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_MulticastFramesFilter = ETH_MulticastFramesFilter_Perfect;
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_UnicastFramesFilter = ETH_UnicastFramesFilter_Perfect;
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_ChecksumOffload = ETH_ChecksumOffload_Enable; /* 在IP包收发时使用硬件计算校验和 */
/*------------------------ DMA -----------------------------------*/
/* When we use the Checksum offload feature, we need to enable the Store and Forward mode:
the store and forward guarantee that a whole frame is stored in the FIFO, so the MAC can insert/verify the checksum,
if the checksum is OK the DMA can handle the frame otherwise the frame is dropped */
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_DropTCPIPChecksumErrorFrame = ETH_DropTCPIPChecksumErrorFrame_Enable;
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_ReceiveStoreForward = ETH_ReceiveStoreForward_Enable;
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_TransmitStoreForward = ETH_TransmitStoreForward_Enable;
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_ForwardErrorFrames = ETH_ForwardErrorFrames_Disable;
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_ForwardUndersizedGoodFrames = ETH_ForwardUndersizedGoodFrames_Disable;
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_SecondFrameOperate = ETH_SecondFrameOperate_Enable;
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_AddressAlignedBeats = ETH_AddressAlignedBeats_Enable;
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_FixedBurst = ETH_FixedBurst_Enable;
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_RxDMABurstLength = ETH_RxDMABurstLength_32Beat;
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_TxDMABurstLength = ETH_TxDMABurstLength_32Beat;
ETH_InitStructure.ETH_DMAArbitration = ETH_DMAArbitration_RoundRobin_RxTx_2_1;
/*
* 初始化时,RJ45变压器如果没有上电,ETH_Init会返回非0值,
* 为确保系统上电后正确初始化网络,需要每500ms尝试初始化一次PHY,直到成功
* DP83848_PHY_ADDRESS为上一章分析并定义的0x01
*/
while( !ETH_Init(Ð_InitStructure, DP83848_PHY_ADDRESS) ) {
vu32 sdelay = 84000000;
while(sdelay--);
}
/* Enable the Ethernet Rx Interrupt */
ETH_DMAITConfig(ETH_DMA_IT_NIS | ETH_DMA_IT_R, ENABLE);
}
上面的代码,配合注释虽然简单明了,但如果你直接copy到项目中编译,肯定会出现大把的错误,显然,从第一个结构体的定义就找不到,下面还有很多ETH的函数也找不到,那么,这个ETH_InitTypeDef结构体,以及下面ETH_DeInit()、ETH_SoftwareReset()、ETH_StructInit()等函数在哪里呢?
2.2 stm32f4x7_eth.c文件和Ethernet库函数
在第一章知识储备中,已经说过了,STM32F4标准库中并未带有ETH方面的库函数,在STM32官网搜索LWIP能够搜索到官方使用LWIP的DEMO,官方文档编号是STSW-STM32070,在这份文档中有LWIP协议栈,并且有官方的调用样例,我们可以从中挖掘到ETH部分的库函数。这份文档解压后,在/STM32F4x7_ETH_LwIP_V1.1.1/Libraries/STM32F4x7_ETH_Driver路径下面的stm32f4x7_eth.c以及配套的.h和一个stm32f4x7_eth_conf_template.h文件是比较关键的,类似于标准库提供的那些I2C,UART,SPI等库函数文件。我们将这三个文件全部引入工程,并且重命名stm32f4x7_eth_conf_template.h为stm32f4x7_eth_conf.h,所有配置均保持跟官方一致的默认配置,这样在本文2.1章节提到的结构体和那些ETH函数,就有定义了,编译起来也不会出错了。有了官方DEMO的样例文件,我们回过头来看一下2.1章节中出现的一大段初始化MAC层的代码,并不是我原创自己想当然瞎写出来的,我们可以考证一下其出处。
打开STM32F4x7_ETH_LwIP_V1.1.1\Project\Standalone\udp_echo_client\src\stm32f4x7_eth_bsp.c文件后,你会发现有相似的代码描述,我们看懂注释后,可以做适当的配置调整。
三、中断配置
这个环节相对比较简单,直接编码:
void ETH_NVIC_Config(void) {
NVIC_InitTypeDef NVIC_InitStructure;
/* Enable the Ethernet global Interrupt */
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannel = ETH_IRQn;
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelPreemptionPriority = 1;
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelSubPriority = 0;
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelCmd = ENABLE;
NVIC_Init(&NVIC_InitStructure);
}
ETH_IRQn宏定义是STM32库中现成的ETH中断描述,中断优先级配置的1-0,相对比较高,但仍留了一位优先级给系统定时器中断排在前面。现在来回顾一下,目前我们已经拥有三个准备好的函数,分别是ETH_GPIO_Config()、ETH_MACDMA_Config()和ETH_NVIC_Config,第一个函数在上一章编写好的,后面两个是刚刚编写的。下面封装一个总体函数:
void ETH_BSP_Config(void) {
ETH_GPIO_Config();
ETH_NVIC_Config(); // Config NVIC for Ethernet
ETH_MACDMA_Config(); // Configure the Ethernet MAC/DMA
}
以上,所有代码皆在stm32f4x7_eth_bsp.c文件中。
四、网络服务启动
我们现在已经完成了大部分的初始化和配置任务,下面,我们需要着手编写以太网服务的启动工作代码,也就是我们这一章节的核心任务,编写DP83848Init()函数:
void DP83848Init(uint8_t* HWADDR){
int i;
/* Configure ethernet (GPIOs, clocks, MAC, DMA) */
ETH_BSP_Config();
/* initialize MAC address in ethernet MAC */
ETH_MACAddressConfig(ETH_MAC_Address0, HWADDR);
/* Initialize Tx Descriptors list: Chain Mode */
ETH_DMATxDescChainInit(DMATxDscrTab, &Tx_Buff[0][0], ETH_TXBUFNB);
/* Initialize Rx Descriptors list: Chain Mode */
ETH_DMARxDescChainInit(DMARxDscrTab, &Rx_Buff[0][0], ETH_RXBUFNB);
/* Enable the TCP, UDP and ICMP checksum insertion for the Tx frames */
for(i = 0; i < ETH_TXBUFNB; i++) {
ETH_DMATxDescChecksumInsertionConfig(&DMATxDscrTab[i], ETH_DMATxDesc_ChecksumTCPUDPICMPFull);
}
ETH_Start();
}
其中,ETH_BSP_Config()来自于我们上一阶段封装好的函数,其余的调用依然来自stm32f4x7_eth.c文件。虽然这里的注释描写得也十分清晰的了,这里有一点需要提一下,在上述代码的第9行和第11行就是配置了两个DMA的链状描述符,关于链状DMA描述符和环装DMA描述符,如果需要理解得更多一点,可以观看原子哥的视频教程,那里面花了一些篇幅介绍,不过我个人感觉视频中讲的也不是特别清楚,视频下载地址:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1jIvvTcy,暂时我们先这么用吧。
按照惯例,上面那一段函数也不是我突发奇想,心血来潮,闭着眼睛毫无根据写下的,我们来看看这段函数的出处,依然在之前那份LWIP文档里面,路径为:STM32F4x7_ETH_LwIP_V1.1.1\Utilities\Third_Party\lwip-1.4.1\port\STM32F4x7\Standalone\ethernetif.c,看第76行low_level_init()函数,顾名思义,low_level_init()就是底层初始化的意思,我们重点观察这个函数的后半部分,前面操作netif结构体的部分我们暂时用不到,后面部分调用ETH库函数的函数就是我们需要的。代码截取如下:
static void low_level_init(struct netif *netif)
{
#ifdef CHECKSUM_BY_HARDWARE
int i;
#endif
/* set MAC hardware address length */
netif->hwaddr_len = ETHARP_HWADDR_LEN;
/* set MAC hardware address */
netif->hwaddr[0] = MAC_ADDR0;
netif->hwaddr[1] = MAC_ADDR1;
netif->hwaddr[2] = MAC_ADDR2;
netif->hwaddr[3] = MAC_ADDR3;
netif->hwaddr[4] = MAC_ADDR4;
netif->hwaddr[5] = MAC_ADDR5;
/* initialize MAC address in ethernet MAC */
ETH_MACAddressConfig(ETH_MAC_Address0, netif->hwaddr);
/* maximum transfer unit */
netif->mtu = 1500;
/* device capabilities */
/* don't set NETIF_FLAG_ETHARP if this device is not an ethernet one */
netif->flags = NETIF_FLAG_BROADCAST | NETIF_FLAG_ETHARP;
/* Initialize Tx Descriptors list: Chain Mode */
ETH_DMATxDescChainInit(DMATxDscrTab, &Tx_Buff[0][0], ETH_TXBUFNB);
/* Initialize Rx Descriptors list: Chain Mode */
ETH_DMARxDescChainInit(DMARxDscrTab, &Rx_Buff[0][0], ETH_RXBUFNB);
#ifdef CHECKSUM_BY_HARDWARE
/* Enable the TCP, UDP and ICMP checksum insertion for the Tx frames */
for(i=0; i<ETH_TXBUFNB; i++)
{
ETH_DMATxDescChecksumInsertionConfig(&DMATxDscrTab[i], ETH_DMATxDesc_ChecksumTCPUDPICMPFull);
}
#endif
/* Note: TCP, UDP, ICMP checksum checking for received frame are enabled in DMA config */
/* Enable MAC and DMA transmission and reception */
ETH_Start();
}
顺便提一下,ethernetif.c这个源文件本身我们是不需要的,我们并不需要LWIP库中的任何代码,所有的一切都是借鉴其网络收发包模块是怎么编写的。
最后,我们再次小结一下,经过不断的对照和参考,我们现在已经有一份完整的DP83848Init()函数,这个函数将放在main()函数开头部分进行整个PHY、MAC、DMA的配置和初始化。
至此,我们这一章的任务就圆满完成了,我尽量做到每一行代码都有其出处,而不是只贴出代码,让读者只知其然不知其所以然,我想我们弄清楚这些出处后,就可以清晰地根据自己的不同设备和场景来移植。








 本文是STM32F4开发系列的第五部分,详细介绍了如何配置STM32F407的MAC层和DMA以实现与DP83848的以太网通信。内容涵盖GPIO初始化、MAC层初始化、中断配置和网络服务启动,提供了一系列初始化函数的实现和来源解析。
本文是STM32F4开发系列的第五部分,详细介绍了如何配置STM32F407的MAC层和DMA以实现与DP83848的以太网通信。内容涵盖GPIO初始化、MAC层初始化、中断配置和网络服务启动,提供了一系列初始化函数的实现和来源解析。
















 8430
8430

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








