1.正则简介
正则表达式,又称规则表达式。(英语:Regular Expression,在代码中常简写为regex、regexp或RE),计算机科学的一个概念。正则表达式通常被用来检索、替换那些符合某个模式(规则)的文本。
目的:
1、给定一个正则表达式和另一个字符串,我们可以达到如下的目的;
2、给定的字符串是否符合正则表达式的过滤逻辑(称作“匹配”);
3、可以通过正则表达式,从字符串中获取我们想要的特定部分。
特点:
正则表达式的特点是:
1、灵活性、逻辑性和功能性非常强;
2、可以迅速地用极简单的方式达到字符串的复杂控制。
3、对于刚接触的人来说,比较晦涩难懂。
2.re模块
2.1re模块操作
在Python中通过re模块来完成正则表达式操作。
2.2re模块常用方法
re.match
re.match(pattern, string, flags=0)
eg:
result = re.match("hello","hello world")
print(result, result.group(), type(result))
在字符串开头匹配pattern,如果匹配成功(可以是空字符串)返回对应的match对象,否则返回None。
re.search
re.search(pattern, string, flags=0)
eg:
result = re.search("hello,"2018hello world")
print(result.group())
扫描整个字符串string,找到与正则表达式pattern的第一个匹配(可以是空字符串),并返回一个对应的match对象。如果没有匹配返回None。
re.fullmatch
re.fullmatch(pattern, string, flags=0)
eg:
result = re.fullmatch("hello","hello1")
print(result)
string是否整个和pattern匹配,如果是返回对应的match对象,否则返回None。
re.findall
findall(pattern, string, flags=0)
eg:
result = re.findall("hello"," hello china hello world")
print(result, type(result))
返回列表
re.split
re.split(pattern, string, maxsplit=0, flags=0)
eg:
result = re.split("hello,"hello china hello world hello zhengzhou", 2)
print(result, type(result))
返回分割列表
re.sub
sub(pattern, repl, string, count=0, flags=0)
eg:
result = re.sub("hello","hi","hello china hello world hello zhengzhou", 2)
print(result, type(result))
使用repl替换pattern匹配到的内容,最多匹配count次
re.iterator
finditer(pattern, string, flags=0)
eg:
result = re.finditer("hello","hello world hello china")
print(result, type(result))
返回迭代器
re.compile
compile(pattern, flags=0)
eg:
pat = re.compile("hello")
print(pat, type(pat))
result = pat.search("helloworld")
print(result, type(result))
编译得到匹配模型“hello”,然后和“helloworld”匹配,有匹配结果返回匹配到的内容,无结果返回None。
2.3flags
re模块的一些函数中将flags作为可选参数,下面列出了常用的几个flag, 它们实际对应的是二进制数,可以通过位或将他们组合使用。flags可能改变正则表达时的行为:
re.I re.IGNORECASE: 匹配中大小写不敏感
re.M re.MULTILINE: "^"匹配字符串开始以及"\n"之后;"$"匹配"\n"之前以及字符串末尾。通常称为多行模式
re.S re.DOTALL: "."匹配任意字符,包括换行符。通常称为单行模式
如果要同时使用单行模式和多行模式,只需要将函数的可选参数flags设置为re.I | re.S即可。
eg:
result = re.match("hello","HeLlo", flags=re.I)
print(result)
result = re.findall("^abc","abcde\nabcd",re.M)
print(result)
result = re.findall("e$","abcde\nabcd",re.M)
print(result)
result = re.findall(".","hello \n china", flags=re.S)
# "." 可以匹配换行符
print(result)
result = re.findall(".","hello \n china", flags=re.M)
# "." 不可以匹配换行符
print(result)
3.单个字符串
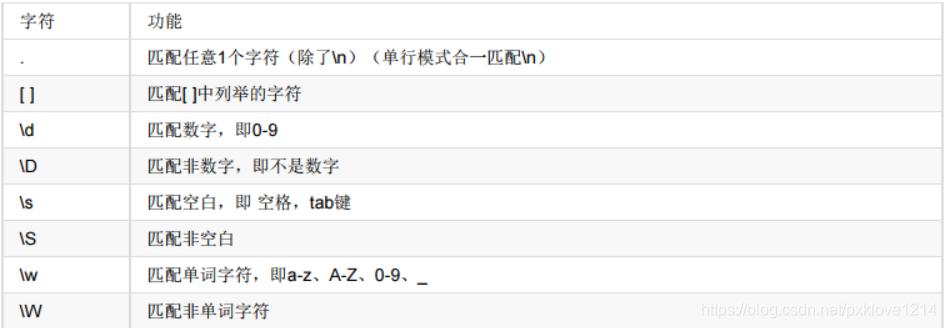
result = re.findall("[0123].ello","0hello 1hello 2 ello 88ello 888ello")
print(result)
result = re.findall("\dhello","hello 1hello 5hello 0hello")
print(result)
result = re.findall("\Dhello","xhello 1hello 5hello 0hello")
print(result)
result = re.findall("\shello","hello hello hello")
print(result)
result = re.findall("\Shello","1hello shello hello")
print(result)
result = re.findall("\wello","hello aello5ello_ello .ello ^ello")
print(result)
result = re.findall("\Wello","hello aello5ello_ello .ello ^ello")
print(result)
3.2特殊贪婪字符 ?
正则匹配默认贪婪模式即匹配尽可能多个字符
result = re.findall("he*","hee heeeee zzheee0")
print(result)
#结果为 ['hee', 'heeeee', 'heee']
当?出现在+、*、{m}之后开启非贪婪模式
result = re.findall("he*?","hee heeeee zzheee0")
print(result)
#结果为 ['h', 'h', 'h']
4.表示数量
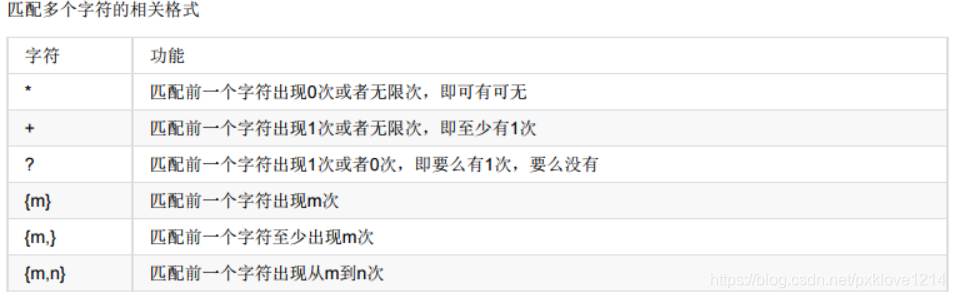
result = re.findall("hi*","hi china hello china")
print(result)
result = re.findall("hi+","hi china hello chiina")
print(result)
result = re.findall("hi?","hi china hello chiina")
print(result)
result = re.findall("hi{2}","hi china hello chiina")
print(result)
result = re.findall("hi{1,}","hi china hello chiina")
print(result)
result = re.findall("hi{1,2}","hi china hello chiiina")
print(result)
5.表示边界
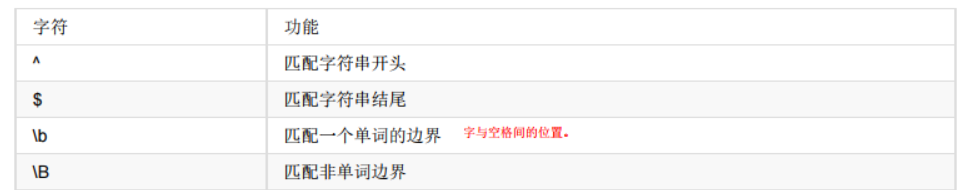
result = re.findall("^hello","hello world hello zhengzhou")
print(result)
result = re.findall("zhengzhou$","hello world hello zhengzhou")
print(result)
# \b表示回退一定要 使用原始语句 r
result = re.findall(r"\bhello\b","hello world hello zhengzhou sayhellook")
print(result)
# \b表示回退一定要 使用原始语句 r
result = re.findall(r"\Bhello\B","hello world hello zhengzhou sayhellook")
print(result)
6.原始字符串
Python中字符串前面加上 r 表示原生字符串
与大多数编程语言相同,正则表达式里使用""作为转义字符,这就可能造成反斜杠困扰。
如果要查找以world作为单词边界的匹配编写如下代码
result = re.findall("\bhello\b","hello world hello zhengzhou sayhellook")
print(result)
匹配失败 应为\b 需要转义
带有转义字符 的写法
result = re.findall("\\bhello\\b","hello world hello zhengzhou sayhellook")
print(result)
效果可以达到,太麻烦
使用原始语句
result = re.findall(r"\bhello\b","hello world hello zhengzhou sayhellook")
print(result)
Python里的原生字符串很好地解决了这个问题,有了原始字符串,你再也不用担心是不是漏写了反斜杠,写出来的表达式
也更直观。
在比如:
# \n 需要转义 如果没有转义则打印换行
print("hello \n world")
#\n 带有转义
print("hello \\n world")
#使用原始语句
print(r"hello \n world")








 本文深入浅出地介绍了正则表达式的概念、特点及其在Python中的应用,详细讲解了re模块的各种方法,如match、search、findall等,并通过实例演示了如何进行字符串的匹配、搜索、替换和分割。
本文深入浅出地介绍了正则表达式的概念、特点及其在Python中的应用,详细讲解了re模块的各种方法,如match、search、findall等,并通过实例演示了如何进行字符串的匹配、搜索、替换和分割。
















 458
458

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








