一.栈和队列介绍
栈基础知识
先进的数据后出
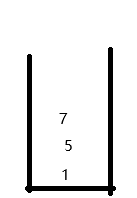
如图数字进入的顺序依次为1 5 7 出来需要从最顶上出来 7 5 1
队列基础知识
先进的数据先出
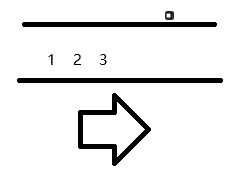
如图数字进入的顺序依为 3 2 1 出来的顺序也是3 2 1
二.栈和队列相关算法题
1.怎么用数组实现不超过固定大小的队列和栈
栈的实现较为简单,因为数组近乎为栈,代码如下
public static class arrayStack{
int index=0;
int [] arr=new int[7];
//假设可以容纳7个 数字
//栈很好模拟从0开始往上加
//要提取的时候可以通过index看最顶部的值即可
//添加数据
public void adddata(int data){
//这里面index在没数字的时候是0
//最大为七个数字对应的是7 也就是<7的时候可以添加数
if (index<arr.length){
arr[index]=data;
index++;
}else {
System.out.println("数量大于7无法添加");
}
}
//删除数据
public void deletedata(){
if (index==0){
//index为0的时候是没数据的,其余情况是可以删的
System.out.println("没有数据可以删除");
}else {
//直接减index即可
index--;
}
}
//查看顶部
public void findtop(){
if (index==0){
//index为0的时候是没数据的,其余情况是可以删的
System.out.println("没有数据可以查看");
}else {
//直接减index即可
System.out.println("顶部为"+arr[index]);
}
}
//查看大小
public void size(){
System.out.println("总共有:"+index+"个数");
}
}
队列需要使用到环形数组
public static class arrayStack{
//环形数组
//添加的数字位置
int push=0;
//推出的数字位置
int poll=0;
int size=0;
//假设可以容纳7个 数字
int limit=7;
int [] arr=new int[7];
//如果符合条件,那就可以让poll和push+1 进行添加或者提取操作
public int nextIndex(int index){
//如果这个index在最高位,那么下一次就该是0了
return index<limit-1 ? index+1:0;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size==0;
}
public void push(int value){
if (size==limit){
throw new RuntimeException("栈满了,无法加入数据");
}
size++;
arr[push]=value;
push=nextIndex(push);
}
public int pop(){
if (size==0){
throw new RuntimeException("栈为空,无法再拿了");
}
size--;
int num=arr[poll];
poll=nextIndex(poll);
return num;
}
public int findtop(int value){
if (size==0){
throw new RuntimeException("栈为空,无数据");
}
return arr[poll];
}
}
2.实现一个特殊的栈,基础功能上,可以同时查找最小值
//可以查询最小数的栈
public static class minStack{
Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> minstack=new Stack<>();
//查找top
public int findtop(){
return stack.peek();
}
//查找大小
public int findSize(){
return stack.size();
}
//添加 添加的时候如果是第一个数,那么两个栈都添加
//如果是第二个数,看min里面的peek是否<该数,如果不小于,两个都+
//如果不大于,就加在stack里面
public void push(int data){
if (stack.size()==0){
stack.push(data);
minstack.push(data);
}else {
if (minstack.peek() < data){
stack.push(data);
}else {
stack.push(data);
minstack.push(data);
}
}
}
//查找最小
public int findmin(){
if (stack.size()==0){
throw new RuntimeException("无数据");
}
return minstack.peek();
}
//删除
public int delete(){
//Integer是包装类,在比较-128-127时,引用的地址值相同
//但是在比较超出这个范围的数时候
//就算值相同,但是地址值不同,二者==的时候,虽然值相同,但是比较的是地址,因此会出错
//所以需要用equals
if (stack.peek().equals(minstack.peek())){
stack.pop();
return minstack.pop();
}else return stack.pop();
}
}
3.用队列模拟栈
//用队列模拟栈
//数据全存放在一个队列里面,当要查看数据时,所有数据倒入另一个队列,同时剩一个
//之后如果是要删,就删,同时返回数据
//如果是查看,那就返回数据同时把这个数据也移动到queue里面
public static class queueToStack{
Queue<Integer> queue1=new ArrayDeque<>();
Queue<Integer> queue2=new ArrayDeque<>();
//是否为空
public Boolean isEmpty(){
//看二者是否均为空,如果不是,那么就是一个为空一个不为空
if (queue1.isEmpty()&&queue2.isEmpty()){
return true;
}else return false;
}
//数量
public int Size(){
//看二者是否均为空,如果不是,那么就是一个为空一个不为空
if (queue1.isEmpty()&&queue2.isEmpty()){
return 0;
}
if (queue1.isEmpty()){
return queue2.size();
}else{ return queue1.size();}
}
//添加
public void push(Integer data){
//看二者是否均为空,如果不是,那么就是一个为空一个不为空
if (queue1.isEmpty()&&queue2.isEmpty()){
queue1.add(data);
}
if (queue1.isEmpty()){
queue2.add(data);
}else{ queue1.add(data);}
}
//查看
public Integer peek(Integer data){
//看二者是否均为空,如果不是,那么就是一个为空一个不为空
if (queue1.isEmpty()&&queue2.isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("没有数据");
}
if (queue1.isEmpty()){
while (queue2.size()!=1){
queue1.add(queue2.poll());
}
Integer num=queue2.poll();
queue1.add(num);
return num;
}else{
while (queue1.size()!=1){
queue2.add(queue1.poll());
}
Integer num=queue1.poll();
queue2.add(num);
return num;
}
}
//删除
public Integer pop(Integer data){
//看二者是否均为空,如果不是,那么就是一个为空一个不为空
if (queue1.isEmpty()&&queue2.isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("没有数据");
}
if (queue1.isEmpty()){
while (queue2.size()!=1){
queue1.add(queue2.poll());
}
Integer num=queue2.poll();
//queue1.add(num);
return num;
}else{
while (queue1.size()!=1){
queue2.add(queue1.poll());
}
Integer num=queue1.poll();
//queue2.add(num);
return num;
}
}
}
4.用栈模拟队列
//用栈模拟队列
public static class stackToqueue{
Stack<Integer> pushStack=new Stack();
Stack<Integer> popStack=new Stack();
//在查数的时候要把push栈 里的数,全放在pop栈里面,之后pop栈里面的peek就是目标值
//但是当pop栈里面有数的时候是无法push的,想要push就要把数全倒pop里面
//同时如果想要往pop里面放东西需要pop栈为空
//查找
public Integer FindNum(){
//如果二者里面都没数据,那就没数据,报错即可
//如果pop里面有数据那就直接排
//如果pop里面没了,注意是没了,才能从push里面倒同时要倒完
if (popStack.empty()&&pushStack.empty()){
throw new RuntimeException("数据为空");
}
if (!popStack.empty()){
return popStack.peek();
}else {
//pop为空,那就可以倒了,但是要全倒
pushAllToPop();
return popStack.peek();
}
}
//增加
public void addToPop(Integer data){
pushStack.push(data);
}
//排出
public Integer PopNum(){
//如果二者里面都没数据,那就没数据,报错即可
//如果pop里面有数据那就直接排
//如果pop里面没了,注意是没了,才能从push里面倒同时要倒完
if (popStack.empty()&&pushStack.empty()){
throw new RuntimeException("数据为空");
}
if (!popStack.empty()){
return popStack.pop();
}else {
//pop为空,那就可以倒了,但是要全倒
pushAllToPop();
return popStack.pop();
}
}
//所有东西导入pop里
public void pushAllToPop(){
//如果pop里面为空就执行这个函数
while (!pushStack.empty()) {
popStack.push(pushStack.pop());
}
}
}






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








